Your What shifts the supply of loanable funds curve images are available. What shifts the supply of loanable funds curve are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the What shifts the supply of loanable funds curve files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for what shifts the supply of loanable funds curve pictures information connected with to the what shifts the supply of loanable funds curve keyword, you have visit the right site. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
What Shifts The Supply Of Loanable Funds Curve. AskedAug 16 2017in Economicsby JeanClaude. The bond demand curve and loanable funds supply curve will shift to the right. This video explains why the supply curve for loanable funds increases. If the supply of loanable funds decreases if people stop saving as much for whatever reason then ceteris paribus the price of loanable funds will increase as the S curve shifts to the left to become S1 along the same D curve.
 Ecn 202 Principles Of Macroeconomics Nusrat Jahan Lecture5 From slidetodoc.com
Ecn 202 Principles Of Macroeconomics Nusrat Jahan Lecture5 From slidetodoc.com
D The supply of loanable funds curve would shift leftward to a curve such as SLF1. If the nominal interest rate is 7 percent and the inflation rate is 1 percent the real interest rate is approximately. Demand for Loanable Funds. E has no effect on the supply of loanable funds curve. What affects the supply of loanable funds. Its price is going to go up.
Expectations For Future Economy direct Anticipation of economic performance.
Demand for Loanable Funds. E has no effect on the supply of loanable funds curve. At lower interest rates firms demand more capital and therefore more loanable funds. Anything which increases national savings other than a decrease in the real interest rate will shift the supply curve of loanable funds to the right. AskedAug 16 2017in Economicsby JeanClaude. Say the government increases the budget deficit.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
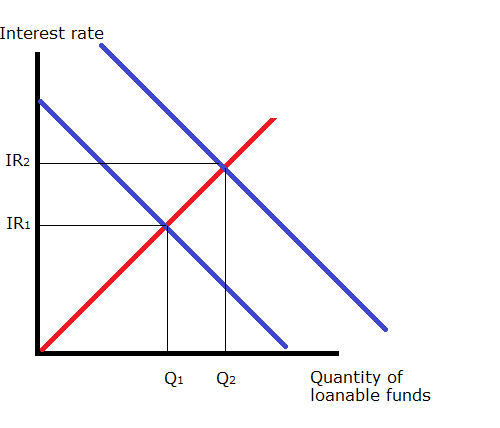
The equilibrium interest rate rE will be found where the two curves intersect. It also affects the supply of and demand for loanable funds. But theres two. We can obtain the total supply curve of loanable funds by a lateral summation of the curves of saving S dishoarding DH bank money BM and disinvestment DI. Changes in government spending.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
Factors that cause the supply curve of loanable funds to shift at any given interest rate include the wealth of fund suppliers the risk of the financial security future spending needs monetary policy objectives and economic conditions. Anything which decreases national savings other than an increase in the real interest rate will shift the supply curve of loanable funds to the left. AskedAug 16 2017in Economicsby JeanClaude. Changes in government spending. Its price is going to go up.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The red curve represents the supply of loanable funds or the amount that individuals wish to save. The supply of loanable funds is generally upward-sloping. Anything which decreases national savings other than an increase in the real interest rate will shift the supply curve of loanable funds to the left. Leads to a leftward shift in the supply of loanable funds a decrease in total investment and an increase in real interest rates. Yes the real interest rate shifts the supply of loanable funds curve because savings ill be increased by the individua View the full answer.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The curve itself doesnt shift. To summarize a decrease in expected inflation will shift the bond supply curve and loanable funds demand curve to the left. What affects the supply of loanable funds. Anything which decreases national savings other than an increase in the real interest rate will shift the supply curve of loanable funds to the left. The supply of loanable funds is generally upward-sloping.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Changes in government spending. A decrease in real wealth a decrease in the real interest rate a decrease in disposable income a decrease in. The Savings Rate direct Consumer or corporate savings levels 2. If the supply of loanable funds decreases if people stop saving as much for whatever reason then ceteris paribus the price of loanable funds will increase as the S curve shifts to the left to become S1 along the same D curve. If aggregate income goes down loanable funds go down interest rates are going to be higher.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The supply of loanable funds curve can be written as r 00005Q. The aggregate loanable fund supply curve SL also slopes upwards to the right showing the greater supply of loanable funds at higher rates of interest. THE INTEREST RATE IN THE LONG RUN In the loanable funds market an increase in the money supply leads to a short-run rise in real GDP and shifts the supply of loanable funds rightward. The increase in deficit prompted the government to increase the demand for loanable funds on the financial market. Federal Reserve Lending direct Lending via discount window 3.
 Source: welkerswikinomics.com
Source: welkerswikinomics.com
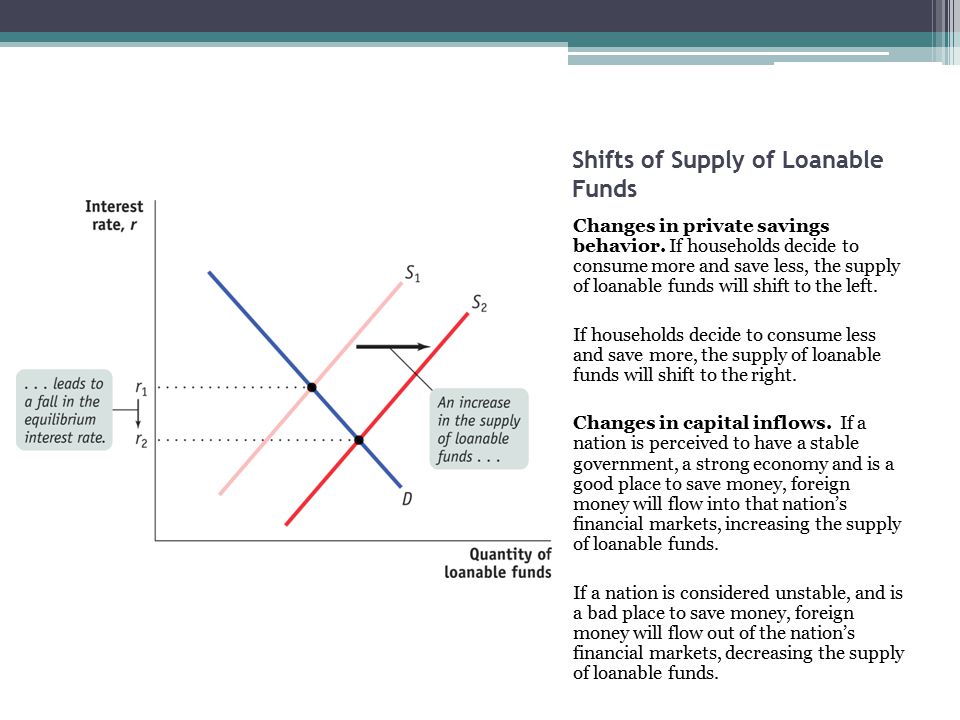
AskedAug 16 2017in Economicsby JeanClaude. Click to see full answer. This change in consumer preferences shifts the supply curve for loanable funds in Panel a of Figure 134 from S 1 to S 2 and raises the interest rate to r 2. The curve itself does not shift There is an downward movement to the right along the demand for loanable funds curve. The bond demand curve and loanable funds supply curve will shift to the right.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
D shifts the supply of loanable funds curve leftward. The price of borrowing money is the interest rate. This video explains why the supply curve for loanable funds increases. If aggregate income goes down loanable funds go down interest rates are going to be higher. Suppose for example that consumers decide to increase current consumption and thus to supply fewer funds to the loanable funds market at any interest rate.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
AskedAug 16 2017in Economicsby Allettext. Leads to a leftward shift in the supply of loanable funds a decrease in total investment and an increase in real interest rates. THE INTEREST RATE IN THE LONG RUN In the loanable funds market an increase in the money supply leads to a short-run rise in real GDP and shifts the supply of loanable funds rightward. The aggregate loanable fund supply curve SL also slopes upwards to the right showing the greater supply of loanable funds at higher rates of interest. The supply of loanable funds curve can be written as r 00005Q.

Anything which increases national savings other than a decrease in the real interest. So in this situation interest rates would go up. What affects the supply of loanable funds. The bond demand curve and loanable funds supply curve will shift to the right. Changes in government spending.
 Source: welkerswikinomics.com
Source: welkerswikinomics.com
There is an downward movement to the left along the supply of loanable funds curve. Economic conditions become more favorable Expected cash flows will increase more positive NPV projects. The supply of loanable funds is generally upward-sloping. If the supply of loanable funds decreases if people stop saving as much for whatever reason then ceteris paribus the price of loanable funds will increase as the S curve shifts to the left to become S1 along the same D curve. This video explains why the supply curve for loanable funds increases.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
D The supply of loanable funds curve would shift leftward to a curve such as SLF1. Federal Reserve Lending direct Lending via discount window 3. If the supply of loanable funds decreases if people stop saving as much for whatever reason then ceteris paribus the price of loanable funds will increase as the S curve shifts to the left to become S1 along the same D curve. C Given the demand for loanable funds curve you were given and the supply of loanable funds curve you derived in b calculate the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds in this market. Anything which decreases national savings other than an increase in the real interest rate will shift the supply curve of loanable funds to the left.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The curve itself doesnt shift. The supply of loanable funds curve can be written as r 00005Q. The Demand and Supply of Loanable Funds. Federal Reserve Lending direct Lending via discount window 3. Anything which increases national savings other than a decrease in the real interest rate will shift the supply curve of loanable funds to the right.
 Source: freeeconhelp.com
Source: freeeconhelp.com
The Demand and Supply of Loanable Funds. The equilibrium interest rate rE will be found where the two curves intersect. The supply of loanable funds is generally upward-sloping. E has no effect on the supply of loanable funds curve. We can obtain the total supply curve of loanable funds by a lateral summation of the curves of saving S dishoarding DH bank money BM and disinvestment DI.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
This change in consumer preferences shifts the supply curve for loanable funds in Panel a of Figure 134 from S 1 to S 2 and raises the interest rate to r 2. Anything which increases national savings other than a decrease in the real interest. So in this situation interest rates would go up. The demand for loanable funds is downward-sloping. Click to see full answer.

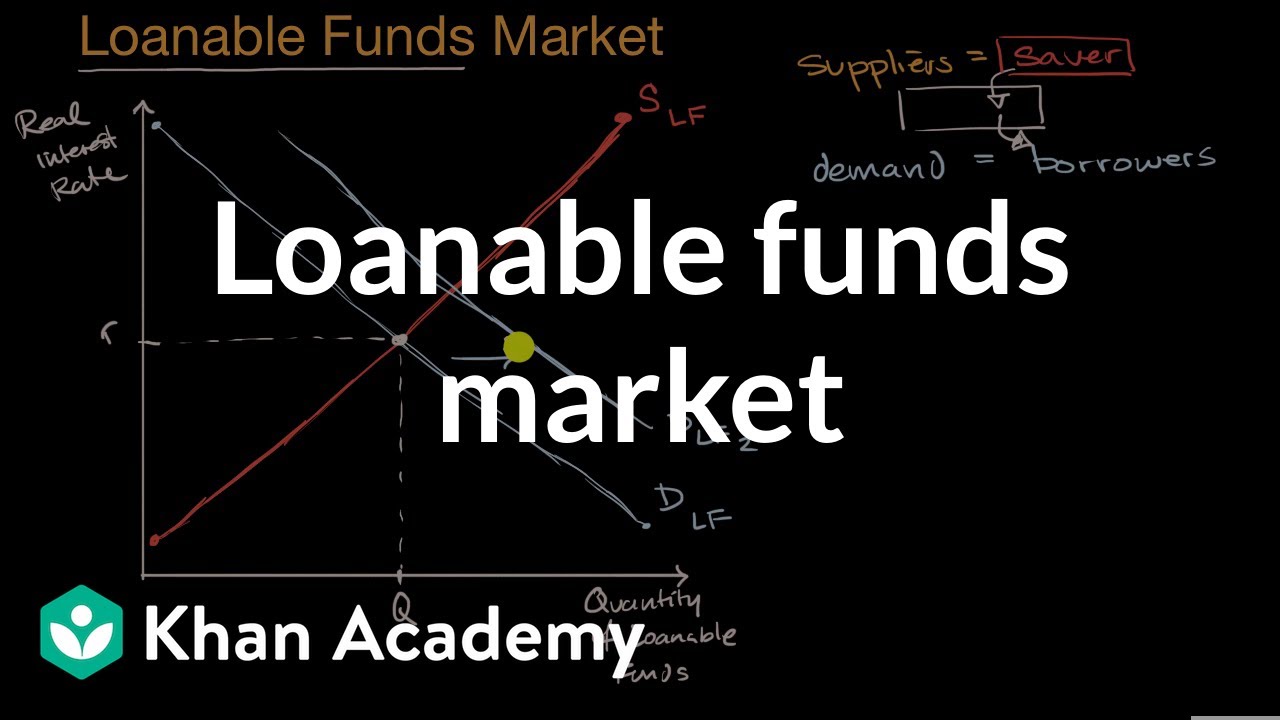
Loanable Funds Theory Business Demand for Loanable Funds There is an inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of loanable funds demanded The curve can shift in response to events that affect business borrowing preferences Example. C Given the demand for loanable funds curve you were given and the supply of loanable funds curve you derived in b calculate the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds in this market. But theres two. The bond demand curve and loanable funds supply curve will shift to the right. Demand for Loanable Funds.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Yes the real interest rate shifts the supply of loanable funds curve because savings ill be increased by the individua View the full answer. Federal Reserve Lending direct Lending via discount window 3. Say the government increases the budget deficit. The supply of loanable funds is generally upward-sloping. If the supply of loanable funds decreases if people stop saving as much for whatever reason then ceteris paribus the price of loanable funds will increase as the S curve shifts to the left to become S1 along the same D curve.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Loanable Funds Theory Business Demand for Loanable Funds There is an inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of loanable funds demanded The curve can shift in response to events that affect business borrowing preferences Example. So once again the same exact curve IS curve. D shifts the supply of loanable funds curve leftward. C Given the demand for loanable funds curve you were given and the supply of loanable funds curve you derived in b calculate the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds in this market. The equilibrium interest rate rE will be found where the two curves intersect.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what shifts the supply of loanable funds curve by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






