Your What would happen in the market for loanable funds images are ready. What would happen in the market for loanable funds are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the What would happen in the market for loanable funds files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for what would happen in the market for loanable funds pictures information linked to the what would happen in the market for loanable funds keyword, you have visit the right site. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
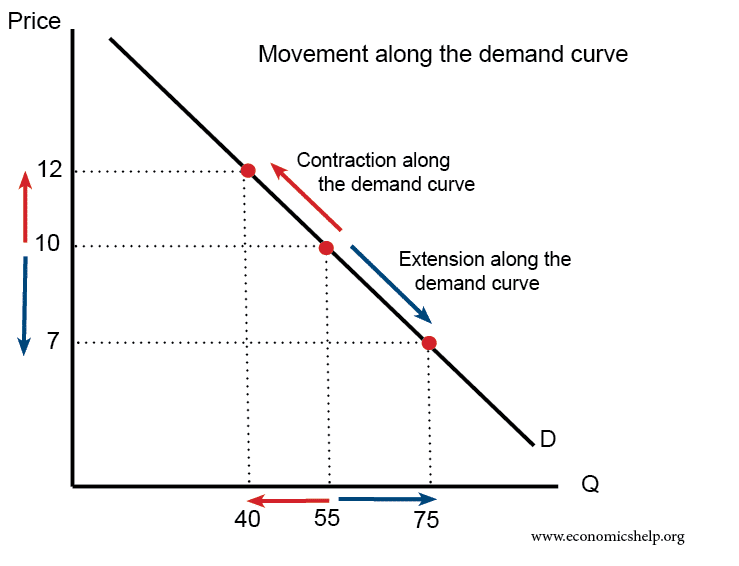
What Would Happen In The Market For Loanable Funds. Transcribed image text. Loanable funds as shown in Figure 3. Borrowers demand loanable funds and savers supply loanable funds. The demand for loanable funds would shift left.

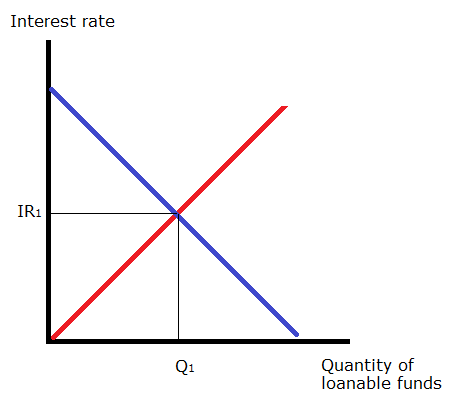
The loanable funds market shows the relationship between the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds. Neither curve shifts but the quantity of loanable funds supplied increases and the quantity demanded decreases as the interest rate rises to equilibrium. What would happen in the market for loanable funds. Investment declines because a budget deficit makes interest rates rise. If there is an increase in savings by the private sector the supply of loanable funds increases shifts right causing the real interest rate to fall. BThe quantity of loanable funds supplied will exceed the quantity of loanable funds demanded and the interest rate will rise.
Debt-to-GDP ratio typically increases during war time.
The supply of loanable funds would shift right. Debt-to-GDP ratio typically increases during war time. AThe quantity of loanable funds demanded will exceed the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the interest rate will rise. If the market rate is below the equilibrium interest rate the market faces excess demand. Interest rates would fall D. A Supply and demand for loanable funds determines the real interest rate B Savers and lenders supply money to the loanable funds market C Government firms and individuals make up the demand in the loanable funds market D The supply of loanable funds is vertical and is set by the Federal Reserve government lowers corporate taxes to.
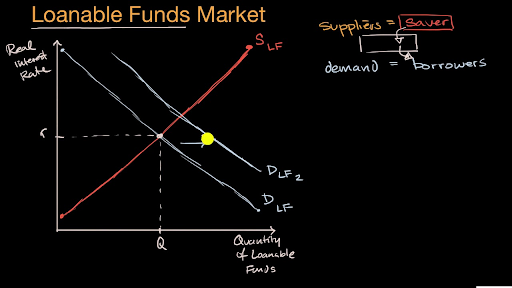
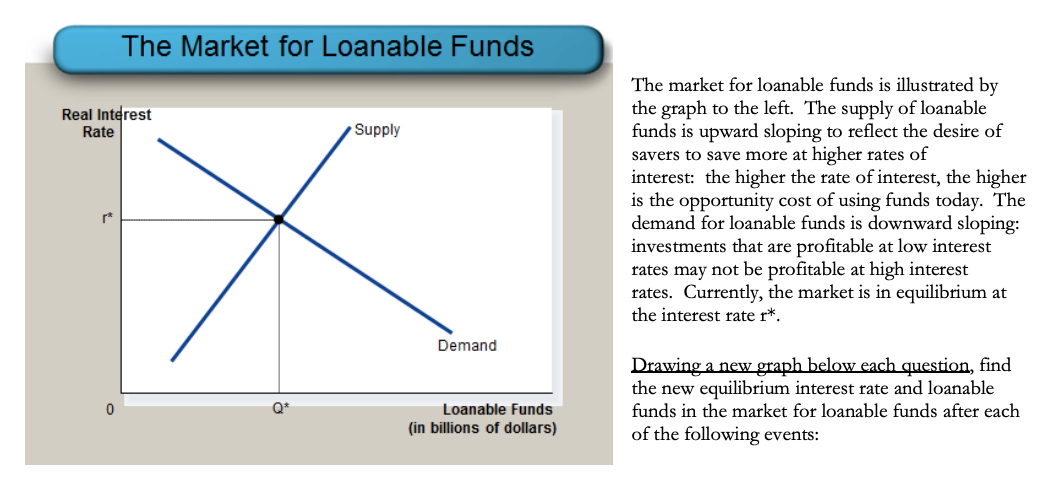
The loanable funds market illustrates the interaction of borrowers and savers in the economy. The loanable funds market is characterized by the following demand function DLF where the demand for loanable funds curve includes only investment demand for loanable funds. The loanable funds market shows the relationship between the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds. What would happen to the market for loanable funds if the government offered tax breaks for companies building new factories. Neither curve shifts but the quantity of loanable funds supplied increases and the quantity demanded decreases as the interest rate rises to equilibrium.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
Interest rates would rise B. Suppose for example that consumers decide to increase current consumption and thus to supply fewer funds to the loanable funds market at any interest rate. If the market rate is below the equilibrium interest rate the market faces excess demand. The quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied and the interest rate will rise. What would happen to the market for loanable funds if the government offered tax breaks for companies building new factories.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
For each of the given scenarios adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow. The loanable funds market is characterized by the following demand function DLF where the demand for loanable funds curve includes only investment demand for loanable funds. Neither curve shifts but the quantity of loanable funds supplied increases and the quantity demanded decreases as the interest rate rises to equilibrium. The supply of loanable funds shifts leftward. What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to decrease the tax rate on interest income.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
The quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied and the interest rate will rise. The demand for loanable funds would shift left. The quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied and the interest rate will rise. What happens in the loanable funds market if the government borrows money is context-dependent. What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to decrease the tax rate on interest income.

Demand decreases O c. The trade balance also moves toward deficit because net capital outflow hence net exports is lower. Debt-to-GDP ratio typically increases during war time. The demand and supply of loanable funds would shift left. Interest rates would be unaffected C.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The quantity of loanable funds traded to increase. Transcribed image text. The loanable funds market illustrates the interaction of borrowers and savers in the economy. If the market rate is below the equilibrium interest rate the market faces excess demand. What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to decrease the tax rate on interest income.

This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market. Interest rates would fall D. When the real interest rate decreases investment spending increases. The supply of loanable funds would shift right. The supply of loanable funds would shift to the right if either.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
People also ask what happens when there is a shortage of loanable funds. If the government institutes policies that diminish incentives to save then in the loanable funds market. The trade balance also moves toward deficit because net capital outflow hence net exports is lower. The quantity of loanable funds traded to increase. Suppose for example that consumers decide to increase current consumption and thus to supply fewer funds to the loanable funds market at any interest rate.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The effect on the interest rate is uncertain. Loanable funds as shown in Figure 3. Interest rates would rise B. Supply decreases QUESTION 20 2 points If the government offers a tax credit to businesses building new physical capital what would happen to the. The following graph shows the market for loanable funds.
![]() Source: policonomics.com
Source: policonomics.com
What occurs in the loanable funds market. The supply of loanable funds would shift right. The demand for loanable funds would shift left. If the government institutes policies that diminish incentives to save then in the loanable funds market. Interest rates would fall as the supply of loanable funds increased.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
A Supply and demand for loanable funds determines the real interest rate B Savers and lenders supply money to the loanable funds market C Government firms and individuals make up the demand in the loanable funds market D The supply of loanable funds is vertical and is set by the Federal Reserve government lowers corporate taxes to. What happens in the loanable funds market if the government borrows money is context-dependent. Demand decreases O c. Interest rates would be unaffected C. Events in the loanable funds market can also affect the quantity of capital firms will hold.
 Source: freeeconhelp.com
Source: freeeconhelp.com
An upward shift in the demand curve for loanable funds increases the real interest rate from r to r 1. The trade balance also moves toward deficit because net capital outflow hence net exports is lower. The demand for loanable funds would shift right. Interest rates would rise B. What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to decrease the tax rate on interest income.
 Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
What happens in the loanable funds market if the government borrows money is context-dependent. For each of the given scenarios adjust the appropriate curve on the graph to help you complete the questions that follow. What would happen in the market for loanable funds. Transcribed image text. The trade balance also moves toward deficit because net capital outflow hence net exports is lower.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Demand decreases O c. The loanable funds market illustrates the interaction of borrowers and savers in the economy. Interest rates would fall D. The loanable funds demand is higher than the supply. The decline in net capital outflow reduces the supply of dollars in the market for foreign exchange raising the real exchange rate.

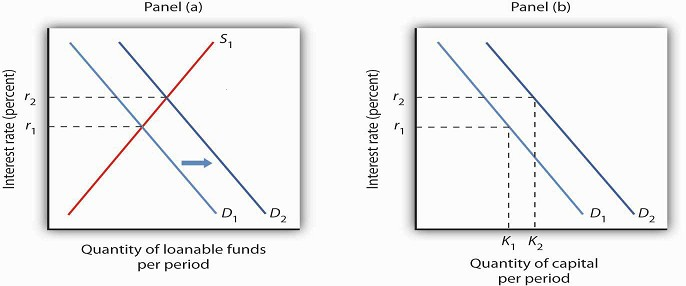
Changes in the Loanable Funds Market and the Demand for Capital. The supply of loanable funds would shift right. What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to decrease the tax rate on interest income. Debt-to-GDP ratio typically increases during war time. This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The loanable funds demand is higher than the supply. This causes the demand for loanable funds to decrease. Additionally what shifts supply of loanable funds. When the real interest rate decreases investment spending increases. What would happen to the market for loanable funds if the government offered tax breaks for companies building new factories.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
R 10 12000Q where r is the real interest rate expressed as a percent eg if r 10 then the interest rate is 10 and Q is the quantity. What happens in the loanable funds market if the government borrows money is context-dependent. Debt-to-GDP ratio typically increases during war time. This causes the demand for loanable funds to decrease. What would happen in the market for loanable funds if the government were to increase the tax on interest income.

Events in the loanable funds market can also affect the quantity of capital firms will hold. The loanable funds market shows the relationship between the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds. The loanable funds market illustrates the interaction of borrowers and savers in the economy. Loanable funds as shown in Figure 3. The following graph shows the market for loanable funds.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what would happen in the market for loanable funds by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.