Your What is a negative demand shock images are ready in this website. What is a negative demand shock are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the What is a negative demand shock files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re searching for what is a negative demand shock pictures information connected with to the what is a negative demand shock topic, you have come to the right site. Our site always gives you hints for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and images that match your interests.
What Is A Negative Demand Shock. High rates of unemployment. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. A shift of the AD curve to the left means that at least one of these components decreased so that a lesser amount of total spending would occur at every price level.

Some of them include. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment1 As dire as they may be supply shock. As a result. A huge negative demand shock in the economy. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Negative supply shocks have many potential causes.
Price wars among firms.
A crash in stock or home prices can cause a negative demand shock as households react to a loss of wealth by cutting back sharply on consumption spending. A crash in stock or home prices can cause a negative demand shock as households react to a loss of wealth by cutting back sharply on consumption spending. Negative supply shocks have many potential causes. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment1 As dire as they may be supply shock. Decreasing the money supply will help with inflation bu. Occur when one firm lowers its.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Exogenous and endogenous demand side shocks An exogenous demand side shock is one caused by a sudden change in a variable outside. What is a negative economic shock. Some of them include. Too little production of an item may result in a positive demand shock while overproduction may result in a negative demand shock. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock.
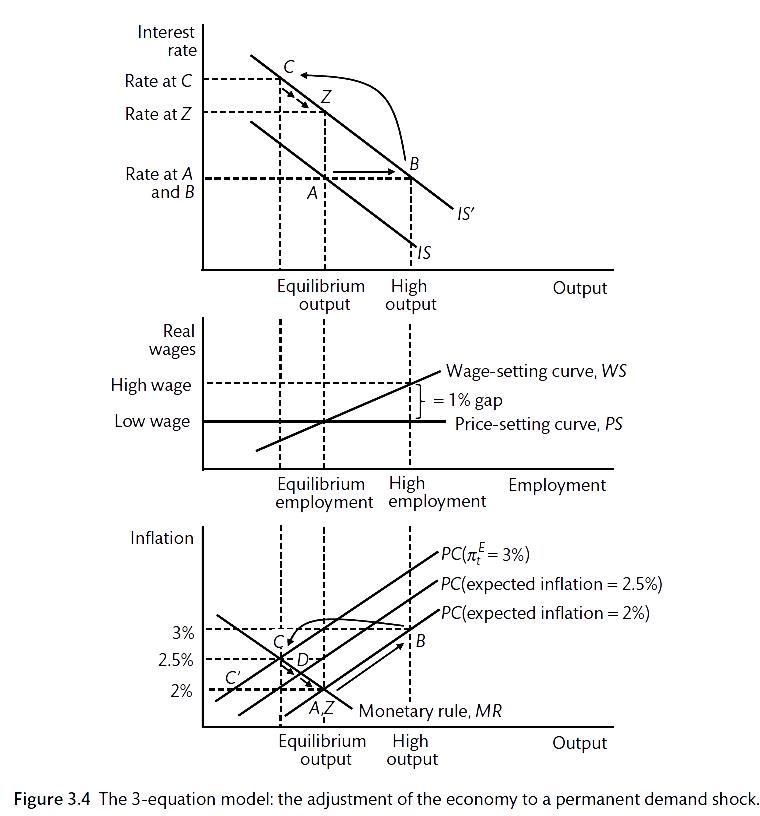 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
Too little production of an item may result in a positive demand shock while overproduction may result in a negative demand shock. Fiscal policy is an example of IS shock. To sum up the negative relationship between price and output is captured by the downward sloping AD curve. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Negative Demand Shocks.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
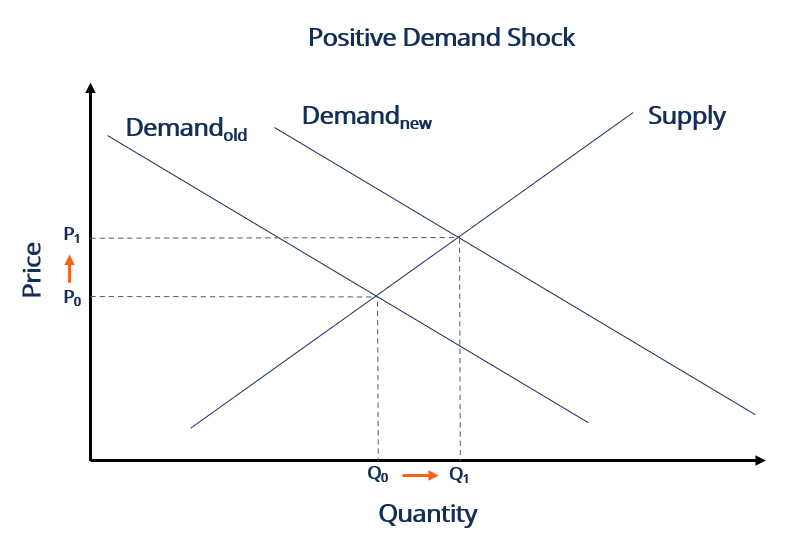
A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. Central bank rate increases. Exogenous and endogenous demand side shocks An exogenous demand side shock is one caused by a sudden change in a variable outside. Imagine a negative real shock like an oil crisis just hit the economy.
 Source: khurak.net
Source: khurak.net
Occur when one firm lowers its. Both a positive demand shock and a negative demand shock will have an effect on the prices of goods and services. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased. Factors that trigger a demand shock vary widely and are not always predictable as in the case of a fad. In the model a deleveraging shock to households reduces their demand for imported final goods as well as their demand for non-traded goods which in turn causes firms to import fewer intermediate inputs.
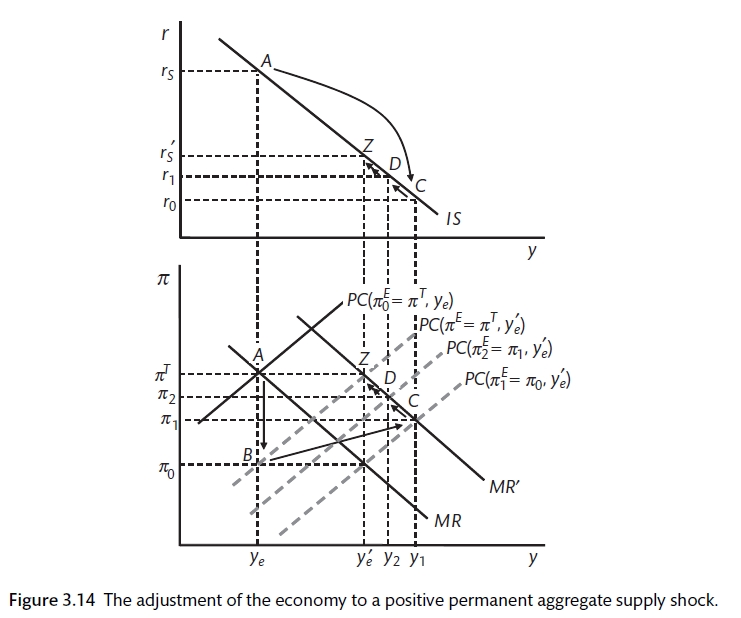 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
Central bank rate increases. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Economic shocks either arise from the demand side or the supply side. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
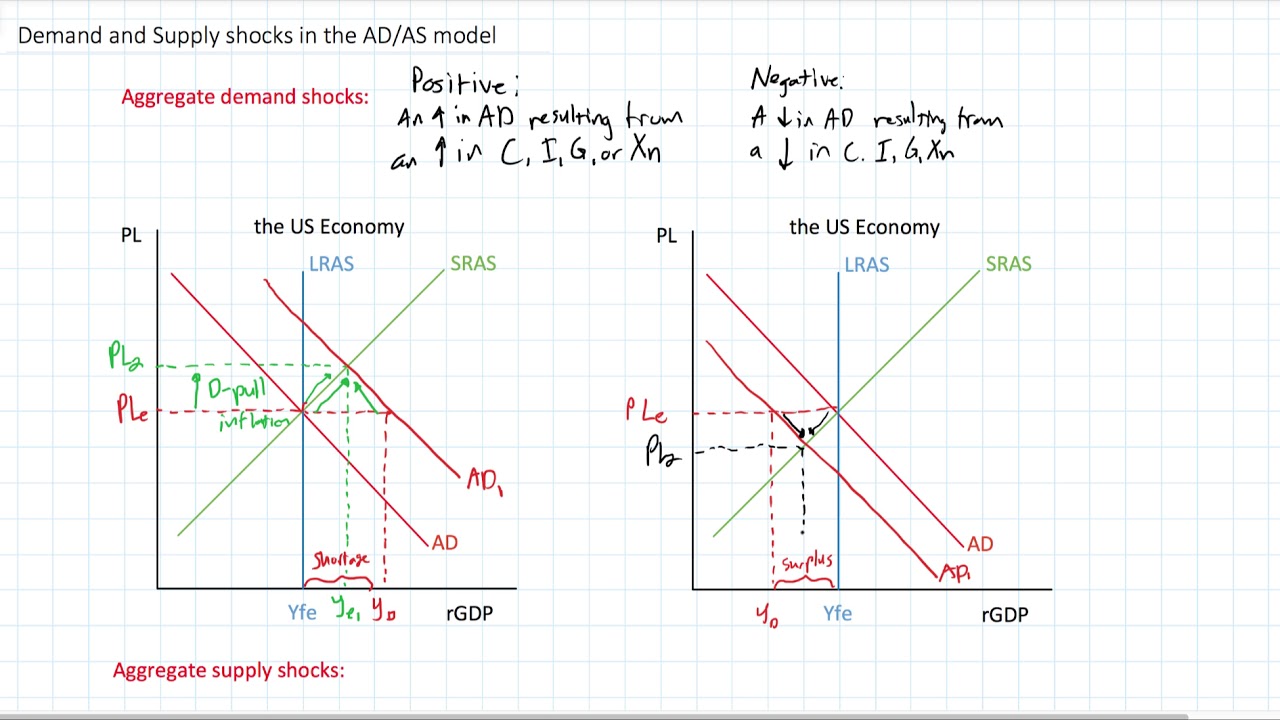
Price wars among firms. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. A demand shock is a sudden surprise event that temporarily increases or decreases demand for particular goods or services. If consumers become pessimistic the economy is likely to experience a.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
We focus on demand shocks other than supply shocks. As a result. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Factors that trigger a demand shock vary widely and are not always predictable as in the case of a fad. Some of them include.
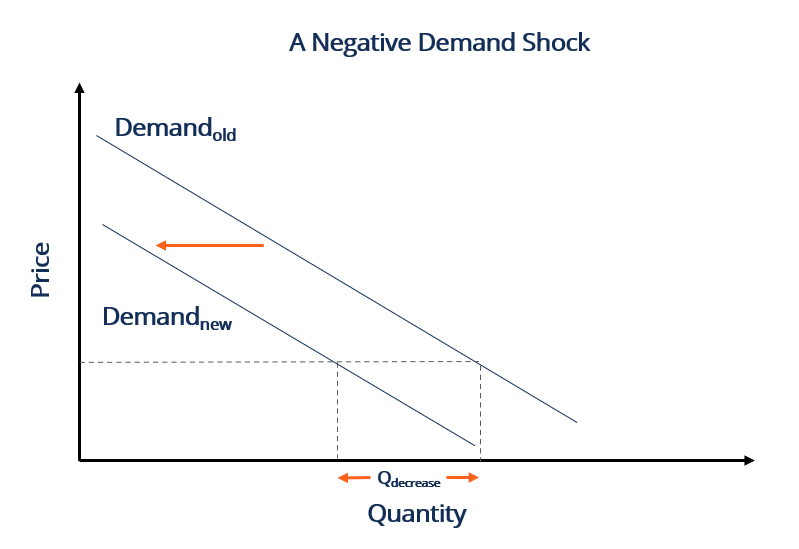 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Negative demand shocks decrease aggregate demand in the economy because people are more inclined to save rather than consume. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. This is called a positive demand shock. We focus on demand shocks other than supply shocks. Indicate that society is not using a large portion of the talent and skills of its people.
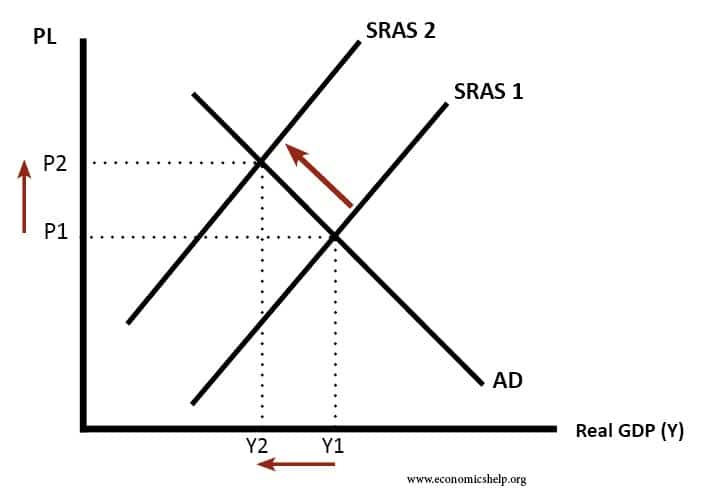 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. We focus on demand shocks other than supply shocks. This is called a negative demand shock. As a result. Price wars among firms.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
High rates of unemployment. Additionally as service sector workers lose their jobs and income they stop purchasing all kinds of goods such as cars and appliances which can also be. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. Occur when one firm lowers its. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. As shown below the entire demand curve shifts left. A huge negative demand shock in the economy. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment. Indicate that society is not using a large portion of the talent and skills of its people.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
As dire as they may be. Economic shocks either arise from the demand side or the supply side. Assuming aggregate demand is unchanged a negative or adverse supply shock causes a products price to spike upward while a positive supply shock decreases the price. Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left. As a result.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. A crash in stock or home prices can cause a negative demand shock as households react to a loss of wealth by cutting back sharply on consumption spending. Additionally as service sector workers lose their jobs and income they stop purchasing all kinds of goods such as cars and appliances which can also be. Price wars among firms. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment1 As dire as they may be supply shock.

We focus on demand shocks other than supply shocks. Imagine a negative real shock like an oil crisis just hit the economy. Negative demand shocks decrease aggregate demand in the economy because people are more inclined to save rather than consume. This is called a positive demand shock. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand.

A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. Negative demand shocks decrease aggregate demand in the economy because people are more inclined to save rather than consume. To sum up the negative relationship between price and output is captured by the downward sloping AD curve. This is called a positive demand shock. Additionally as service sector workers lose their jobs and income they stop purchasing all kinds of goods such as cars and appliances which can also be.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Either shock will have an. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. How should the Fed respond. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself.
 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Too little production of an item may result in a positive demand shock while overproduction may result in a negative demand shock. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. 3 Monetary policy cause IS LM curve to shift. This is called a negative demand shock. Fiscal policy is an example of IS shock.
 Source: europarl.europa.eu
Source: europarl.europa.eu
A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and. There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. Demand shocks The equilibrium position of national income will change ceteris paribus following an economic shock. Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is a negative demand shock by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






