Your What changes the supply of loanable funds images are available in this site. What changes the supply of loanable funds are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the What changes the supply of loanable funds files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for what changes the supply of loanable funds pictures information linked to the what changes the supply of loanable funds keyword, you have come to the right site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
What Changes The Supply Of Loanable Funds. The supply curve is upward sloping because as the interest rate increases people will want to save more. Supply The supply of loanable funds represents the behavior of all of the savers in an economy. As I said earlier the interest rate represents the return you get when you lend money. But since the savings portion of the schedule varies with the level of disposable income it follows that the total supply schedule of loanable funds also varies with income making the rate of interest.
 Question From Www Econ101help Com Suppose The Government Borrows 20 Billion More Next Year Than This Year This Or That Questions The Borrowers Negativity From pinterest.com
Question From Www Econ101help Com Suppose The Government Borrows 20 Billion More Next Year Than This Year This Or That Questions The Borrowers Negativity From pinterest.com
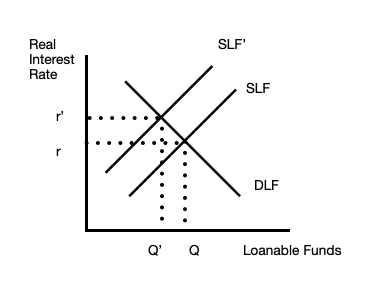
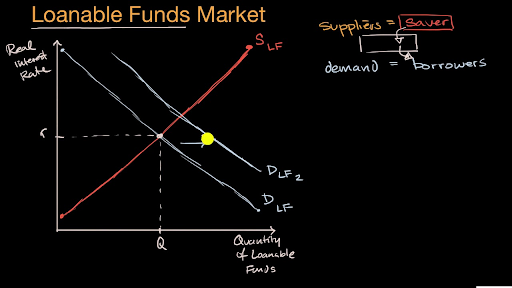
Neither curve shifts but the quantity of loanable funds supplied increases and the quantity demanded decreases as the interest rate rises to equilibrium. When the real interest rate increases investment spending decreases. When investors shift funds out of stocks they move it into money market securities causing an increase in the supply of loanable funds and lower interest rates. Does not influence the supply of or the demand for loanable funds. This is bad for the growth of capital stock and slows down the rate of long run economic growth. According to the loanable funds theory formulated by the Swedish economist.
Here a decrease in consumer saving causes a shift in the supply of.
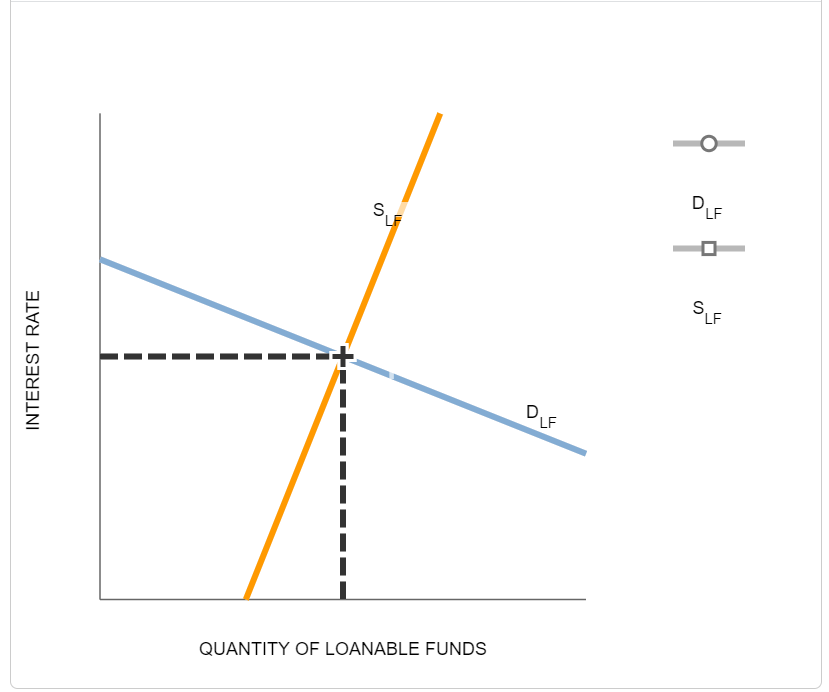
The interest rate is determined in the market for loanable funds. These same entities demand loanable funds demanding more when the level of interest rates is low and less when interest rates are higher. Such policies would increase the demand for loanable funds. The Loanable Funds Market The loanable funds market is made up of borrowers who demand funds D lf and lenders who supply funds S lf. Changes both the supply of and demand for loanable funds. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Changes both the supply of and demand for loanable funds. Public saving and so shift the supply of. Results in an excess supply in the money market that spills over into the market for loanable funds thereby increasing the supply of LF. If there is a decrease in savings by the private sector the supply of loanable funds decreases shifts left causing the real interest rate to rise. A Supply and demand for loanable funds determines the real interest rate B Savers and lenders supply money to the loanable funds market C Government firms and individuals make up the demand in the loanable funds market D The supply of loanable funds is vertical and is set by the Federal Reserve government lowers corporate taxes to.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The supply of loanable funds increases with increasing interest rate because there is a competition between using the money now for personal consumption and delaying consumption by lending the money out so that the lender will have more later on. This is bad for the growth of capital stock and slows down the rate of long run economic growth. Such policies would increase the demand for loanable funds. If there is a decrease in savings by the private sector the supply of loanable funds decreases shifts left causing the real interest rate to rise. The higher the level of interest rates the more such entities are willing to supply loan funds.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
When investors shift funds out of stocks they move it into money market securities causing an increase in the supply of loanable funds and lower interest rates. The interest rate is determined in the market for loanable funds. If there is a decrease in savings by the private sector the supply of loanable funds decreases shifts left causing the real interest rate to rise. What causes shifts in the loanable funds market. Professor Alvin H Hansen argues that the schedule of loanable funds is compounded of savings plus net additions to loanable funds from new money and dishoarding idle balances.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Some government policies such as investment tax credits basically lower the cost of borrowing money at every real interest rate. Figure 4-51 Market for Loanable Funds QUANTITY OF LOANABLE FUNDS REAL INTEREST RATE Q lf D lf S lf i. The interest rate is determined in the market for loanable funds. What causes shifts in the loanable funds market. A change in disposable income expected future income wealth or default risk changes the supply of loanable funds.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Supply The supply of loanable funds represents the behavior of all of the savers in an economy. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. A change in disposable income expected future income wealth or default risk changes the supply of loanable funds. If Canada increases its budget deficit it will reduce a. The lower real interest rate increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded and increases investment.
Supply The supply of loanable funds represents the behavior of all of the savers in an economy. This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market. The higher the level of interest rates the more such entities are willing to supply loan funds. Here a decrease in consumer saving causes a shift in the supply of. These same entities demand loanable funds demanding more when the level of interest rates is low and less when interest rates are higher.

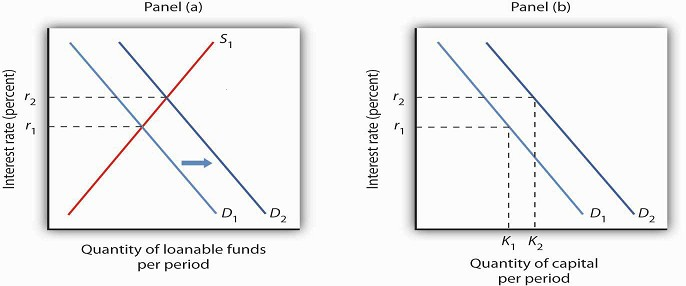
Other policies such as budget deficits might increase the demand for loanable funds. The supply of loanable funds increases with the increase in interest rates. Supply The supply of loanable funds represents the behavior of all of the savers in an economy. When a change in the supply of money leads to a change in the interest rate the resulting change in real GDP. A change that begins in the loanable funds market can affect the quantity of capital firms demand.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Changes both the supply of and demand for loanable funds. So in the long run the money demand curve shifts rightward and the equilibrium interest rate rises back to its original level. When investors shift funds out of stocks they move it into money market securities causing an increase in the supply of loanable funds and lower interest rates. What causes shifts in the loanable funds market. The supply of loanable funds increases with the increase in interest rates.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
The supply curve is upward sloping because as the interest rate increases people will want to save more. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. A change that begins in the loanable funds market can affect the quantity of capital firms demand. When a change in the supply of money leads to a change in the interest rate the resulting change in real GDP. A change in disposable income expected future income wealth or default risk changes the supply of loanable funds.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
According to the loanable funds theory formulated by the Swedish economist. Represents a change in the quantity of loanable funds demanded in response to a change in interest rates. Figure 4-51 Market for Loanable Funds QUANTITY OF LOANABLE FUNDS REAL INTEREST RATE Q lf D lf S lf i. The supply of loanable funds increases with the increase in interest rates. Public saving and so shift the supply of.
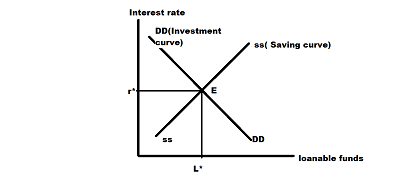 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Public saving and so shift the supply of. But since the savings portion of the schedule varies with the level of disposable income it follows that the total supply schedule of loanable funds also varies with income making the rate of interest. The lower the level of interest the less they are willing to supply. Individuals supply loanable funds through savings. When investors shift funds out of stocks they move it into money market securities causing an increase in the supply of loanable funds and lower interest rates.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This is bad for the growth of capital stock and slows down the rate of long run economic growth. Private saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left. Other policies such as budget deficits might increase the demand for loanable funds. A change in disposable income expected future income wealth or default risk changes the supply of loanable funds. Public saving and so shift the supply of.
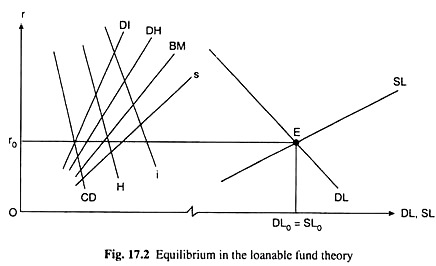 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market. The supply curve is upward sloping because as the interest rate increases people will want to save more. Changes both the supply of and demand for loanable funds. The supply for loanable funds S LF curve slopes upward because the higher the real interest rate the higher the return someone gets from loaning his or her money. Results in an excess supply in the money market that spills over into the market for loanable funds thereby increasing the supply of LF.
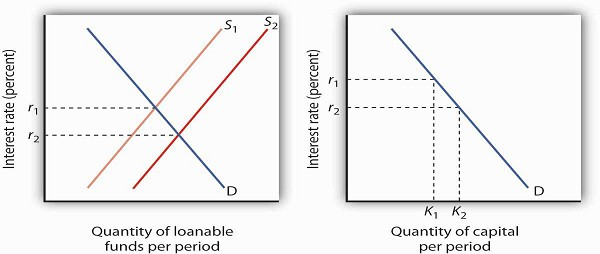 Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
This is bad for the growth of capital stock and slows down the rate of long run economic growth. A change that begins in the loanable funds market can affect the quantity of capital firms demand. Individuals supply loanable funds through savings. Private saving and so shift the supply of loanable funds left. The supply for loanable funds shifts left and the demand shifts right.
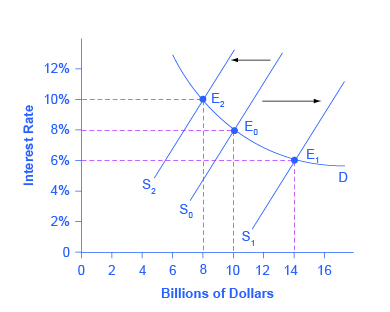 Source: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Source: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
As I said earlier the interest rate represents the return you get when you lend money. A change in disposable income expected future income wealth or default risk changes the supply of loanable funds. The lower real interest rate increases the quantity of loanable funds demanded and increases investment. The lower the level of interest the less they are willing to supply. Public saving and so shift the supply of.
But since the savings portion of the schedule varies with the level of disposable income it follows that the total supply schedule of loanable funds also varies with income making the rate of interest. Why is the supply of loanable funds upward sloping. When demand for investment decreases quantity quantity of loanable funds decreases and real interest rate decreases. Neither curve shifts but the quantity of loanable funds supplied increases and the quantity demanded decreases as the interest rate rises to equilibrium. Figure 4-51 Market for Loanable Funds QUANTITY OF LOANABLE FUNDS REAL INTEREST RATE Q lf D lf S lf i.
 Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
A change that begins in the loanable funds market can affect the quantity of capital firms. When demand for investment decreases quantity quantity of loanable funds decreases and real interest rate decreases. The supply of loanable funds increases with the increase in interest rates. Why is the supply of loanable funds upward sloping. The supply of loanable funds increases with increasing interest rate because there is a competition between using the money now for personal consumption and delaying consumption by lending the money out so that the lender will have more later on.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Changes both the supply of and demand for loanable funds. A change in disposable income expected future income wealth or default risk changes the supply of loanable funds. When the real interest rate increases investment spending decreases. This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market. If the government has a budget surplus it increases the supply of loanable funds the real interest rate falls which decreases household saving and decreases the quantity of private funds supplied.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what changes the supply of loanable funds by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.