Your Supply and demand model explained images are ready in this website. Supply and demand model explained are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Supply and demand model explained files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for supply and demand model explained pictures information connected with to the supply and demand model explained keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Supply And Demand Model Explained. It also allows for intrinsic random variation of the curves over time. To build a useful macroeconomic model we need a model that shows what determines total supply or total demand for the economy and how total demand and total supply interact at the macroeconomic level. In a capitalistic society prices are not determined by a central. This module will explain aggregate supply aggregate demand and the equilibrium between them.
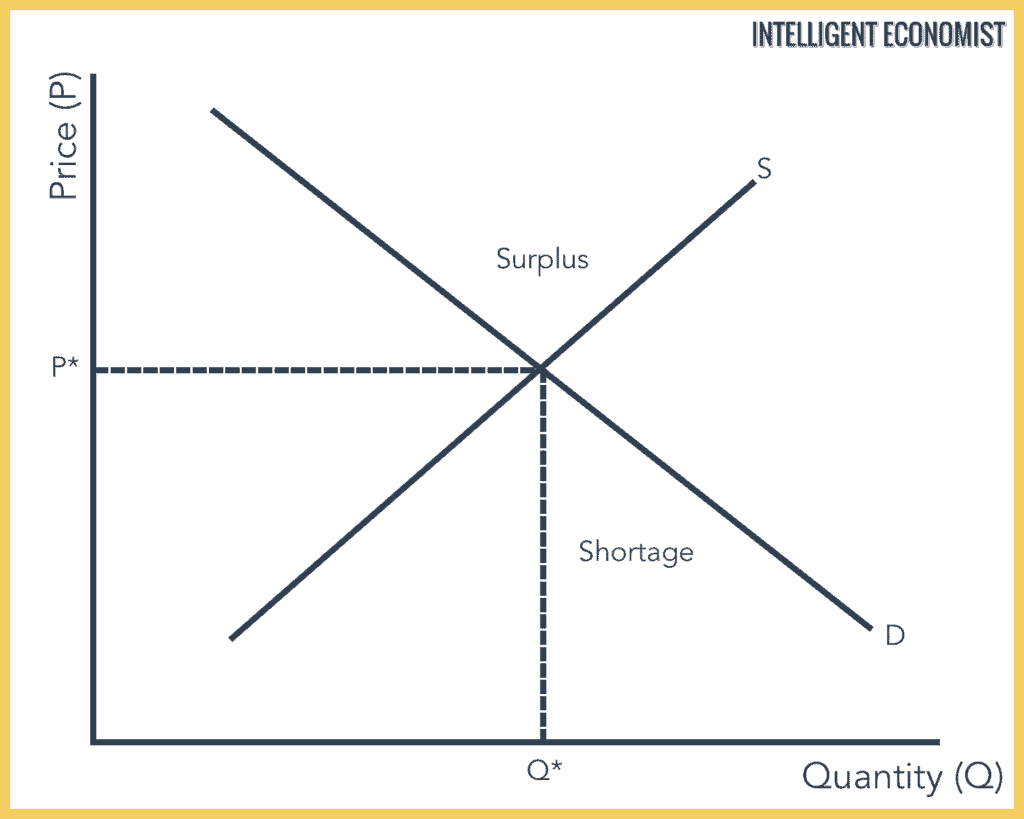 Supply And Demand Intelligent Economist From intelligenteconomist.com
Supply And Demand Intelligent Economist From intelligenteconomist.com
The model incorporates temperature and seasonality e ects and gas-availability as factors by expressing the supply and demand curves as explicit functions of these factors. SUPPLY AND DEMAND Law of Demand. 21 Supply and Demand. Other things equal means that other factors that affect demand do NOT change. A supply schedule depicted graphically as a supply curve is a table that shows the. We assume by this.
We assume by this.
Real GDP and inflation. We call this the aggregate demandaggregate supply model. Other things equal price and the quantity demanded are inversely related. The Determination of Price and Quantity The logic of the model of demand and supply is simple. Supply and demand in economics relationship between the quantity of a commodity that producers wish to sell at various prices and the quantity that consumers wish to buy. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Other things equal means that other factors that affect demand do NOT change. Other things equal means that other factors that affect demand do NOT change. It also allows for intrinsic random variation of the curves over time. Movements in the supply curve b allow us to observe the demand curve. Suppose that the supply curve shifts and the new supply equation is QP525 15.
 Source: research.stlouisfed.org
Source: research.stlouisfed.org
Suppose that the supply curve shifts and the new supply equation is QP525 15. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators. Other things equal means that other factors that affect demand do NOT change. A curve that shows the relationship in. Movements in the supply curve b allow us to observe the demand curve.
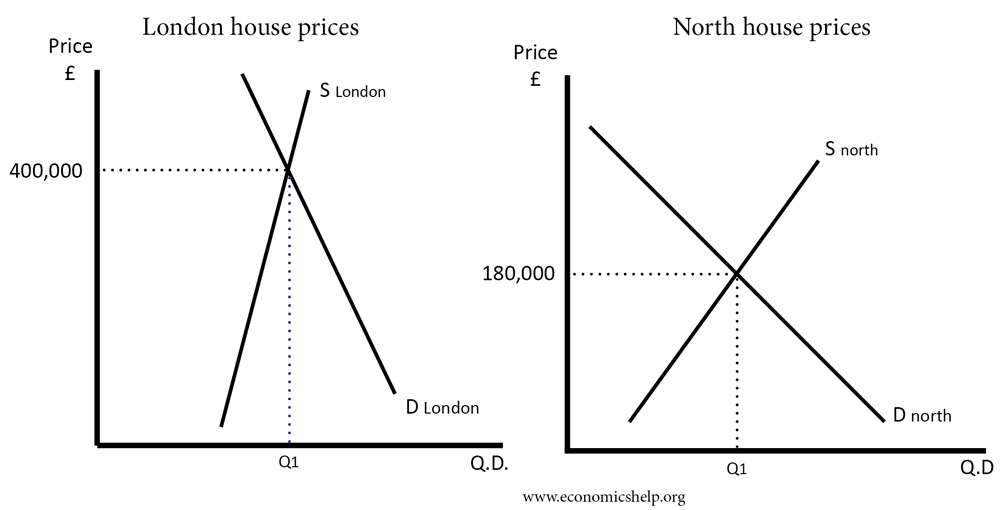 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Every term is important –1. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. Movements in the demand curve a mean that the equilibrium points trace out the supply curve. Long-run aggregate supply curve. The model incorporates temperature and seasonality e ects and gas-availability as factors by expressing the supply and demand curves as explicit functions of these factors.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It helps us understand why and how prices change and what happens when the government intervenes in a market. Explain how the circular flow model provides an overview of demand and supply in product and factor markets and how the model suggests ways in which these markets are linked. A curve that shows the relationship in. SUPPLY AND DEMAND Law of Demand. A competitive market can be determined as the intersection of supply and demand curves.
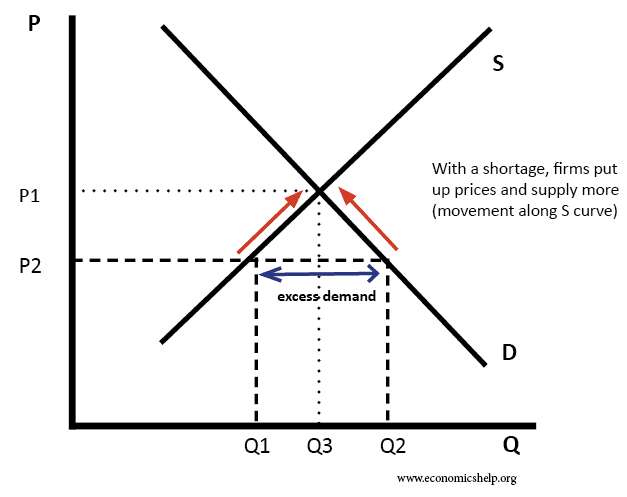 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Movements in the demand curve a mean that the equilibrium points trace out the supply curve. SUPPLY AND DEMAND 41 Introduction Classical economic theory presents a model of supply and demand that explains the equilibrium of a single product market. Economists measure these costs and benefits as marginal extra costs and extra benefits on the curves. It is the main model of price determination used in economic theory. A supply schedule depicted graphically as a supply curve is a table that shows the.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The basic model of supply and demand is the workhorse of microeconomics. For the equations defined in part a show that when you substitute the equilibrium price into either the supply or the demand equation you get the same equilibrium quantity. We call this the aggregate demandaggregate supply model. The model incorporates temperature and seasonality e ects and gas-availability as factors by expressing the supply and demand curves as explicit functions of these factors. This module will explain aggregate supply aggregate demand and the equilibrium between them.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Forming the basis for introductory concepts of economics the supply and demand model refers to the combination of buyers preferences comprising the demand and the sellers preferences comprising the supply which together determine the market prices and product quantities in any given market. A curve that shows the relationship in. The AD-AS aggregate demand-aggregate supply model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level. The model incorporates temperature and seasonality e ects and gas-availability as factors by expressing the supply and demand curves as explicit functions of these factors. It helps us understand why and how prices change and what happens when the government intervenes in a market.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Suppose that the supply curve shifts and the new supply equation is QP525 15. So the law of supply and demand can be summed up as the relationship between demand for a product or service the supply of that product or service and the price that consumers are. Generally speaking an equilibrium is defined to be the price-quantity pair where the quantity demanded. Simply defined supply and demand says that prices are low when there are plenty of products available for purchase. 21 Supply and Demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Simply defined supply and demand says that prices are low when there are plenty of products available for purchase. Movements in the demand curve a mean that the equilibrium points trace out the supply curve. SUPPLY AND DEMAND Law of Demand. Every term is important –1. The model incorporates temperature and seasonality e ects and gas-availability as factors by expressing the supply and demand curves as explicit functions of these factors.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The logical justification of Supply and Demand curves and what they represent. Multiple examples of shocks to Supply and Demand curves and an explanation of why the cause stock or index prices to rise or fall. Other things equal means that other factors that affect demand do NOT change. I walk through the basic supply and demand model calling attention to some things frequently overlookedsupplydemand econ101 introductorymicroeconomics m. We call this the aggregate demandaggregate supply model.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Economists measure these costs and benefits as marginal extra costs and extra benefits on the curves. We assume by this. For the equations defined in part a show that when you substitute the equilibrium price into either the supply or the demand equation you get the same equilibrium quantity. When supplies are scarce prices are driven up and demand decreases. Long-run aggregate supply curve.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It is important to under-. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. Economists measure these costs and benefits as marginal extra costs and extra benefits on the curves. Using the model to understand or explain general market conditions rather than the behavior of individual stocks. Supply and demand in economics relationship between the quantity of a commodity that producers wish to sell at various prices and the quantity that consumers wish to buy.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Suppose that the supply curve shifts and the new supply equation is QP525 15. A competitive market can be determined as the intersection of supply and demand curves. The supply-demand model combines two important concepts. Other things equal price and the quantity demanded are inversely related. Movements in the supply curve b allow us to observe the demand curve.
 Source: no.pinterest.com
Source: no.pinterest.com
We call this the aggregate demandaggregate supply model. Explain how the circular flow model provides an overview of demand and supply in product and factor markets and how the model suggests ways in which these markets are linked. When supplies are scarce prices are driven up and demand decreases. I walk through the basic supply and demand model calling attention to some things frequently overlookedsupplydemand econ101 introductorymicroeconomics m. The logical justification of Supply and Demand curves and what they represent.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Economists measure these costs and benefits as marginal extra costs and extra benefits on the curves. It also allows for intrinsic random variation of the curves over time. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators. Generally speaking an equilibrium is defined to be the price-quantity pair where the quantity demanded. QP12 3 Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Using the model to understand or explain general market conditions rather than the behavior of individual stocks. In this section we combine the demand and supply curves we have just studied into a new model. SUPPLY AND DEMAND Law of Demand. Suppose that the supply curve shifts and the new supply equation is QP525 15. Movements in the supply curve b allow us to observe the demand curve.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
SUPPLY AND DEMAND Law of Demand. Other things equal price and the quantity demanded are inversely related. For the equations defined in part a show that when you substitute the equilibrium price into either the supply or the demand equation you get the same equilibrium quantity. A competitive market can be determined as the intersection of supply and demand curves. SUPPLY AND DEMAND 41 Introduction Classical economic theory presents a model of supply and demand that explains the equilibrium of a single product market.
 Source: efficy.com
Source: efficy.com
We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators. We assume by this. Long-run aggregate supply curve. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. To build a useful macroeconomic model we need a model that shows what determines total supply or total demand for the economy and how total demand and total supply interact at the macroeconomic level.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title supply and demand model explained by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.