Your What is negative supply shock images are ready. What is negative supply shock are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the What is negative supply shock files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for what is negative supply shock pictures information connected with to the what is negative supply shock interest, you have visit the right site. Our site always provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
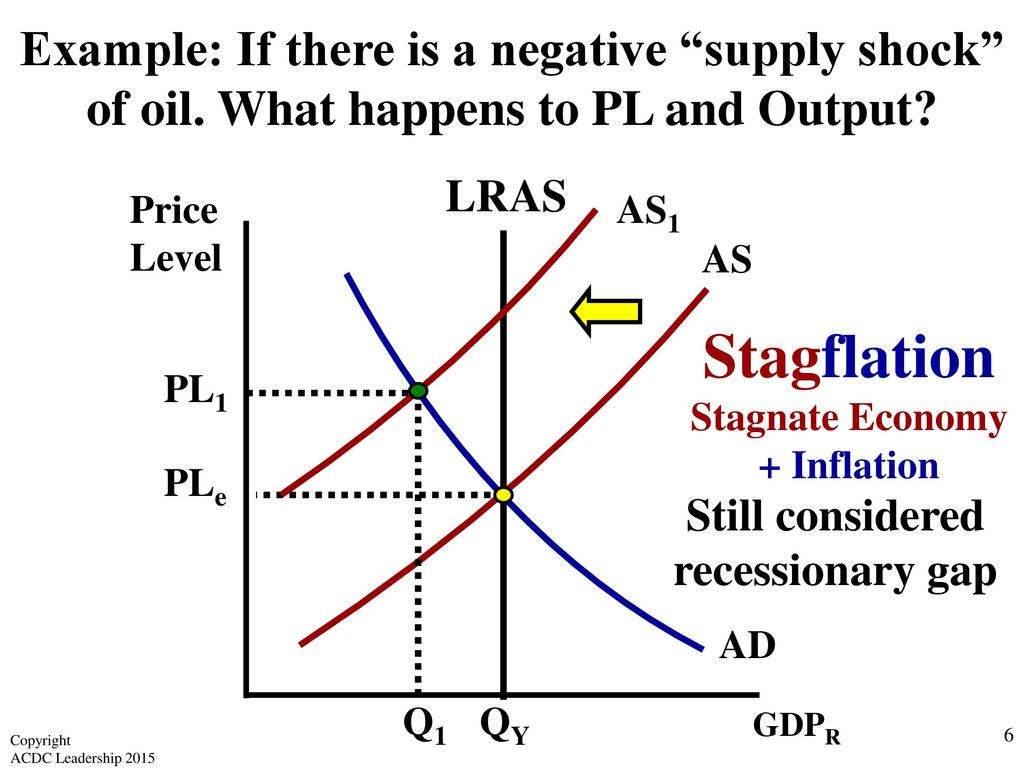
What Is Negative Supply Shock. As supply shocks change output and inflation growth in opposite directions they will obviously have a smaller impact on nominal GDP. A negative supply shock sudden supply decrease will raise prices and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left. Shock may be adverse or favourable. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased.
 Shifters Of Aggregate Demand Shifters Of Aggregate Supply Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Shifters Of Aggregate Demand Shifters Of Aggregate Supply Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
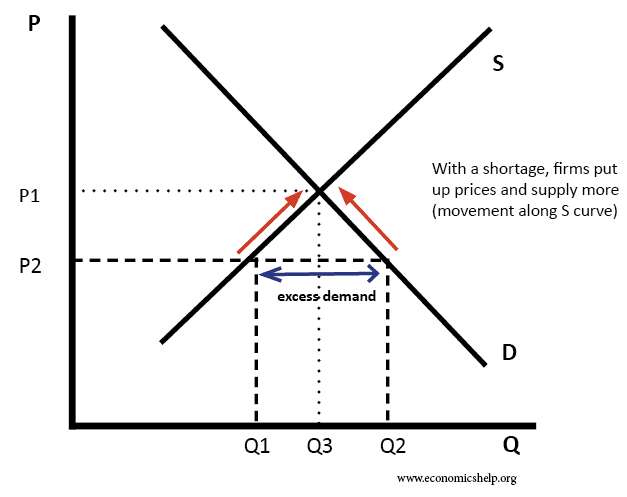
A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. A supply shock is a disturbance to the economy whose first impact is a shift in the AS curve. Shocks may be negative or positive. These changes are called shocks to the economy. A supply shock is a sudden and dramatic change in the supply of a good. The recession of 1974-75 was caused by adverse supply shocks primarily the Oil Crisis which occurred when the Arab members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries OPEC embargoed petroleum exports driving up the price of.
Negative supply shock good news shock agents want to borrow not save at best if they cant they consume zero same as dropping out which is neutral Proposition.
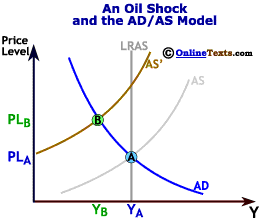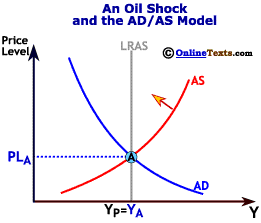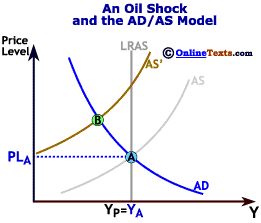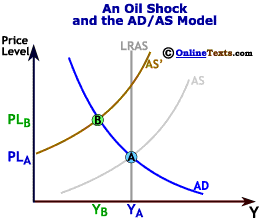
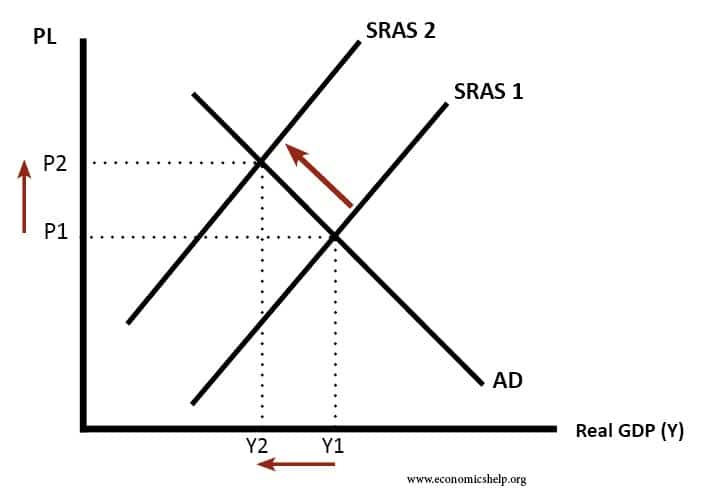
The initial position is at point A producing output quantity Y 1 at price level P 1. It has no direct effect on demand or supply of money. Natural disasters and industrial accidents are a common cause for negative supply shock as they damage supplies or make it impossible to move them. A supply shock is a dramatic reaction to the price of a good or product because of some event that makes people believe that the supply of a product or. The following are illustrative examples. Negative real shocks are more complicated than shocks to aggregate demand.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The initial position is at point A producing output quantity Y 1 at price level P 1. Some of them include. A negative supply shock sudden supply decrease will raise prices and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left. Negative Supply exists to create tools for film photographers around the world that want to spend more time photographing and less time scanning. A positive supply shock increases output causing prices to decrease while a negative supply shock decreases output causing prices to increase.
 Source: econweb.com
Source: econweb.com
The following are illustrative examples. Technological Change An innovation dramatically increases the supply of a commodity sending prices tumbling. A negative supply shock sudden supply decrease will raise prices and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left. A supply shock is a dramatic reaction to the price of a good or product because of some event that makes people believe that the supply of a product or. Single-sector Incomplete Markets Negative Supply Shock Rise natural rate Increase excess demand.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left which tends to raise prices and reduce output. Keeping an eye on spending would allow policymakers to keep inflation within reasonable bounds even if they were unsure about the economys potential growth rate. So this is my supply curve and this is my supply curve with the negative supply shop and this right here. Supply creates its own excess demand. A positive supply shock increases output causing prices to decrease while a negative supply shock decreases output causing prices to increase.
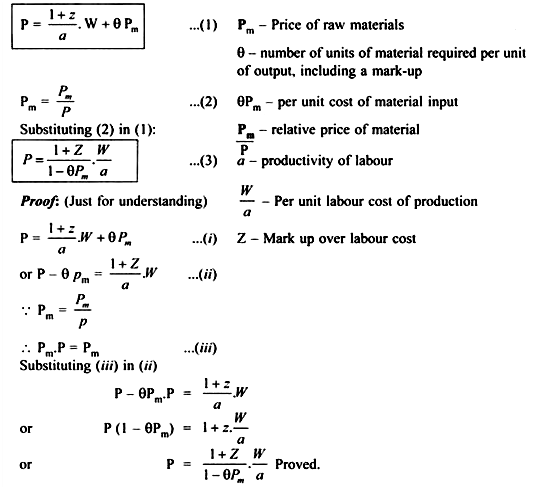 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Negative supply shocks decrease the supply of something. Single-sector Incomplete Markets Negative Supply Shock Rise natural rate Increase excess demand. As supply shocks change output and inflation growth in opposite directions they will obviously have a smaller impact on nominal GDP. Supply shocks may wear their way out the economic system quickly leading to a one-off effect or they may create an extended period of turbulence. A positive supply shock increases output causing prices to decrease while a negative supply shock decreases output causing prices to increase.

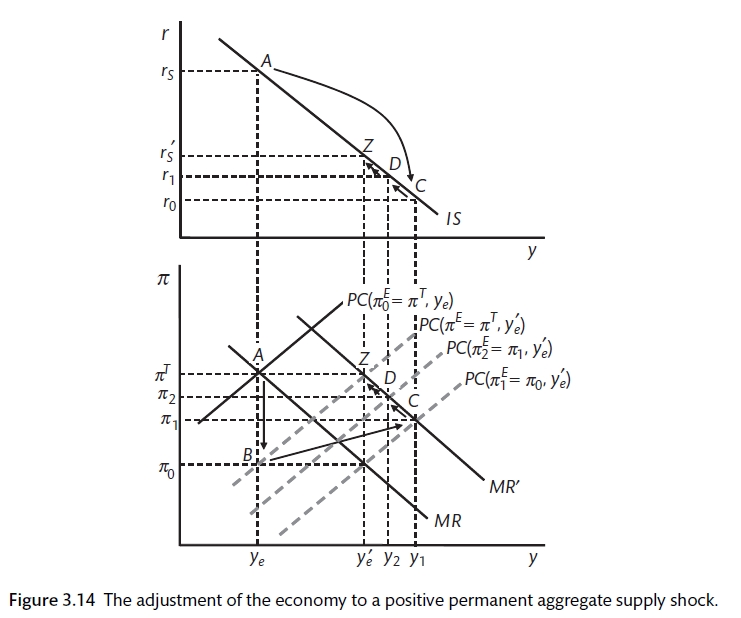
A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve. It has no direct effect on demand or supply of money. What causes a shift in the IS curve. Supply shocks may wear their way out the economic system quickly leading to a one-off effect or they may create an extended period of turbulence. A supply shock is an unexpected event that changes the supply of a product or commodity resulting in a sudden change in price.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. What causes a shift in the IS curve. Any change in the AD and the AS will lead to fluctuations in the economy as a whole. Supply creates its own excess demand.
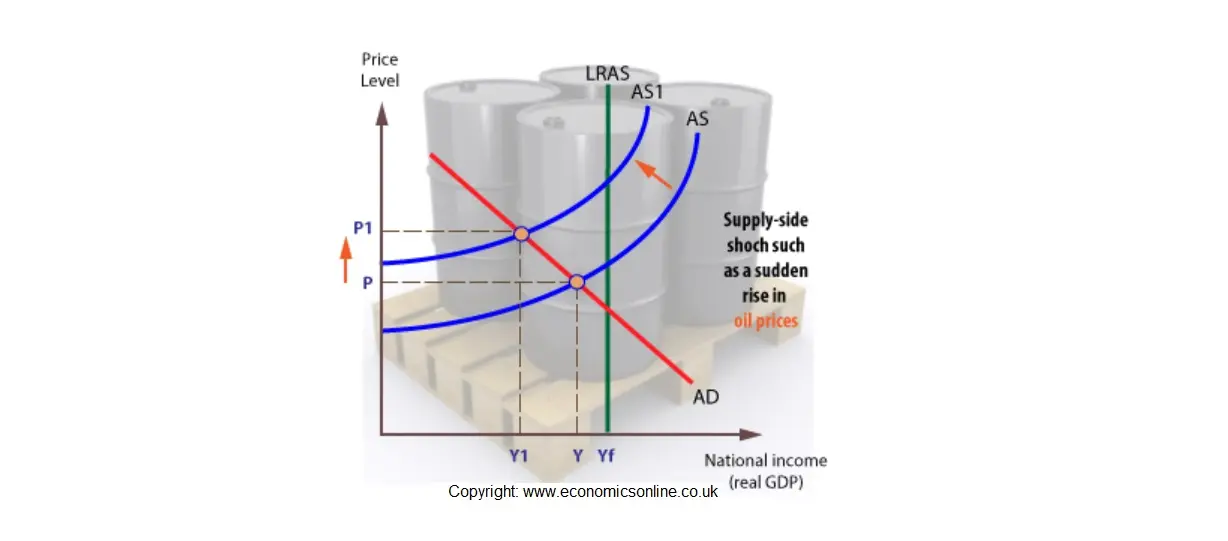 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Negative supply shocks have many potential causes. Some of them include. The supply curve shifts left from AS 1 to AS 2 while the demand curve stays in the same position. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. Keeping an eye on spending would allow policymakers to keep inflation within reasonable bounds even if they were unsure about the economys potential growth rate.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The following are illustrative examples. Shock may be adverse or favourable. Negative Demand Shocks. Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left which tends to raise prices and reduce output. In what way is a permanent negative supply shock worse than a temporary negative supply shop.

A supply shock is a sudden and dramatic change in the supply of a good. These changes are called shocks to the economy. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. What causes a shift in the IS curve.
 Source: bfi.uchicago.edu
Source: bfi.uchicago.edu
Shock may be adverse or favourable. Negative real shocks are more complicated than shocks to aggregate demand. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. These changes are called shocks to the economy.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
The following are illustrative examples. A supply shock is a sudden and unexpected change in a cost variable such as oil prices commodity prices or wages. Keeping an eye on spending would allow policymakers to keep inflation within reasonable bounds even if they were unsure about the economys potential growth rate. A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve. Any change in the AD and the AS will lead to fluctuations in the economy as a whole.
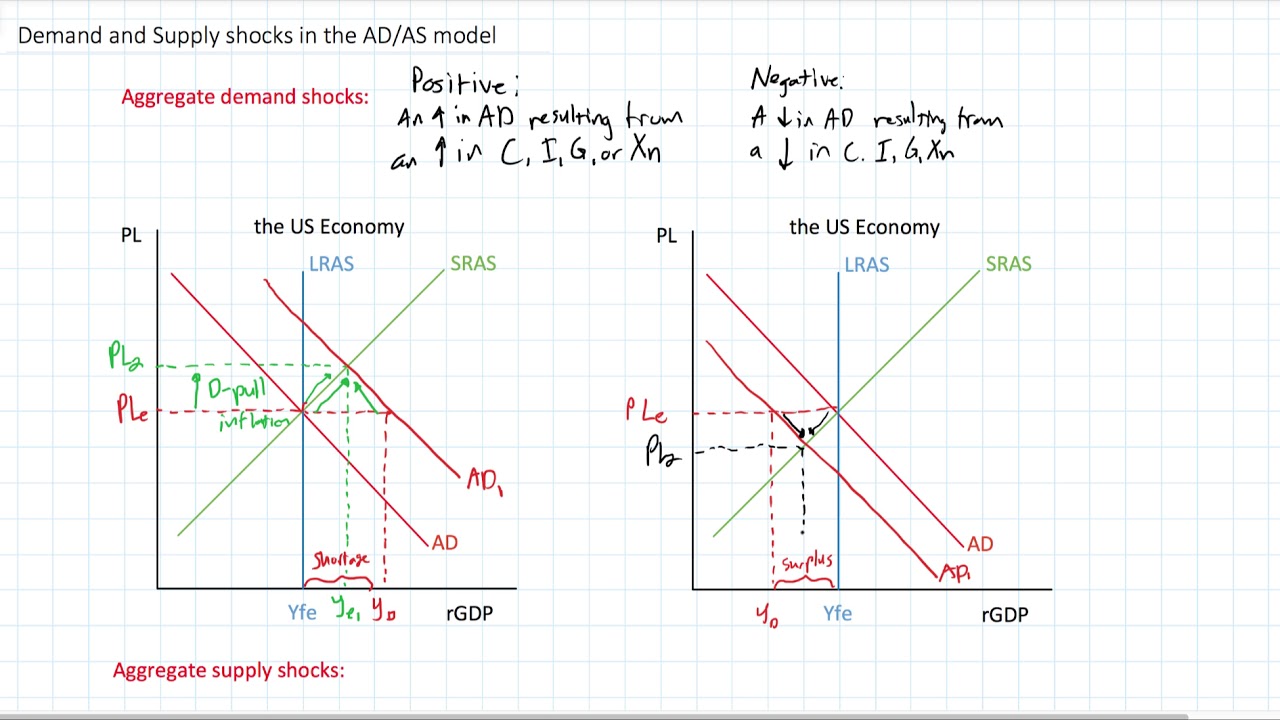 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
As supply shocks change output and inflation growth in opposite directions they will obviously have a smaller impact on nominal GDP. A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Shock may be adverse or favourable.
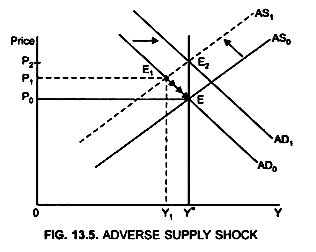 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
These changes are called shocks to the economy. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. In a case of an adverse supply shock. This involves either a sudden increase in supply or a sudden decrease. A supply shock is a disturbance to the economy whose first impact is a shift in the AS curve.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Negative real shocks are more complicated than shocks to aggregate demand. A negative supply shock can cause stagflation due to a combination of raising prices and falling output. What is a negative supply shock. Refinery fires for example may decrease available refined oil products like gasoline. A positive supply shock increases output causing prices to decrease while a negative supply shock decreases output causing prices to.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Demand will rise and prices will increase in response. A negative supply shock eg an increase in the price of oil or a slowdown in productivity reduces the potential output of an economy for given levels of inputs and the price level. Supply shock definition. Our first product the Film Carrier MK1 allows you to digitize negatives and positives using your digital camera and a macro lens in as little as 5 minutes with tools you may already have. Negative Demand Shocks.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Some of them include. Any change in the AD and the AS will lead to fluctuations in the economy as a whole. A real-life example of this occurred in the 1970s. In what way is a permanent negative supply shock worse than a temporary negative supply shop. Refinery fires for example may decrease available refined oil products like gasoline.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. When there is a supply shock this has an adverse effect on aggregate supply. Supply creates its own excess demand.
 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
A supply shock is a sudden and unexpected change in a cost variable such as oil prices commodity prices or wages. A supply shock is a sudden and unexpected change in a cost variable such as oil prices commodity prices or wages. A negative supply shock sudden supply decrease will raise prices and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left. Refinery fires for example may decrease available refined oil products like gasoline. The initial position is at point A producing output quantity Y 1 at price level P 1.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is negative supply shock by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.