Your When does the supply curve shift right images are available. When does the supply curve shift right are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the When does the supply curve shift right files here. Download all free images.
If you’re looking for when does the supply curve shift right images information related to the when does the supply curve shift right keyword, you have visit the right blog. Our website always gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
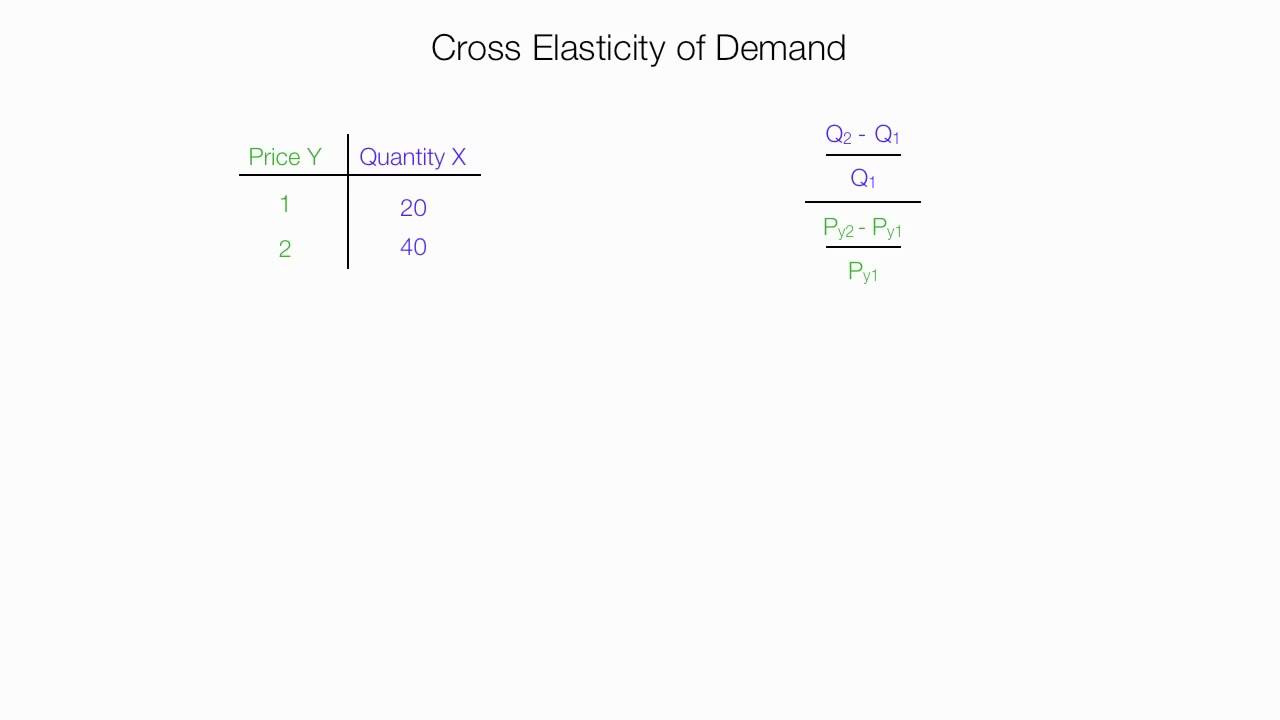
When Does The Supply Curve Shift Right. Supply curve shift. The ceteris paribus assumption. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. An increase in the supply of coffee shifts the supply curve to the right as shown in Panel c of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply.
 Shifts In Supply From economicsonline.co.uk
Shifts In Supply From economicsonline.co.uk
What happens when supply curve shifts right. The shift in supply curve is when the price of the commodity remains constant but there is a change in quantity supply due to some other factors causing the curve to shift to a particular side. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another factor such as number of buyers has slumped. A positive change in supply when demand is constant shifts the supply curve to the right which results in an intersection that yields lower prices and higher quantity. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible.
An increase in the supply of coffee shifts the supply curve to the right as shown in Panel c of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply.
The supply curve shifts down the demand curve so price and quantity follow the law of demand. What is Supply Curve. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. The supply curve shifts left or right when supply changes. The equilibrium price falls to 5 per pound. Shift in Supply Curve.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
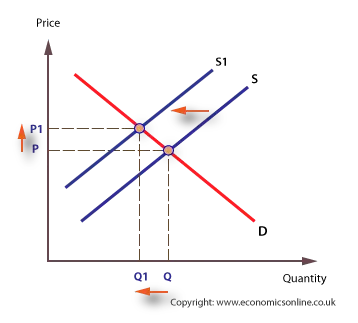
Input prices the number of sellers technology natural and social factors and expectations are some of. The equilibrium price falls to 5 per pound. Supply curves relate prices and quantities supplied assuming no other factors change. An increase in the change in supply shifts the supply curve to the right while a decrease in the change in supply shifts the supply curve left. What happens when supply curve shifts right.
 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. The equilibrium price falls to 5 per pound. The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because the quantity supplied increases. The shift in supply curve is when the price of the commodity remains constant but there is a change in quantity supply due to some other factors causing the curve to shift to a particular side. Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because the quantity supplied increases. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. Shift in Supply Curve. More is provided for sale at each price. Input prices the number of sellers technology natural and social factors and expectations are some of.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
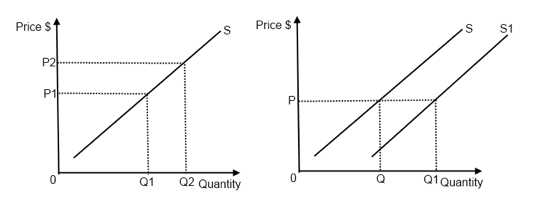
Click to see full answer. This can be shown as a rightward shift in the supply curve which will cause a decrease in the equilibrium price along with an increase in the equilibrium quantity. Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves. A positive change in supply when demand is constant shifts the supply curve to the right which results in an intersection that yields lower prices and higher quantity. Changes in production cost and related factors can cause an entire supply curve to shift right or left.
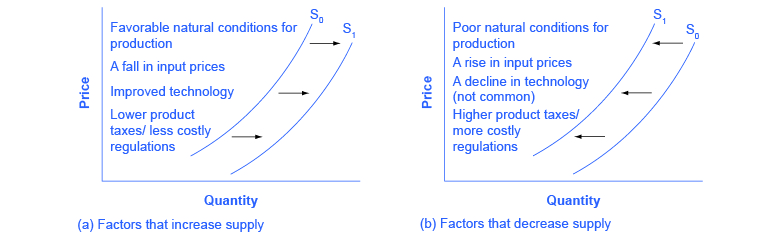 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
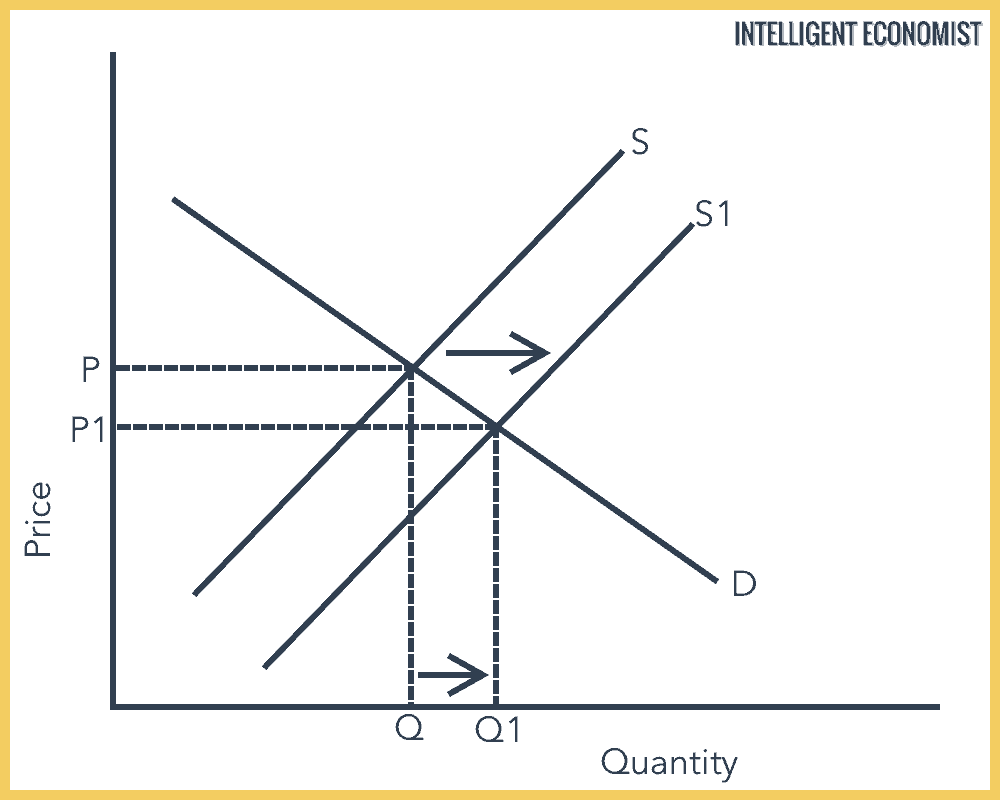
What happens when supply curve shifts right. Changes in production cost and related factors can cause an entire supply curve to shift right or left. A change in supply leads to a shift in the supply curve which causes an imbalance in the market that is corrected by changing prices and demand. The supply curve can shift position. Figure 1 in Shifts in Aggregate Supply by OpenStaxCollege CC BY 40.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another factor such as number of buyers has slumped. Figure 1 in Shifts in Aggregate Supply by OpenStaxCollege CC BY 40. The supply curve shifts down the demand curve so price and quantity follow the law of demand. Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves.
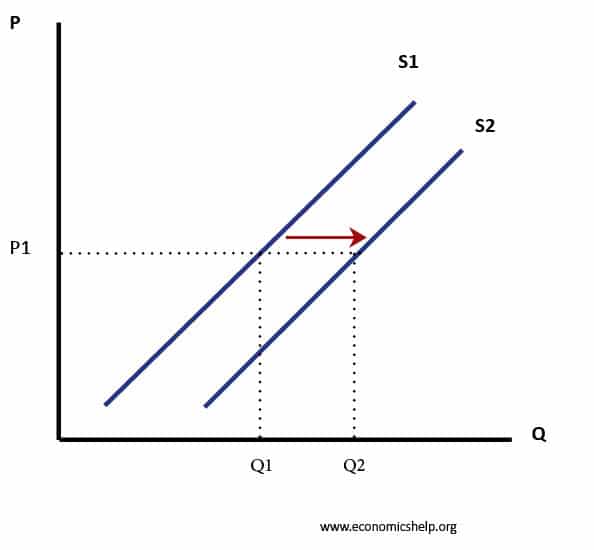 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because the quantity supplied increases. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. What causes as curve to shift up. A change in supply leads to a shift in the supply curve which causes an imbalance in the market that is corrected by changing prices and demand. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible.

Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves. The supply curve shifts left or right when supply changes. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced. Input prices the number of sellers technology natural and social factors and expectations are some of. Shift of the demand curve to the right indicates an increase in demand at whatever price because a factor such as consumer trend or taste has risen for it.

The ceteris paribus assumption. Input prices the number of sellers technology natural and social factors and expectations are some of. When there is technological advancement there are better seeds testing methods that will produce quality cultivation. Pe and QYrepresent the equilibrium price level and full employment GDP. A shift in the SRAS curve to the right results in a greater real GDP and downward pressure on the price level if aggregate demand remains unchanged.
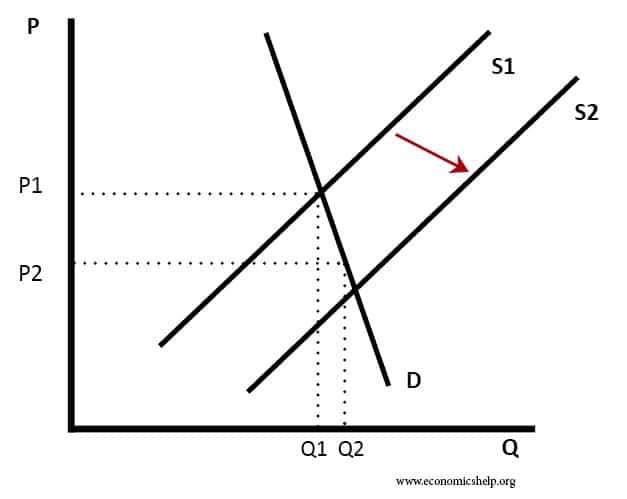 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
This is called a positive supply shock. If the supply curve shifts to the right this is an increase in supply. More is provided for sale at each price. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced. Number of sellers - more sellers result in more supply shifting the supply curve to the right.
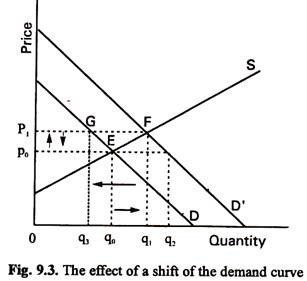 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Supply curves relate prices and quantities supplied assuming no other factors change. Prices of relevant inputs - if the cost of resources used to produce a good increases sellers will be less inclined to supply the same quantity at a given. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another factor such as number of buyers has slumped. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. Click to see full answer.

Click to see full answer. A negative change in supply shifts the curve to the left causing prices to rise and the quantity to decrease. What is Supply Curve. If the supply curve shifts to the right this is an increase in supply. This can be shown as a rightward shift in the supply curve which will cause a decrease in the equilibrium price along with an increase in the equilibrium quantity.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
What is Supply Curve. This can be shown as a rightward shift in the supply curve which will cause a decrease in the equilibrium price along with an increase in the equilibrium quantity. In this case the supply curve will shift towards the right that is there is an increase in supply. What happens when supply curve shifts right. An increase in the supply of coffee shifts the supply curve to the right as shown in Panel c of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply.
 Source: arinjayacademy.com
Source: arinjayacademy.com
A negative change in supply shifts the curve to the left causing prices to. What causes as curve to shift up. What happens when supply curve shifts right. A positive change in supply when demand is constant shifts the supply curve to the right which results in an intersection that yields lower prices and higher quantity. The supply curve shifts down the demand curve so price and quantity follow the law of demand.

This causes a higher or lower quantity to be supplied at a given price. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced. What shifts an AS curve. What happens when supply curve shifts right. The equilibrium price falls to 5 per pound.
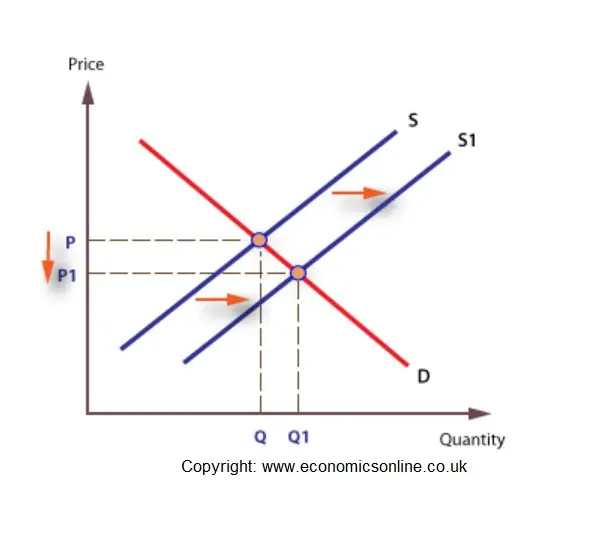 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
A positive change in supply when demand is constant shifts the supply curve to the right which results in an intersection that yields lower prices and higher quantity. The supply curve shifts left or right when supply changes. Shift in Supply Curve. If the supply curve moves inwards there is a decrease in supply meaning that less will be supplied at each price. Input prices the number of sellers technology natural and social factors and expectations are some of.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The equilibrium price falls to 5 per pound. This can be shown as a rightward shift in the supply curve which will cause a decrease in the equilibrium price along with an increase in the equilibrium quantity. Figure 1 in Shifts in Aggregate Supply by OpenStaxCollege CC BY 40. The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because the quantity supplied increases. What happens when supply curve shifts right.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. A discovery of new oil will make oil more abundant. This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS1. Prices of relevant inputs - if the cost of resources used to produce a good increases sellers will be less inclined to supply the same quantity at a given.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title when does the supply curve shift right by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.