Your Supply demand curve tax increase images are ready. Supply demand curve tax increase are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Supply demand curve tax increase files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for supply demand curve tax increase pictures information connected with to the supply demand curve tax increase keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
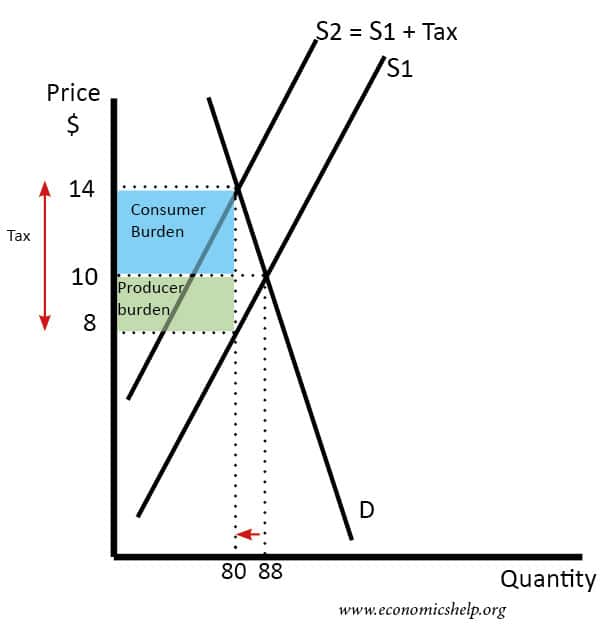
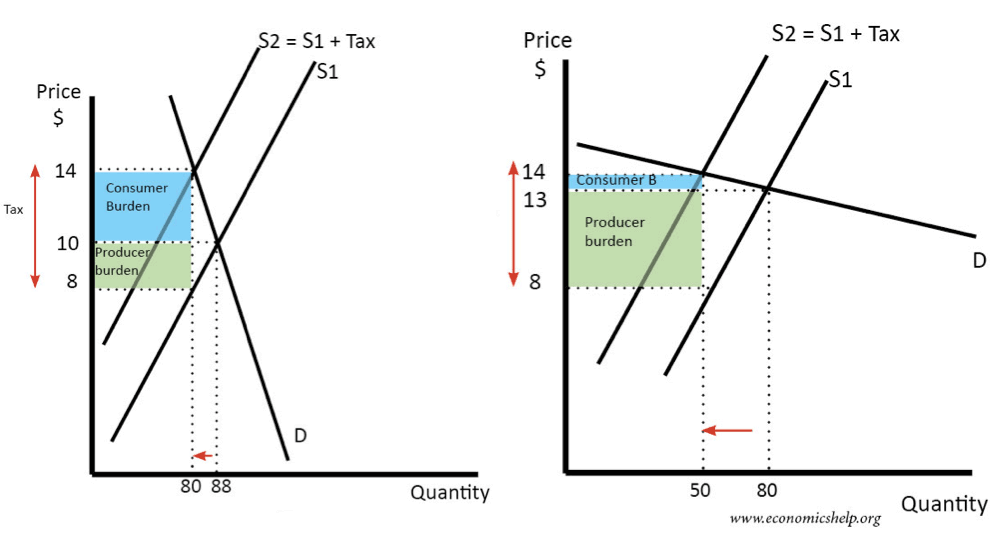
Supply Demand Curve Tax Increase. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. The demand curve and shifted supply curve create a new equilibrium which is burdened by the tax. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall.
 Effect Of Tax Depending On Elasticity Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Effect Of Tax Depending On Elasticity Economics Help From economicshelp.org
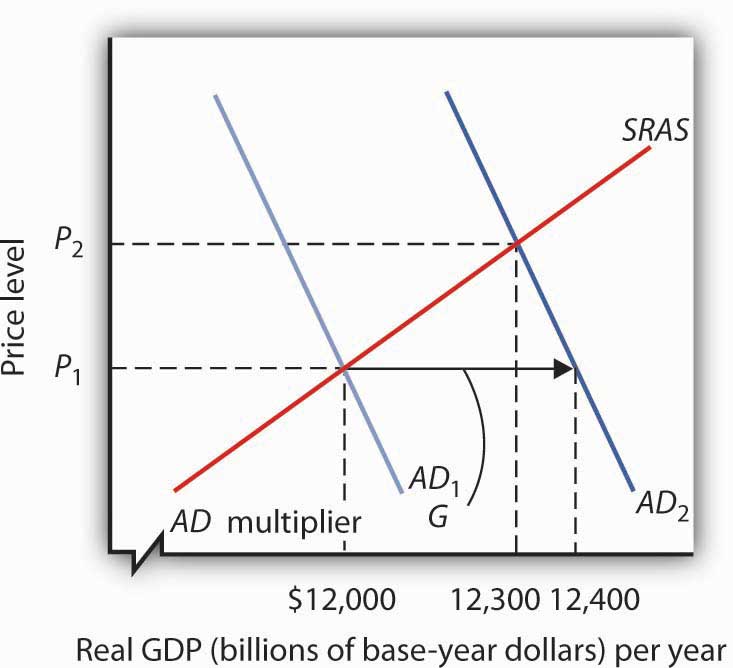
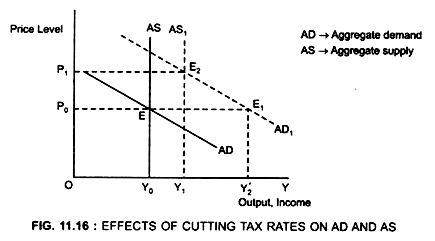
The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. It helps us understand why and how prices change and what happens when the government intervenes in a market. If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax. B increases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts rightward. The supply curve for cars will shift to the right. In the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply a tax rate increase will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in aggregate expenditures induced by the tax rate boost times the new value of the multiplier.
Q_D Q_S QD.
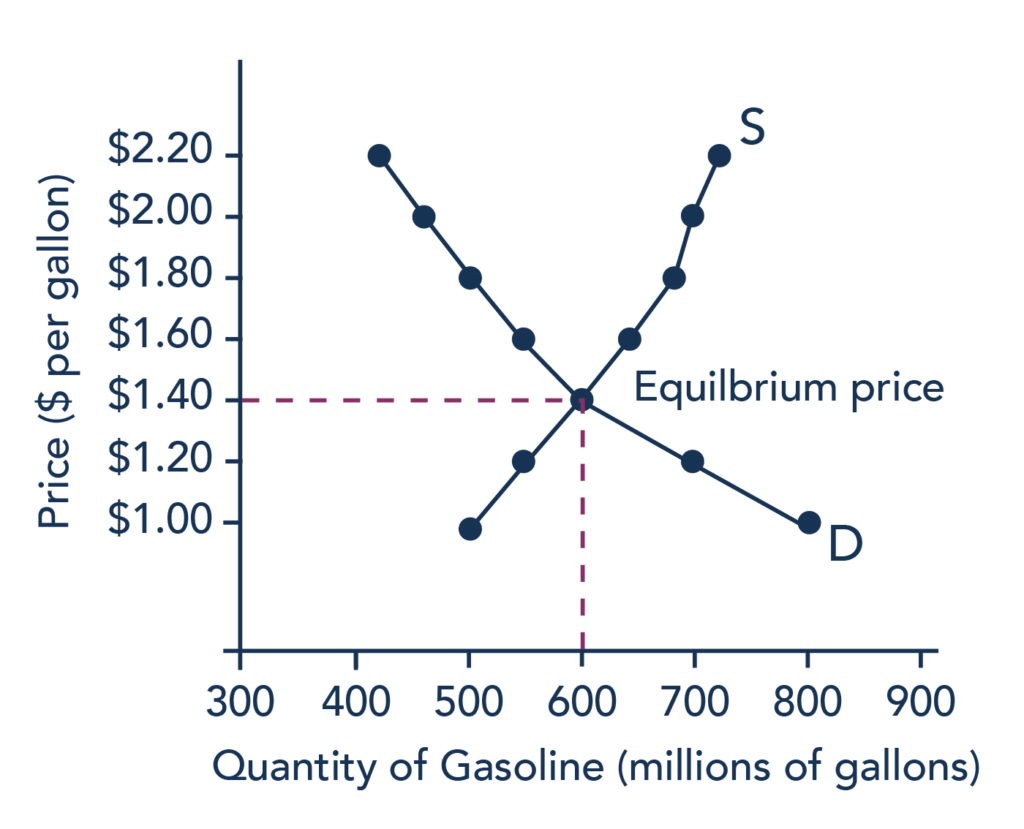
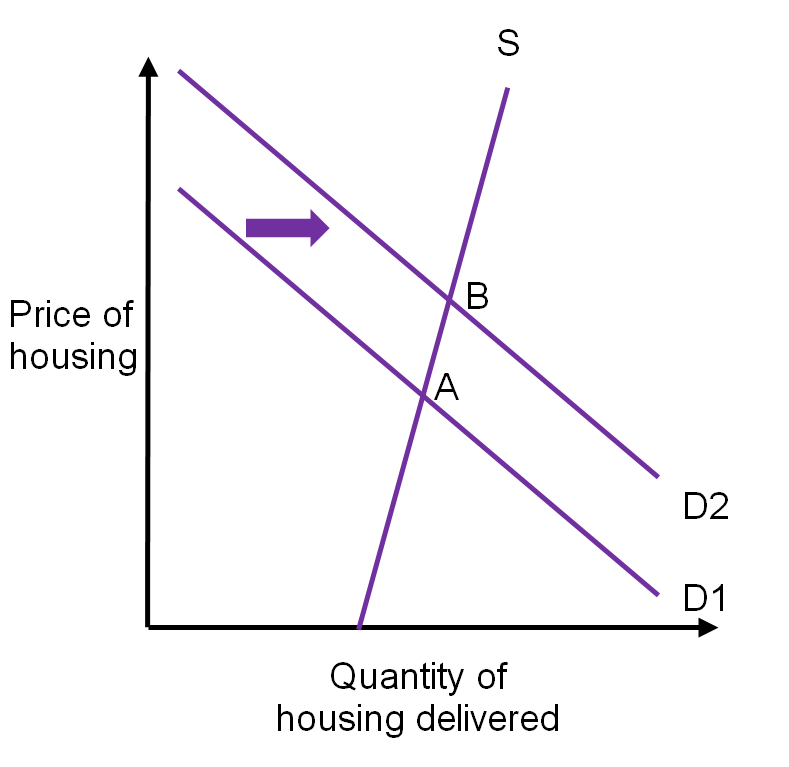
The basic model of supply and demand is the workhorse of microeconomics. And plot the demand and supply curves if the government has imposed an indirect tax at a rate of. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. Consumption goes down leading to a decrease in outputincome. The supply curve for cars will shift to the right.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. Does not shift or lead to a movement along the aggregate demand curve. The increase in demand increase in supply. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Taxes are among the market and regulatory conditions that define the demand curve.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
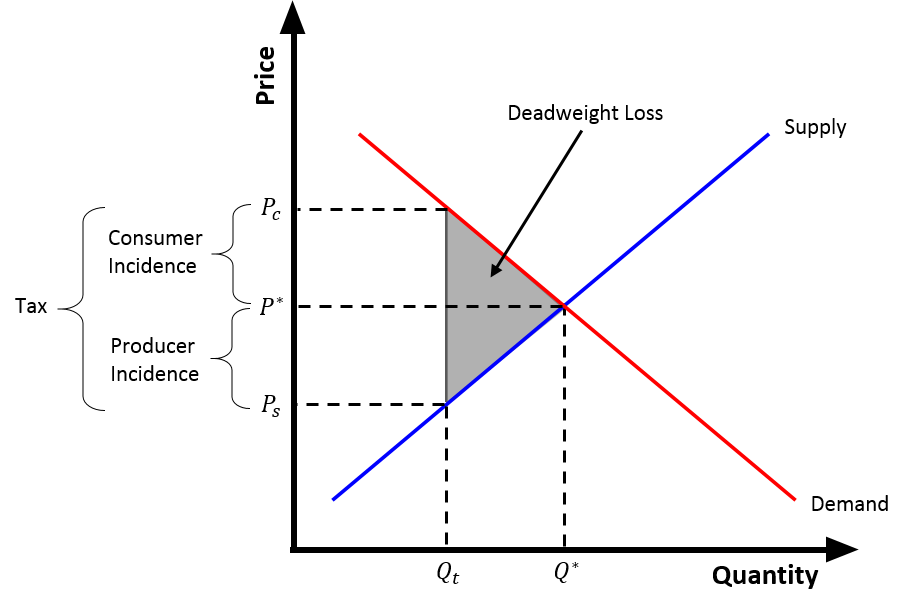
Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply. Q_D Q_S QD. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Third the long run aggregate supply can diminish because reduced taxes can lead to crowding out of more investment.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The equilibrium quantity of cars will decrease. A tax increase A decreases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts leftward. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left the consumer price increases and sellers price decreases. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Tax increases do not affect the demand curve nor do they increase supply or demand more or less. In Figure 1 a demand curve is added into this instance of competitive market. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Consumption goes down leading to a decrease in outputincome.
 Source: instructables.com
Source: instructables.com
None of the above. It is important to under-stand precisely what these curves represent. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply. In Figure 1 a demand curve is added into this instance of competitive market.

Q_D Q_S QD. The equilibrium quantity of cars will decrease. Third the long run aggregate supply can diminish because reduced taxes can lead to crowding out of more investment. Q_D Q_S QD. The supply curve for cars will shift to the left.
 Source: theigc.org
Source: theigc.org
If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. The supply curve for cars will shift to the right. Typically if we have a tax increase aggregate demand will shift left immediately because of the reduction in consumption going on in the economy. A tax increase A decreases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts leftward.
 Source: assignmentexpert.com
Source: assignmentexpert.com
An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply. If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left the consumer price increases and sellers price decreases. Investment also affects the long-run aggregate supply curve since a change in the capital stock changes the potential level of real GDP. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply. The decrease in income reduces the demand for money.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Given that the supply of money is xed the interest rate must decrease to push up the demand for money and maintain the equilibrium. The increase in demand increase in supply. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. B increases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts rightward.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Suppliers produce two goods cheese and butter. Second long run aggregate supply can increase because low taxes increase savings and investment in physical capital or improve productivity due to the enhanced incentive. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. The increase in demand increase in supply. First let us calculate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity that were before the imposed tax.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Does not shift or lead to a movement along the aggregate demand curve. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. The supply curve for cars will shift to the right. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax.
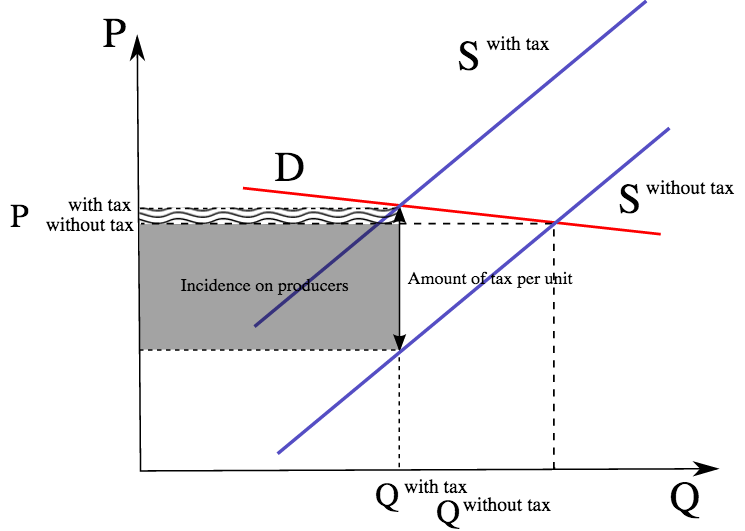
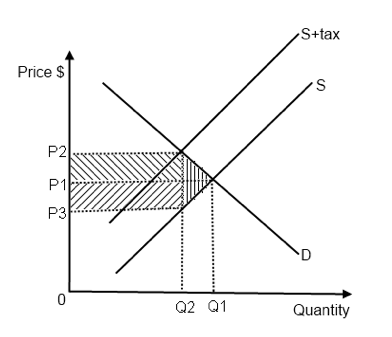
The supply curve for cars will shift to the right. The supply-demand model combines two important concepts. The supply curve for cars will shift to the left. The decrease in income reduces the demand for money. The tax size predicts the new level of quantity supplied which is reduced in comparison to the initial level.
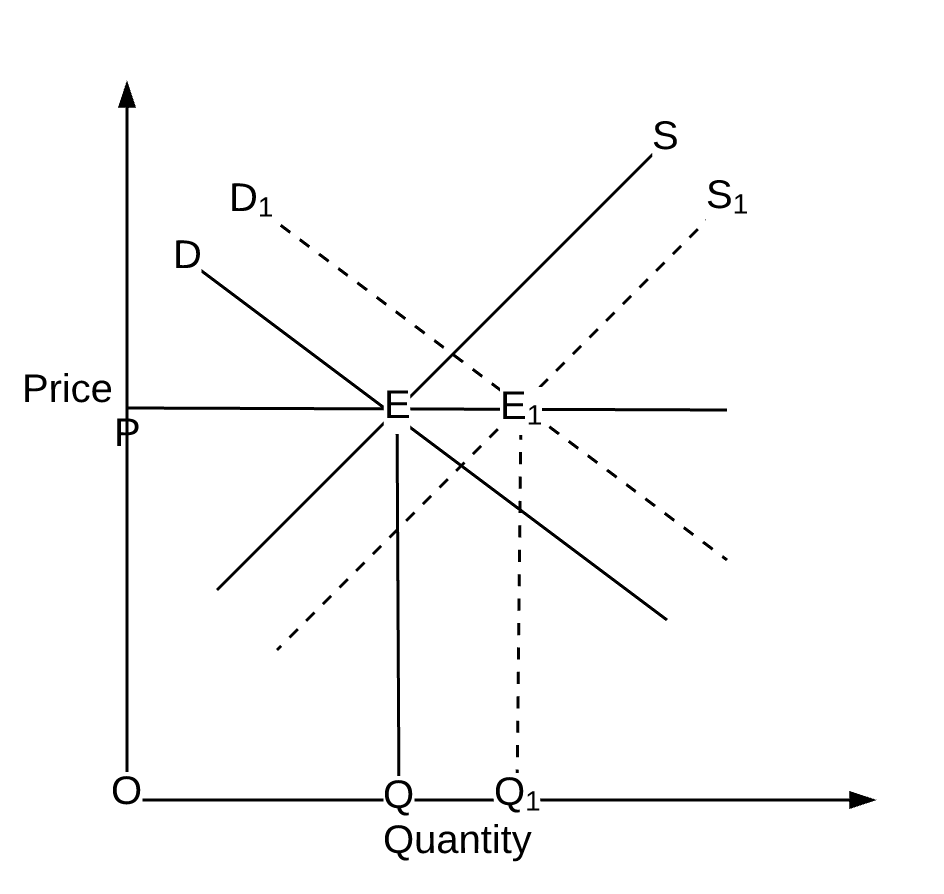 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
But because the money went from consumers to the government and then is loaned out to businesses the increase in investment will slowly shift aggregate demand back to where it was originally. The tax size predicts the new level of quantity supplied which is reduced in comparison to the initial level. Given that the supply of money is xed the interest rate must decrease to push up the demand for money and maintain the equilibrium. Suppliers produce two goods cheese and butter. With the use of aggregate demand curve one can see that if there is a change in personal income tax rates there will be a shift in the aggregate demand curve or the aggregate demand will increase or decrease.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. It is obvious that. As the price rises to the new equilibrium level the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. The tax size predicts the new level of quantity supplied which is reduced in comparison to the initial level. The equilibrium price of cars will increase.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. However the equilibrium quantity rises. With the use of aggregate demand curve one can see that if there is a change in personal income tax rates there will be a shift in the aggregate demand curve or the aggregate demand will increase or decrease. The decrease in income reduces the demand for money.
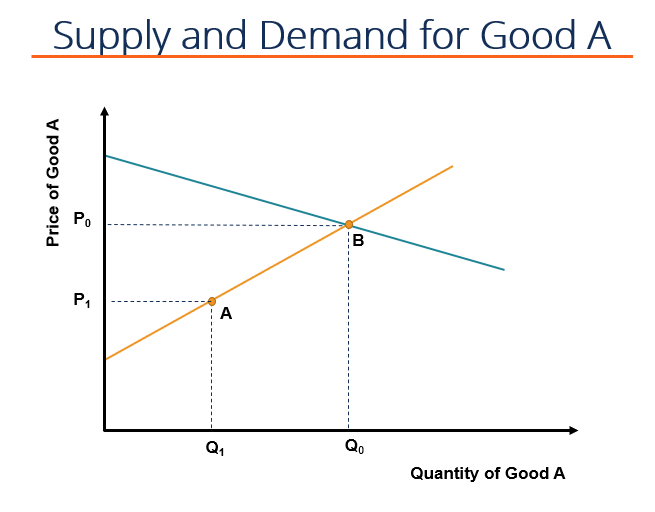 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
However the equilibrium quantity rises. But because the money went from consumers to the government and then is loaned out to businesses the increase in investment will slowly shift aggregate demand back to where it was originally. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left the consumer price increases and sellers price decreases. Aggregate demand is affected by some concepts like personal income taxes.

As the price rises to the new equilibrium level the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. Second long run aggregate supply can increase because low taxes increase savings and investment in physical capital or improve productivity due to the enhanced incentive. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply. It helps us understand why and how prices change and what happens when the government intervenes in a market. The demand curve and shifted supply curve create a new equilibrium which is burdened by the tax.
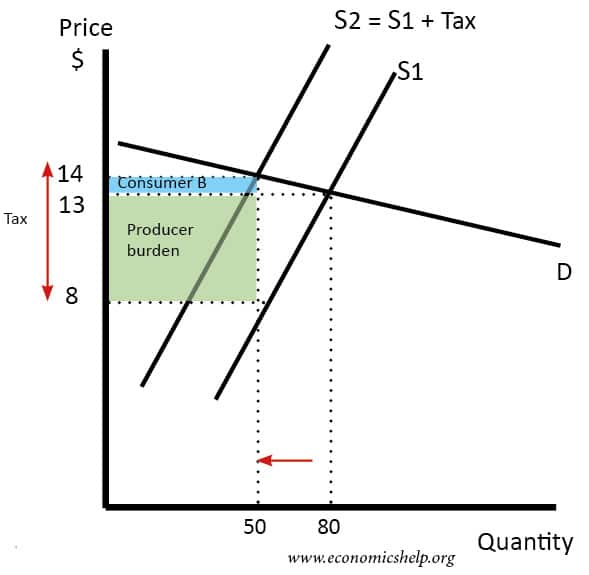 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Q D Q S. Q_D Q_S QD. However the equilibrium quantity rises. It is obvious that. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title supply demand curve tax increase by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.