Your With an increase in supply demand remains images are available. With an increase in supply demand remains are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the With an increase in supply demand remains files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for with an increase in supply demand remains pictures information related to the with an increase in supply demand remains topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site always provides you with hints for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
With An Increase In Supply Demand Remains. Supply and demand rise and fall until an equilibrium price is reached. Decrease in aggregate supply while aggregate demand has significant decreases. If there is an increase in supply with a given demand curve there will be excess supply in the market. Under the circumstances own price of the commodity remains fixed.
 Pin By Hisham Hambal On Economics Policy Word Search Puzzle Words Economics From pinterest.com
Pin By Hisham Hambal On Economics Policy Word Search Puzzle Words Economics From pinterest.com
Decrease in aggregate supply while aggregate demand remains unchanged. If quantity demand decreases and supply remains unchanged a surplus occurs leading to a lower price until the quantity demanded is pushed back to equilibrium. Quantity demanded will increase. Increase in demand decrease in supply. However the equilibrium quantity rises. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall.
Quantity supplied will decrease.
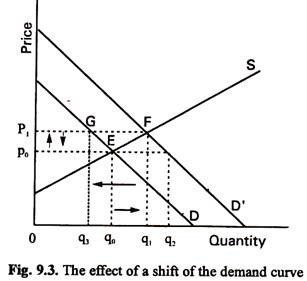
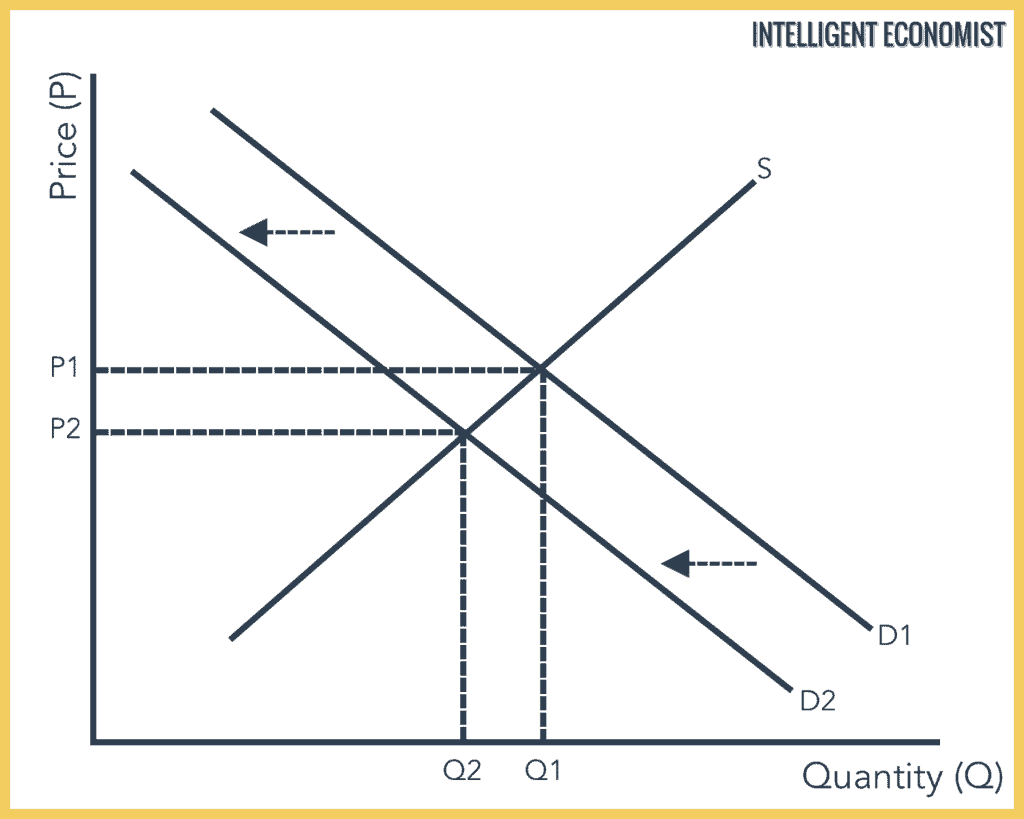
Due to excess supply the price of the product goes down. It is highly unlikely that the change in supply and demand perfectly offset one another so that equilibrium remains the same. Figure 35 c and d An increase in supply shift to right while demand remains constant as shown in c of Figure 35 decreases price P 1 to P 2 and increases quantity Q 1 to. Due to excess supply the price of the product goes down. Decrease in aggregate supply while aggregate demand remains unchanged. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Economic activity in the manufacturing sector grew in November with the overall economy achieving an 18th consecutive month of growth say the nations supply executives in the latest Manufacturing ISM Report On Business. Supply curve for X to the left. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. Supply curve for X to the right. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If X is a normal good a rise in money income will shift the. However when demand increases and supply remains the same the higher demand leads to a higher equilibrium price and vice versa. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases a shortage occurs leading to a higher equilibrium price. Due to the price fall the consumer will purchase more quantity in comparison to.
 Source: research.stlouisfed.org
Source: research.stlouisfed.org
If supply declines and demand remains constant equilibrium price will fall. If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. Decrease in aggregate supply while aggregate demand has significant decreases. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
When demand exceeds supply prices tend to rise. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases a surplus occurs leading to a lower equilibrium price. Growth in real output ie real GDP will increase the demand for money and will increase the nominal interest rate if the money supply is held constant. Increase in demand decrease in supply. If demand decreases and supply decreases then equilibrium quantity goes down and equilibrium price could go up down or stay the same.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It is highly unlikely that the change in supply and demand perfectly offset one another so that equilibrium remains the same. There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall. Supply curve for X to the left. Due to excess supply the price of the product goes down.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
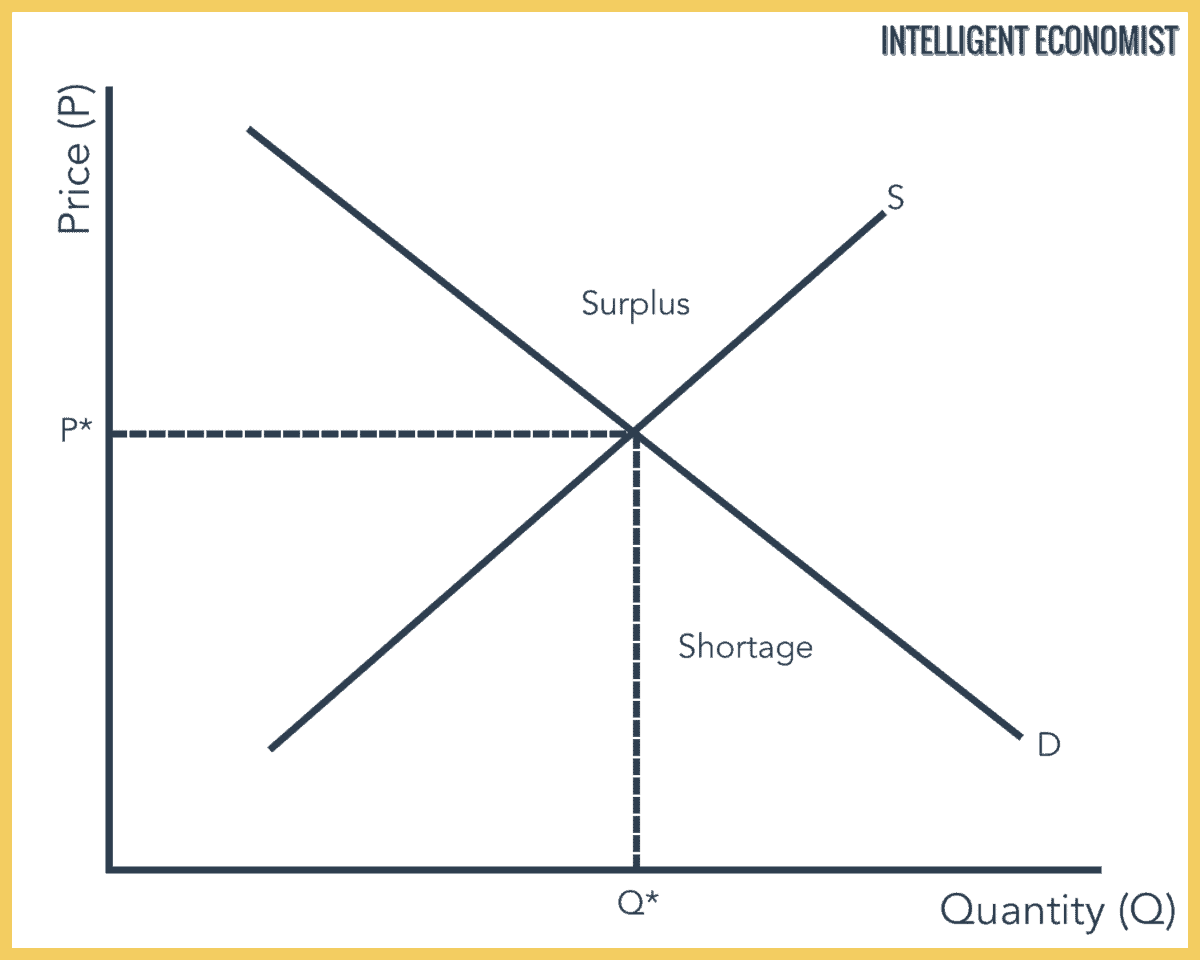
An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. The following points highlight the three effects of changes in demand and supply on the equilibrium price and quantity. Equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of supply and demand. If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. If quantity demand decreases and supply remains unchanged a surplus occurs leading to a lower price until the quantity demanded is pushed back to equilibrium.
 Source: env-econ.net
Source: env-econ.net
Quantity supplied will decrease. However when demand increases and supply remains the same the higher demand leads to a higher equilibrium price and vice versa. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. Due to excess supply the price of the product goes down. Increase in demand decrease in supply.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Consumer Demand Remains High Supply Chain Improves Slightly in November. Inversely a decrease in demand shift to the left while supply remains constant as shown in b decreases price P 3 to P 4 and quantity Q 3 to Q 4 exchanged. When demand exceeds supply prices tend to rise. No change in Price for Riders. Quantity supplied will decrease.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall. Decrease the supply of B and increase the demand for C. If demand decreases and supply decreases then equilibrium quantity goes down and equilibrium price could go up down or stay the same. When the increase in demand is equal to the decrease in supply the shifts in both supply and demand curves are proportionately equal.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It is highly unlikely that the change in supply and demand perfectly offset one another so that equilibrium remains the same. If quantity demand decreases and supply remains unchanged a surplus occurs leading to a lower price until the quantity demanded is pushed back to equilibrium. This means prices will drop so that the stores can sell all the bananas they have. Lets take bananas as an example and say the weather is perfect for growing bananas which increases the supply. If there is an increase in supply with a given demand curve there will be excess supply in the market.
 Source: acqnotes.com
Source: acqnotes.com
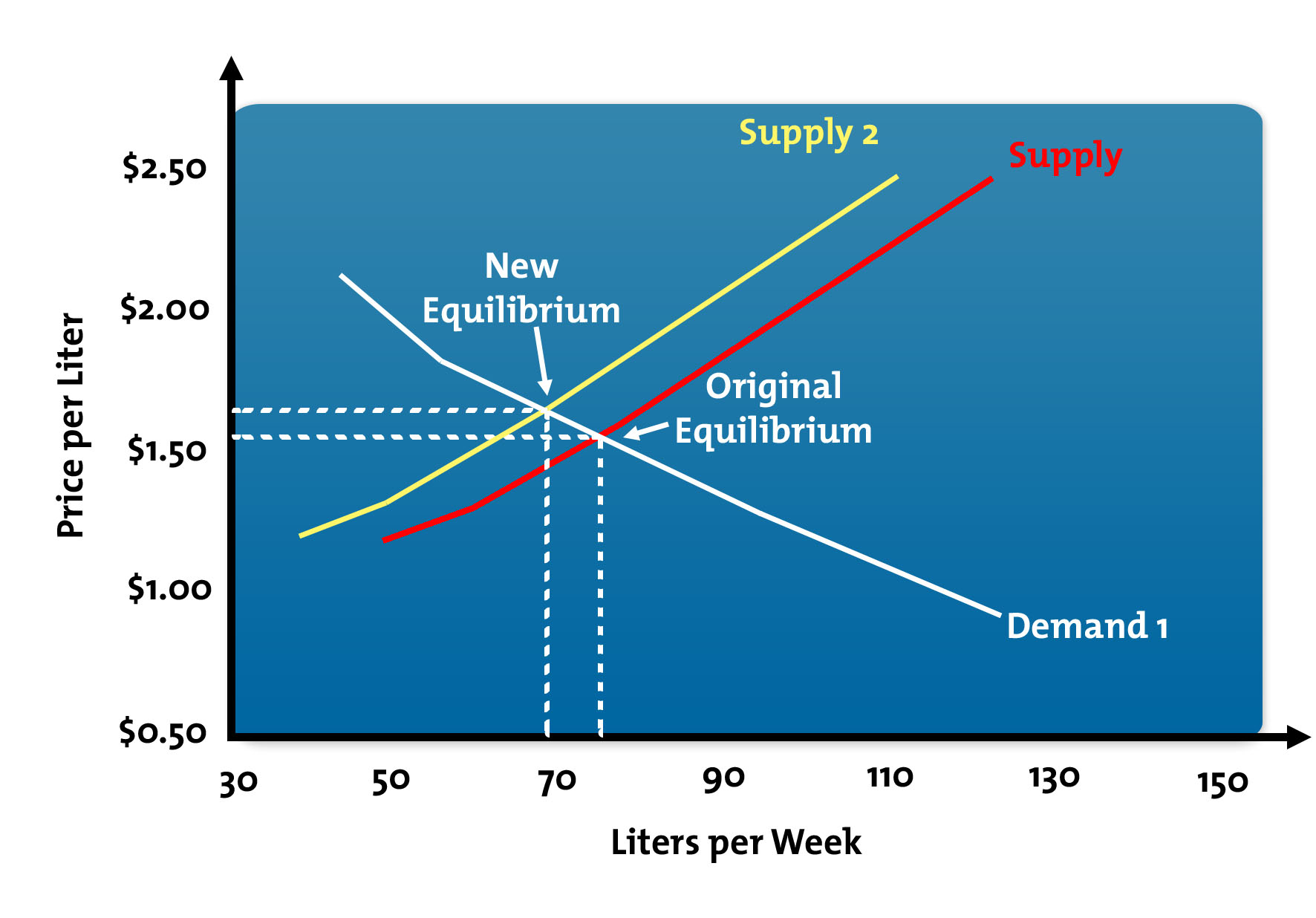
The increase in demand increase in supply. Quantity supplied will increase. Figure 35 c and d An increase in supply shift to right while demand remains constant as shown in c of Figure 35 decreases price P 1 to P 2 and increases quantity Q 1 to. If supply increases and demand remains the same then the price decreases. On the other hand if the supply of money increases in tandem with the demand for money the Fed can help to stabilize nominal interest rates and related quantities including inflation.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
If supply declines and demand remains constant equilibrium price will fall. Decrease in aggregate supply while aggregate demand has significant decreases. Quantity supplied will increase. Supply curve for X to the left. Increase in demand decrease in supply.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
If there is an increase in supply with a given demand curve there will be excess supply in the market. Growth in real output ie real GDP will increase the demand for money and will increase the nominal interest rate if the money supply is held constant. Lets take bananas as an example and say the weather is perfect for growing bananas which increases the supply. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. Figure 35 c and d An increase in supply shift to right while demand remains constant as shown in c of Figure 35 decreases price P 1 to P 2 and increases quantity Q 1 to.
 Source: mindtools.com
Source: mindtools.com
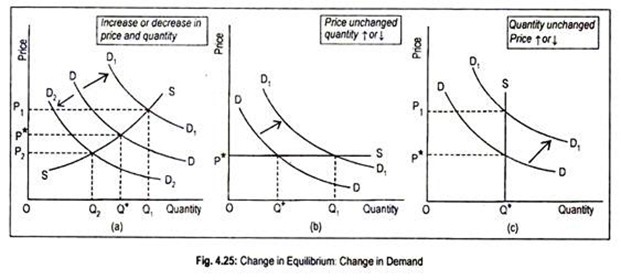
Effectively the equilibrium quantity remains the same however the equilibrium price rises. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. Supply curve for X to the left. If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. Effectively the equilibrium quantity remains the same however the equilibrium price rises.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If quantity demand remains unchanged and supply increases a surplus occurs leading to a lower price until the quantity supplied is pushed back to equilibrium. When demand exceeds supply prices tend to rise. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. If X is a normal good a rise in money income will shift the. If demand decreases and supply decreases then equilibrium quantity goes down and equilibrium price could go up down or stay the same.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Quantity supplied will increase. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. Due to excess supply the price of the product goes down. Decrease the supply of B and increase the demand for C.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Quantity demanded will increase. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases a shortage occurs leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases and supply decreases then equilibrium quantity goes down and equilibrium price could go up down or stay the same. Consumer Demand Remains High Supply Chain Improves Slightly in November. As both demand and supply increase in the same proportion equilibrium price remains the same at OP but equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to OQ¹.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
Supply and demand rise and fall until an equilibrium price is reached. Decrease in aggregate supply while aggregate demand remains unchanged. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise. Due to excess supply the price of the product goes down. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases a surplus occurs leading to a lower equilibrium price.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title with an increase in supply demand remains by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.