Your Tax curve supply and demand images are available in this site. Tax curve supply and demand are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Tax curve supply and demand files here. Get all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for tax curve supply and demand pictures information related to the tax curve supply and demand topic, you have visit the right blog. Our site always gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Tax Curve Supply And Demand. As the price of the apples increases producers are. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers. Elastic Demand and Inelastic Supply.
 Effect Of Tax Depending On Elasticity Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Effect Of Tax Depending On Elasticity Economics Help From economicshelp.org
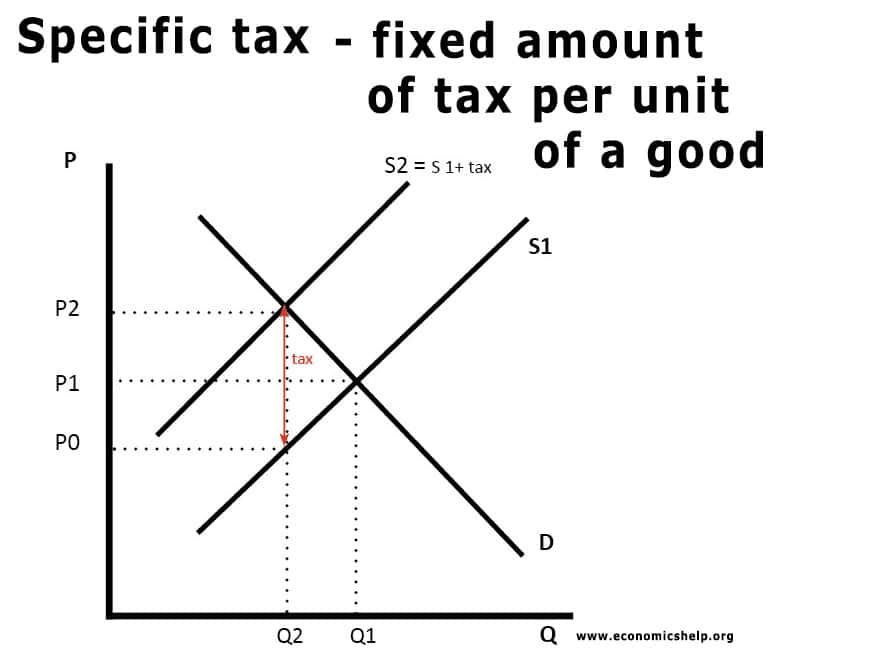
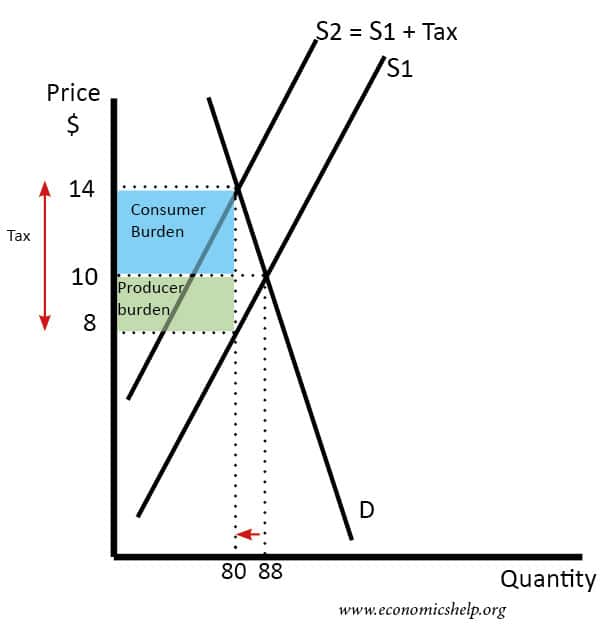
Because the graphs for demand and supply curves both have price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis the demand curve and supply curve for a particular good or service can appear on the same graph. D P or we can draw it graphically as in Figure 22. Lets consider how the increase in taxes affects the demand and supply curves. The example of cigarette taxes introduced previously demonstrated that because demand is inelastic taxes are not effective at reducing the equilibrium quantity of smoking and they mainly pass along to consumers in the form of higher prices. Similar to the demand curve a movement along the supply curve from point A to point B is called a change in the quantity supplied. The extent of change is the price or the extent to which tax can be passed on to buyers depends on the degree of supply elasticity.
To apply to movements along the supply curve.
In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. You should also verify that these demand and supply curves imply a market price of 1 and quantity of 100 bgyr. Shifts from D to D. Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers. The extent of change is the price or the extent to which tax can be passed on to buyers depends on the degree of supply elasticity. Economists are often concerned with the effect of government policies like taxes or subsidies on the interaction of supply and demand.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. If the tax is instead imposed on consumers the demand curve shifts down by the amount of the tax 50 cents to D 2. When a tax is imposed on consumers the demand curve will. To apply to movements along the supply curve. Therefore when the supply is elastic and demand is inelastic the majority of the burden of tax is on the part of consumers or buyers.

The above figure has clearly shown the given case. Q_D 20 P QD. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. You should also verify that these demand and supply curves imply a market price of 1 and quantity of 100 bgyr. Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. QD 150 - 50Pb Demand QS 60 40Ps. A tax paid by buyers shifts the demand curve while a tax paid by sellers shifts the supply curve. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P - t.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Additionally the Demonstration shows and calculates the revenue for the government raised by the tax. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. Does taxes increase aggregate demand. However the outcome is the same regardless of who pays the tax. You should also verify that these demand and supply curves imply a market price of 1 and quantity of 100 bgyr.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
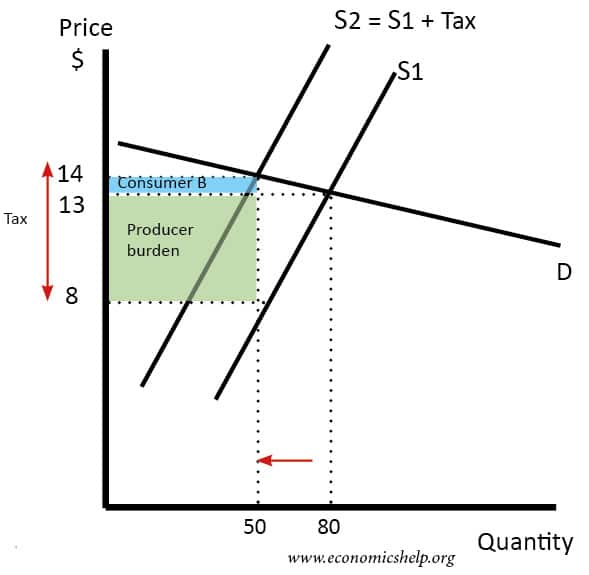
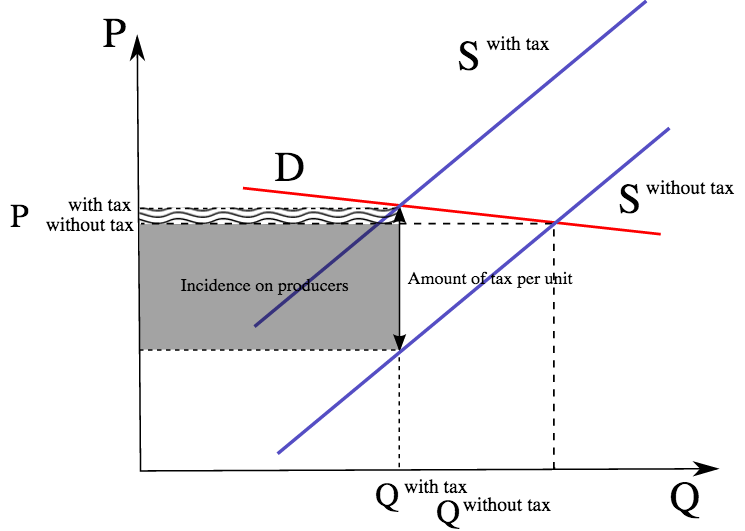
Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve. A tax on a good raises the price buyers pay lowers the price sellers receive and reduces the quantity sold. Therefore when the supply is elastic and demand is inelastic the majority of the burden of tax is on the part of consumers or buyers. However the outcome is the same regardless of who pays the tax. Intersection of these two curves define equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities prior to the imposition of sales tax.

We can use these linear demand and supply curves to calculate the effect of a 50 cents per gallon tax. When a tax is imposed on consumers the demand curve will. A tax paid by buyers shifts the demand curve while a tax paid by sellers shifts the supply curve. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. To apply to movements along the supply curve.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers. Since the demand curve represents the consumers willingness to pay the demand curve will shift down as a result of the tax. However the outcome is the same regardless of who pays the tax. The effect of the tax cut on the short-run aggregate supply SRAS curve depends on which model you use. Therefore when the supply is elastic and demand is inelastic the majority of the burden of tax is on the part of consumers or buyers.

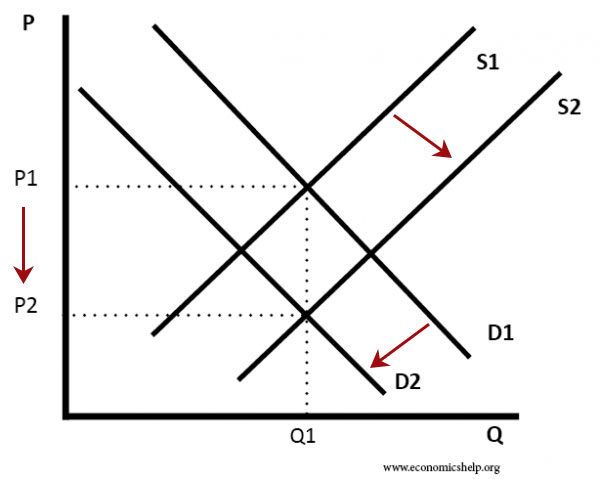
Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall. Q S 4 P 5. 20P and the function of the supply of potatoes is given by. Because the graphs for demand and supply curves both have price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis the demand curve and supply curve for a particular good or service can appear on the same graph. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3.
 Source: assignmentexpert.com
Source: assignmentexpert.com
You should also verify that these demand and supply curves imply a market price of 1 and quantity of 100 bgyr. When a tax is imposed on consumers the demand curve will. A tax paid by buyers shifts the demand curve while a tax paid by sellers shifts the supply curve. AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. The example of cigarette taxes introduced previously demonstrated that because demand is inelastic taxes are not effective at reducing the equilibrium quantity of smoking and they mainly pass along to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Tax incidence depends on the price elasticities of supply and demand. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. Q S 4 P 5. If the tax is instead imposed on consumers the demand curve shifts down by the amount of the tax 50 cents to D 2. How do you calculate tax on supply and demand curve.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Note that the demand curve in that figure labeled. Changes along the supply curve are caused by a change in the price of the good. Therefore when the supply is elastic and demand is inelastic the majority of the burden of tax is on the part of consumers or buyers. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. The variation of the surplus of each agents is quite telling.

This Demonstration shows the effect of an excise tax on a perfectly competitive market. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. However the outcome is the same regardless of who pays the tax. To apply to movements along the supply curve. In this case the supply curve is relatively inelastic and the demand curve is highly elastic.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Q_D 20 P QD. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. The downward shift in the demand curve when the tax is. D P or we can draw it graphically as in Figure 22. Shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes.
 Source: tutor2u.net
Source: tutor2u.net
Changes along the supply curve are caused by a change in the price of the good. The above figure has clearly shown the given case. In the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply a tax rate increase will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in aggregate expenditures induced by the tax rate boost. Therefore when the supply is elastic and demand is inelastic the majority of the burden of tax is on the part of consumers or buyers. Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
As the price of the apples increases producers are. Tax increases do not affect the demand curve nor do they increase supply or demand more or less. Q D 2 0 P. Since the demand curve represents the consumers willingness to pay the demand curve will shift down as a result of the tax. 430 demonstrates the sharing of the burden of a sales tax between buyers and sellers.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
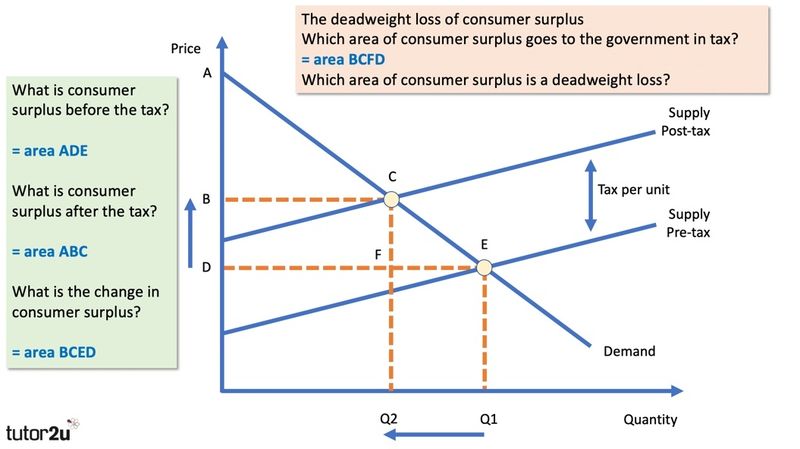
Understanding the basics of the effect of tax on the demand curve is important. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. When the tax is introduced the consumer surplus orange and producer surplus blue shrink while deadweight loss purple the inefficiency caused by the tax increases. As the price of the apples increases producers are.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
To apply to movements along the supply curve. Since the demand curve represents the consumers willingness to pay the demand curve will shift down as a result of the tax. Tax incidence depends on the price elasticities of supply and demand. Elastic Demand and Inelastic Supply. The effect of the tax cut on the short-run aggregate supply SRAS curve depends on which model you use.
 Source: hifreqecon.com
Source: hifreqecon.com
The demand curve because of the tax t. Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers. D P or we can draw it graphically as in Figure 22. However the outcome is the same regardless of who pays the tax. Does taxes increase aggregate demand.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title tax curve supply and demand by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.