Your What causes a decrease in aggregate supply images are available in this site. What causes a decrease in aggregate supply are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the What causes a decrease in aggregate supply files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for what causes a decrease in aggregate supply images information related to the what causes a decrease in aggregate supply topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
What Causes A Decrease In Aggregate Supply. Its all about money supply and truthfully now more and more based on psychology marketing and other variables that CREATE a demand. Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible. When the price level falls and the money wage rate is constant the real wage rate rises and employment decreases. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages an increase in production costs changes in producer taxes and subsidies and changes in inflation.
 Deflationary Gap From id.pinterest.com
Deflationary Gap From id.pinterest.com
If successful the cuts will shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply because the price level for a supply of goods will be reduced which often leads to an increase in demand for those goods. Increases in the price of such inputs represent a negative supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to shift to the left. Aggregate supply is a measure of the total goods and services produced by an economy at various price levels either in the short run or in the long run. When these other factors change they cause a shift in the entire AS curve and are sometimes called aggregate supply shifters. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. Taxes and other costs - costs such as regulation and taxation costs can place a burden on the unit costs of production lowering the aggregate supply of an economy.
One of the more common reasons for decreases in aggregate demand have to do with changes in the distribution of income within the economy.
A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. Increases in the price of such inputs represent a negative supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to shift to the left. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. Because higher inflation leads to more output higher inflation is also associated with lower unemployment in.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
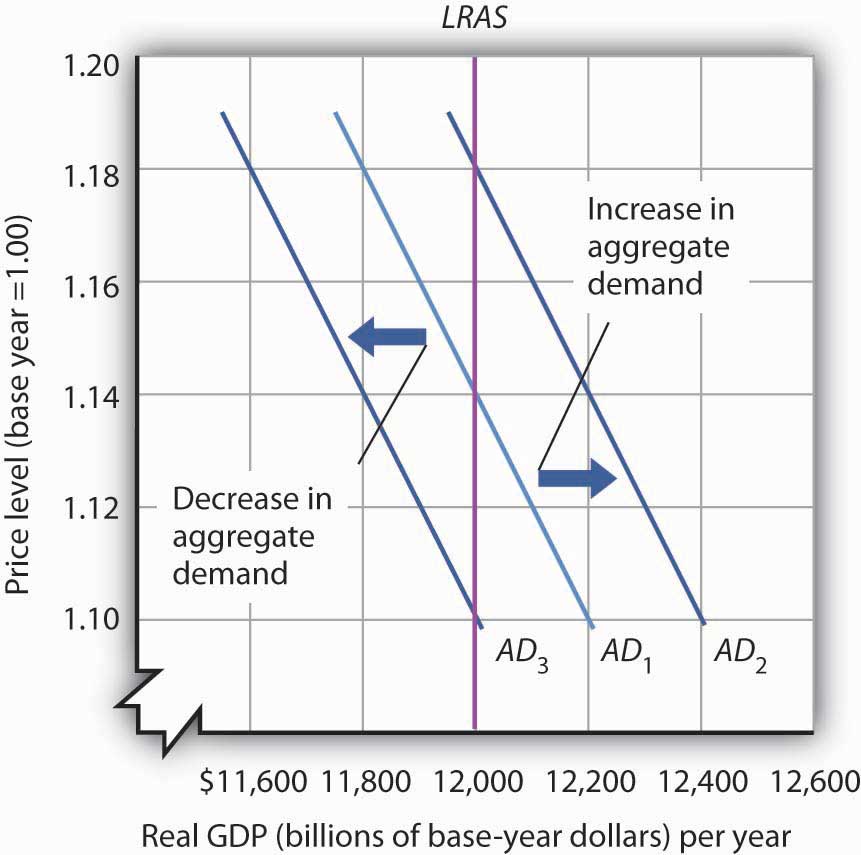
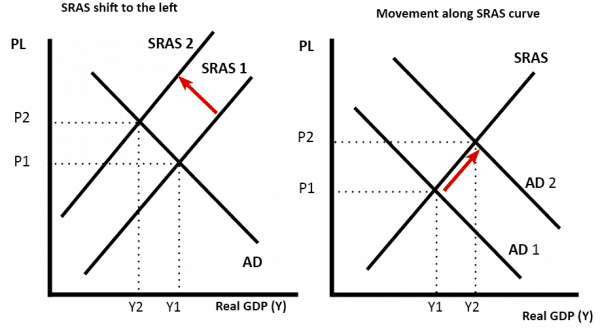
The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. Whatever affects the spending power of the buying market. Long-run aggregate supply curve. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. When these other factors change they cause a shift in the entire AS curve and are sometimes called aggregate supply shifters. Higher prices for inputs that are widely used across the entire economy such as labor or energy can have a macroeconomic impact on aggregate supply. If successful the cuts will shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply because the price level for a supply of goods will be reduced which often leads to an increase in demand for those goods. According to macroeconomic theory a demand shock is an important change somewhere in the economy that affects many spending decisions and causes a sudden and unexpected shift in the aggregate.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
How Changes in Input Prices Shift the AS Curve. The aggregate supply curve can also shift due to shocks to input goods or labor. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. Its all about money supply and truthfully now more and more based on psychology marketing and other variables that CREATE a demand. These aggregate supply shifters include Changes in Resource Prices Changes in Resource Productivity Business Taxes and Subsidies and Government Regulations.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
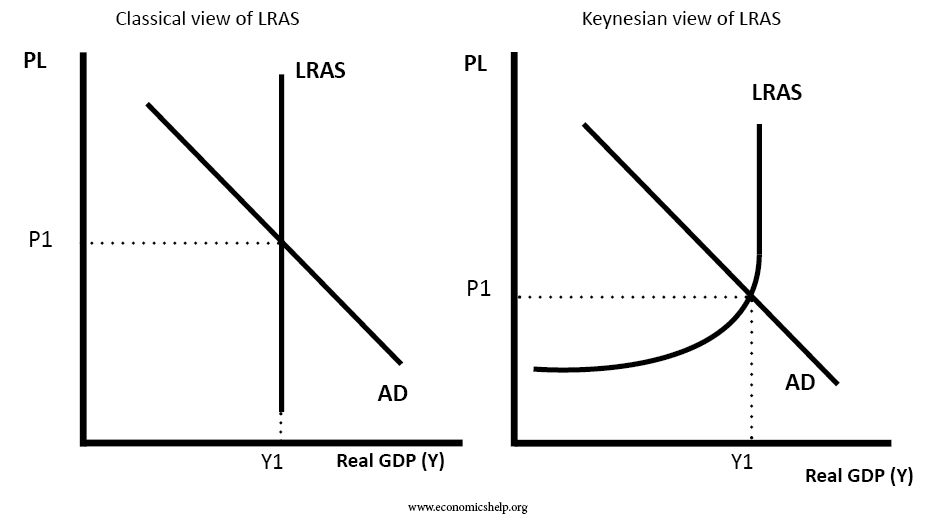
Jeff aggregate supply and demand macroeconomics Here is a list of effects that can shift the aggregate supply curves. When the price level falls and the money wage rate is constant the real wage rate rises and employment decreases. If successful the cuts will shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply because the price level for a supply of goods will be reduced which often leads to an increase in demand for those goods. Increases in the price of such inputs represent a negative supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to shift to the left. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The Aggregate demand is a graph of the total demand for a product at different price. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages. Anything that causes the amount of workers to increase in an economy will cause aggregate supply to increase or shift to the right. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. Which of the following would most likely cause a decrease in the aggregate supply.
 Source: id.pinterest.com
Source: id.pinterest.com
Taxes and other costs - costs such as regulation and taxation costs can place a burden on the unit costs of production lowering the aggregate supply of an economy. Material Prices - higher material prices and other inputs will increase the unit labour costs of production and lower aggregate supply. According to macroeconomic theory a demand shock is an important change somewhere in the economy that affects many spending decisions and causes a sudden and unexpected shift in the aggregate. If successful the cuts will shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply because the price level for a supply of goods will be reduced which often leads to an increase in demand for those goods. Supply-side tax cuts are aimed to stimulate capital formation.
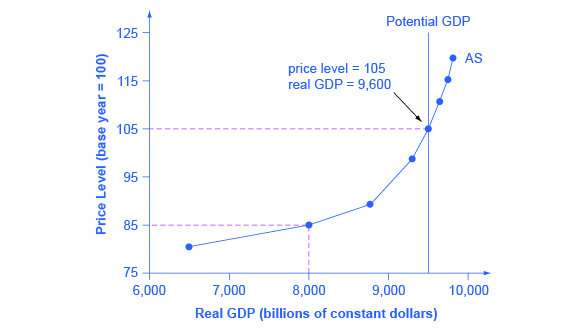 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages. A curve that shows the relationship in. Know more about it here.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible. Increase per-unit production costs and thus decrease aggregate supply The passage of new legislation requiring more extensive government regulation of business will most likely. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. One of the more common reasons for decreases in aggregate demand have to do with changes in the distribution of income within the economy. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages.
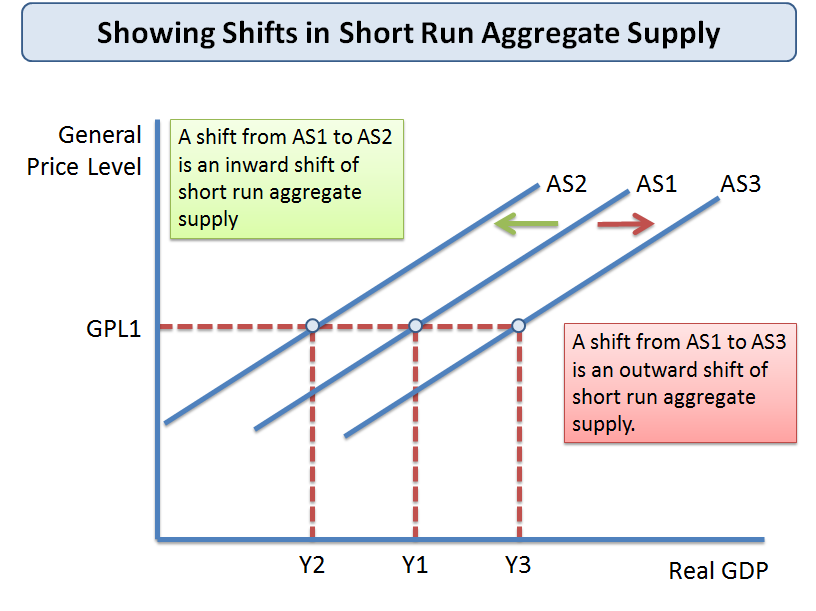 Source: gpeco.weebly.com
Source: gpeco.weebly.com
These include any change in the endowments of the factors of production including labor capital or technology. If the wages and salaries of consumers who normally spend a great deal of disposable income on certain products should be adversely impacted by unemployment or reduction in wages due to a recession then the demand for. Material Prices - higher material prices and other inputs will increase the unit labour costs of production and lower aggregate supply. The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. These include any change in the endowments of the factors of production including labor capital or technology.

The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. Because higher inflation leads to more output higher inflation is also associated with lower unemployment in. For example an unexpected early freeze could destroy a large number of agricultural crops a shock that would shift the AS curve to the left since there would be fewer.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible. The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. Know more about it here. Its all about money supply and truthfully now more and more based on psychology marketing and other variables that CREATE a demand. Taxes and other costs - costs such as regulation and taxation costs can place a burden on the unit costs of production lowering the aggregate supply of an economy.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Higher prices for inputs that are widely used across the entire economy such as labor or energy can have a macroeconomic impact on aggregate supply. Its all about money supply and truthfully now more and more based on psychology marketing and other variables that CREATE a demand. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. Anything that causes the amount of workers to increase in an economy will cause aggregate supply to increase or shift to the right. What are the shifters of aggregate supply.

Jeff aggregate supply and demand macroeconomics Here is a list of effects that can shift the aggregate supply curves. Its all about money supply and truthfully now more and more based on psychology marketing and other variables that CREATE a demand. Increase per-unit production costs and thus decrease aggregate supply The passage of new legislation requiring more extensive government regulation of business will most likely. One of the more common reasons for decreases in aggregate demand have to do with changes in the distribution of income within the economy. Second SRAS also tells us there is a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.

Anything that causes the amount of workers to increase in an economy will cause aggregate supply to increase or shift to the right. Anything that causes the amount of workers to increase in an economy will cause aggregate supply to increase or shift to the right. Increases in the price of such inputs represent a negative supply shock shifting the SRAS curve to shift to the left. What are the shifters of aggregate supply. Taxes and other costs - costs such as regulation and taxation costs can place a burden on the unit costs of production lowering the aggregate supply of an economy.
 Source: web.mnstate.edu
Source: web.mnstate.edu
These aggregate supply shifters include Changes in Resource Prices Changes in Resource Productivity Business Taxes and Subsidies and Government Regulations. The quantity of real GDP supplied decreases. The Aggregate demand is a graph of the total demand for a product at different price. Changes in labor force. If the wages and salaries of consumers who normally spend a great deal of disposable income on certain products should be adversely impacted by unemployment or reduction in wages due to a recession then the demand for.
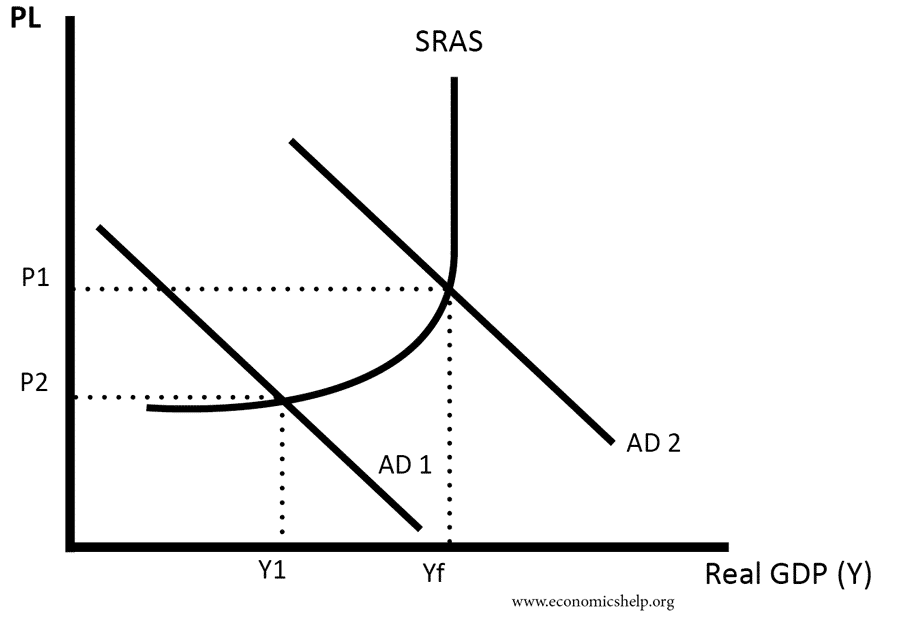 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Higher prices for inputs that are widely used across the entire economy such as labor or energy can have a macroeconomic impact on aggregate supply. Second SRAS also tells us there is a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. According to macroeconomic theory a demand shock is an important change somewhere in the economy that affects many spending decisions and causes a sudden and unexpected shift in the aggregate. Changes in Aggregate Supply. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages.
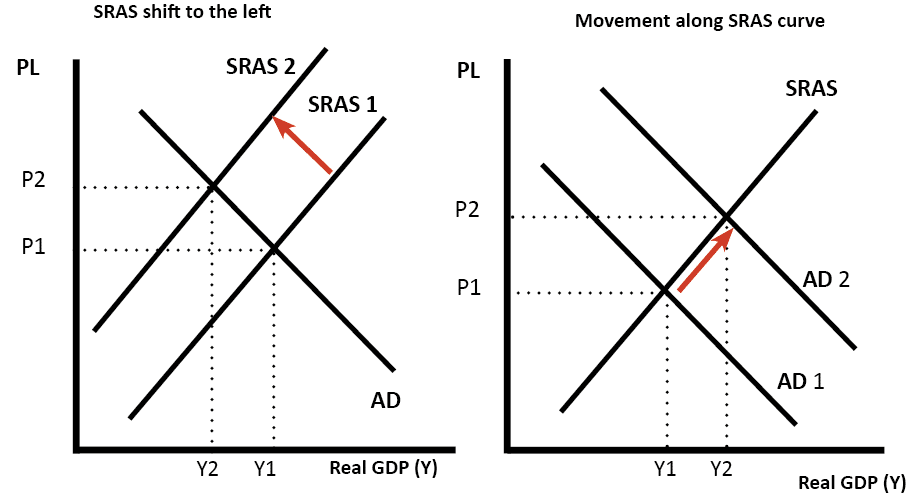 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. What are the shifters of aggregate supply. Changes in labor force. When the economy reaches its level of full capacity full employment when the economy is on the production possibility frontier the aggregate supply curve becomes inelastic because even at higher prices firms cannot produce more in the short term. A curve that shows the relationship in.
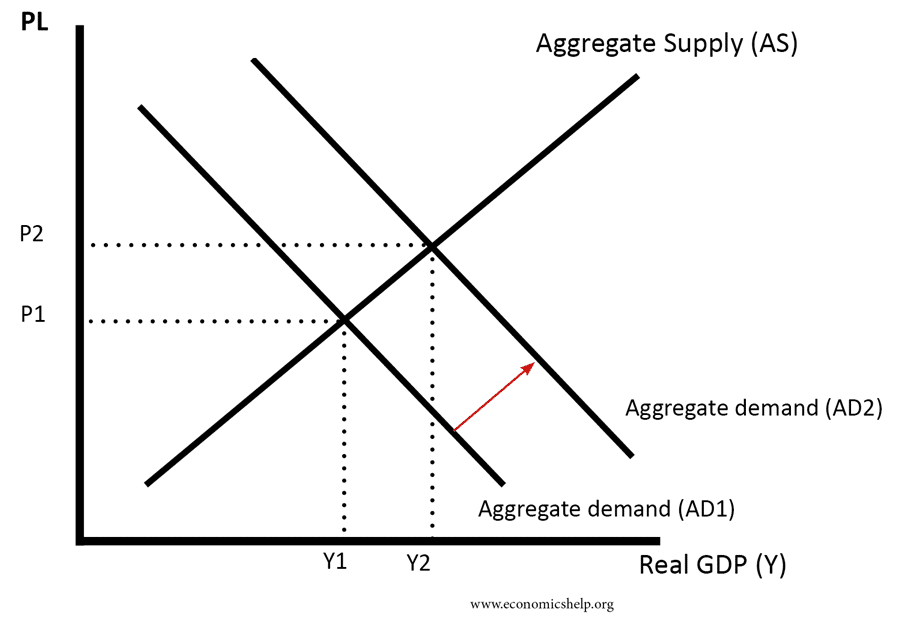 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages an increase in production costs changes in producer taxes and subsidies. Supply-side tax cuts are aimed to stimulate capital formation. Answer 1 of 3. A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables including changes in the size and quality of labor technological innovations an increase in wages an increase in production costs changes in producer taxes and subsidies and changes in inflation. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what causes a decrease in aggregate supply by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.