Your Why does supply curve shift right images are available in this site. Why does supply curve shift right are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Why does supply curve shift right files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for why does supply curve shift right pictures information connected with to the why does supply curve shift right keyword, you have come to the right site. Our website always provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Why Does Supply Curve Shift Right. Prices of relevant inputs - if the cost of resources used to produce a good increases sellers will be less inclined to supply the same quantity at a given price and the supply curve will shift to the left. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. The result is higher prices at a lower quantity. If the supply curve shifts to the right this is an increase in supply.
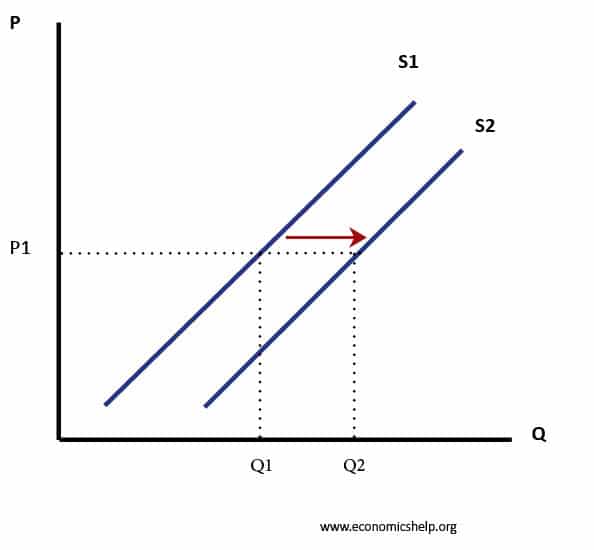 Factors Affecting Supply Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Factors Affecting Supply Economics Help From economicshelp.org
The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left as wages increase. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right. Excess demand may occur. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. A fall in supply will mean that the curve moves leftwards. Quantity supplied can increase as a result of a reduced cost in production of a commodity.
Increased cost of production limits the quantity supplied by producers to the market at any price making the supply curve to move toward the left.
Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right. 2 Workers and firms adjust their expectations of wages and prices downward and they push. Fiscal stimulus that is increasing government spending andor decreasing taxes shifts the IS curve to the right raising interest rates while increasing output. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right. This could be caused by a number of factors including a rise in income a rise in the price of a substitute or a fall in the price of a complement. The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left as wages increase.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The long run adjustment to a negative supply shock results in short run aggregate supply shifting to the right. Increased cost of production limits the quantity supplied by producers to the market at any price making the supply curve to move toward the left. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right. Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right. 7 Why does the short-run aggregate supply curve shift to the right in the long run following a decrease in aggregat 0 I do not want to answer this Question 1 Workers and firms adjust their expectations of wages and prices downward and they accept lower.
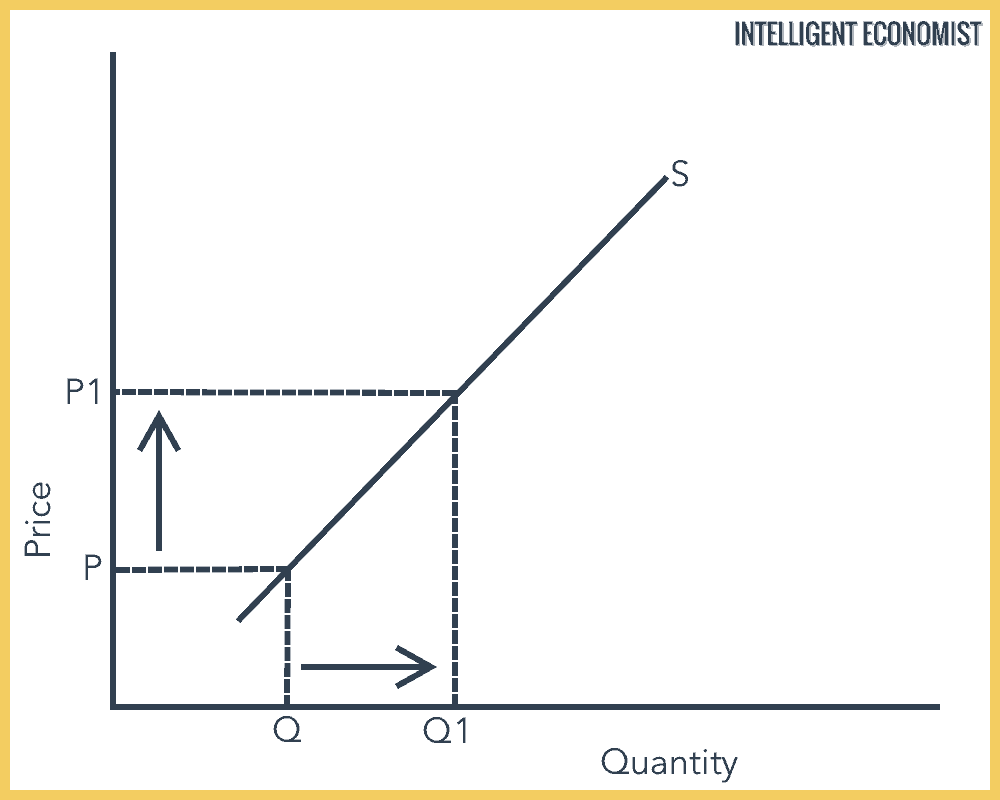 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
I believe that one cause this could happen is if something caused the cost of the item to go down - technology improved productivity etc - to make it worthwhile to produce more even if price does not go up. Conversely a decline in the price of a key input like oil represents a positive supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to the right providing an incentive for more to be produced at every given price level for outputs. 2 Workers and firms adjust their expectations of wages and prices downward and they push. Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right.

This could be caused by a number of factors including a rise in income a rise in the price of a substitute or a fall in the price of a complement. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right. Fiscal stimulus that is increasing government spending andor decreasing taxes shifts the IS curve to the right raising interest rates while increasing output. Prices of relevant inputs - if the cost of resources used to produce a good increases sellers will be less inclined to supply the same quantity at a given price and the supply curve will shift to the left. Shifts in Aggregate Supply.
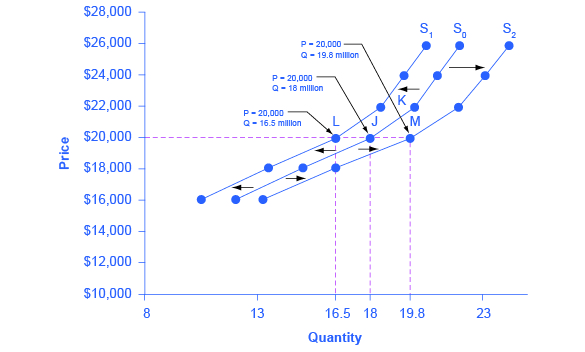 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. A fall in supply will mean that the curve moves leftwards. Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
More is provided for sale at each price. Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve. Why does the supply curve shift to the right. Conversely a decline in the price of a key input like oil represents a positive supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to the right providing an incentive for more to be produced at every given price level for outputs. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another. The relationship still holds - higher price more supply but the shifting curve says for any price more supply than when before the curve shifted. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right. An increase in the change in supply shifts the supply curve to the right while a decrease in the change in supply shifts the supply curve left.

The long run adjustment to a negative supply shock results in short run aggregate supply shifting to the right. The long run adjustment to a negative supply shock results in short run aggregate supply shifting to the right. The relationship still holds - higher price more supply but the shifting curve says for any price more supply than when before the curve shifted. Prices of relevant inputs - if the cost of resources used to produce a good increases sellers will be less inclined to supply the same quantity at a given price and the supply curve will shift to the left. Excess demand may occur.
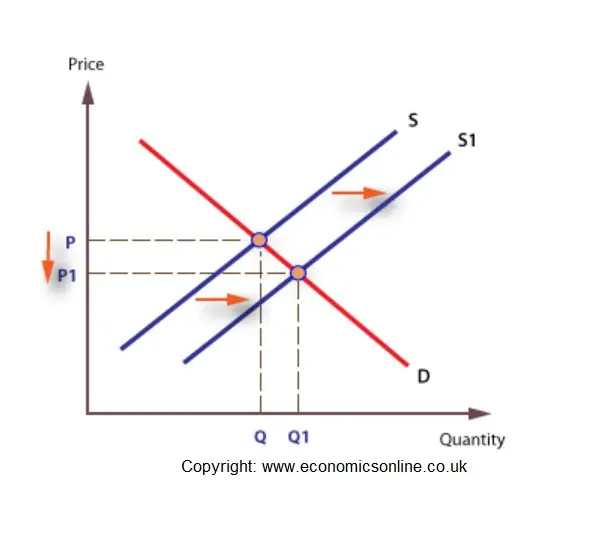 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Higher prices for key inputs shifts AS to the left. A fall in supply will mean that the curve moves leftwards. Why does the supply curve shift to the right. The relationship still holds - higher price more supply but the shifting curve says for any price more supply than when before the curve shifted. The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left as wages increase.
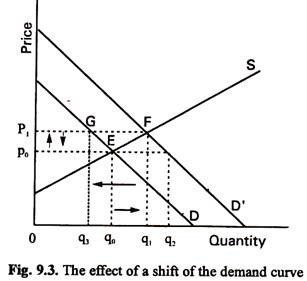 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
This means that at a certain price level the rising cost of inputs into the goods including wages will cause less of that good to. Shift of the demand curve to the right indicates an increase in demand at whatever price because a factor such as consumer trend or taste has risen for it. If the supply curve moves inwards there is a decrease. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. Why does the demand curve goes from left to right.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Quantity supplied can increase as a result of a reduced cost in production of a commodity. This means that at a certain price level the rising cost of inputs into the goods including wages will cause less of that good to. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. If the supply curve shifts to the right this is an increase in supply. Higher prices for key inputs shifts AS to the left.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve. Prices of relevant inputs - if the cost of resources used to produce a good increases sellers will be less inclined to supply the same quantity at a given price and the supply curve will shift to the left. Conversely a decline in the price of a key input like oil represents a positive supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to the right providing an incentive for more to be produced at every given price level for outputs. Excess demand may occur. More is provided for sale at each price.
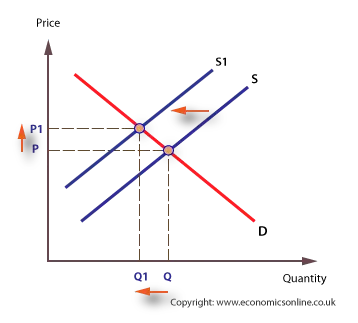 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
The rightward shift occurs in supply curve when the quantity of supplied commodity increases at same price due to favorable changes in non-price factors of production of the commodity. An increase in the change in supply shifts the supply curve to the right while a decrease in the change in supply shifts the supply curve left. Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. The relationship still holds - higher price more supply but the shifting curve says for any price more supply than when before the curve shifted.
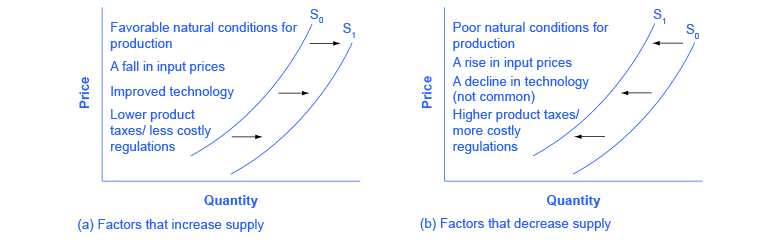 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Why does the supply curve shift to the right. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another. The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left as wages increase. Because graphically the long run supply curve is horizontal and the supply shock moved the supply curve horizontally. When workers wages rise the supply curve shifts to the left.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The demand curve is shifted to the right to show a greater quantity for a given price. The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left as wages increase. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve.

The rightward shift occurs in supply curve when the quantity of supplied commodity increases at same price due to favorable changes in non-price factors of production of the commodity. Quantity supplied can increase as a result of a reduced cost in production of a commodity. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. A decrease in aggregate demand will cause the short-run aggregate supply curve shift to rightward or downward direction because workers and firms will adjust their expectation of wages and prices downwards and they will accept lower wages and prices. Excess demand may occur.
 Source: arinjayacademy.com
Source: arinjayacademy.com
This increase will result in the downward shift of the supply curve toward the right. Why does the supply curve shift to the right. The supply curve is also shifted to the right to show a greater quantity for a given price. Increases in demand are shown by a shift to the right in the demand curve. Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right.
 Source: web.mnstate.edu
Source: web.mnstate.edu
More is provided for sale at each price. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another. Why does the supply curve shift to the right. Increased cost of production limits the quantity supplied by producers to the market at any price making the supply curve to move toward the left. A decrease in aggregate demand will cause the short-run aggregate supply curve shift to rightward or downward direction because workers and firms will adjust their expectation of wages and prices downwards and they will accept lower wages and prices.
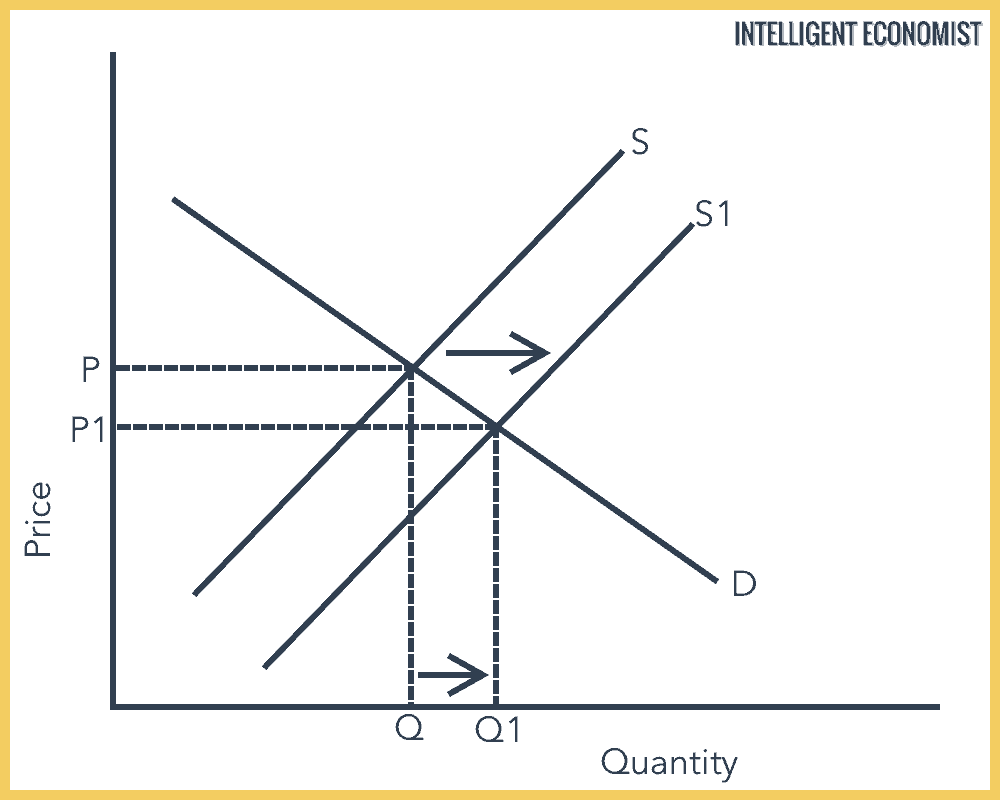 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. If the supply curve shifts to the right this is an increase in supply. This could be caused by a number of factors including a rise in income a rise in the price of a substitute or a fall in the price of a complement. 7 Why does the short-run aggregate supply curve shift to the right in the long run following a decrease in aggregat 0 I do not want to answer this Question 1 Workers and firms adjust their expectations of wages and prices downward and they accept lower. Because graphically the long run supply curve is horizontal and the supply shock moved the supply curve horizontally.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title why does supply curve shift right by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






