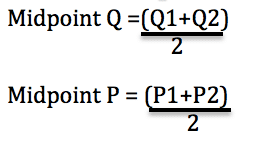Your Supply and demand curve shifts table images are available. Supply and demand curve shifts table are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Supply and demand curve shifts table files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for supply and demand curve shifts table pictures information linked to the supply and demand curve shifts table topic, you have come to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
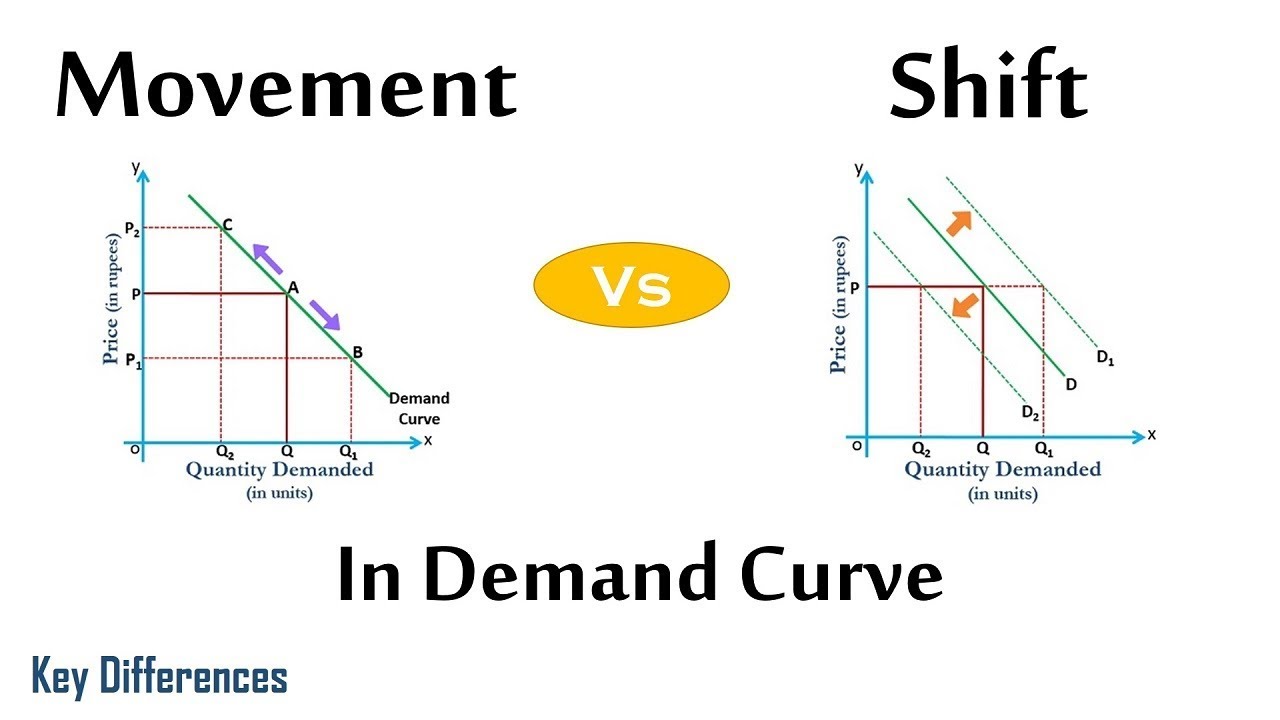
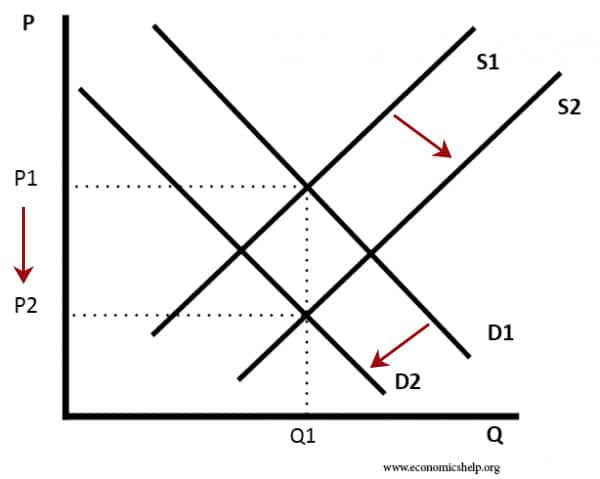
Supply And Demand Curve Shifts Table. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. Q2 instead of Q1 are offered at the given price OP. Note that the two exchange rates are inverses. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.
 Movement Vs Shift In Demand Curve Difference Between Them With Examples Comparison Chart Youtube From youtube.com
Movement Vs Shift In Demand Curve Difference Between Them With Examples Comparison Chart Youtube From youtube.com
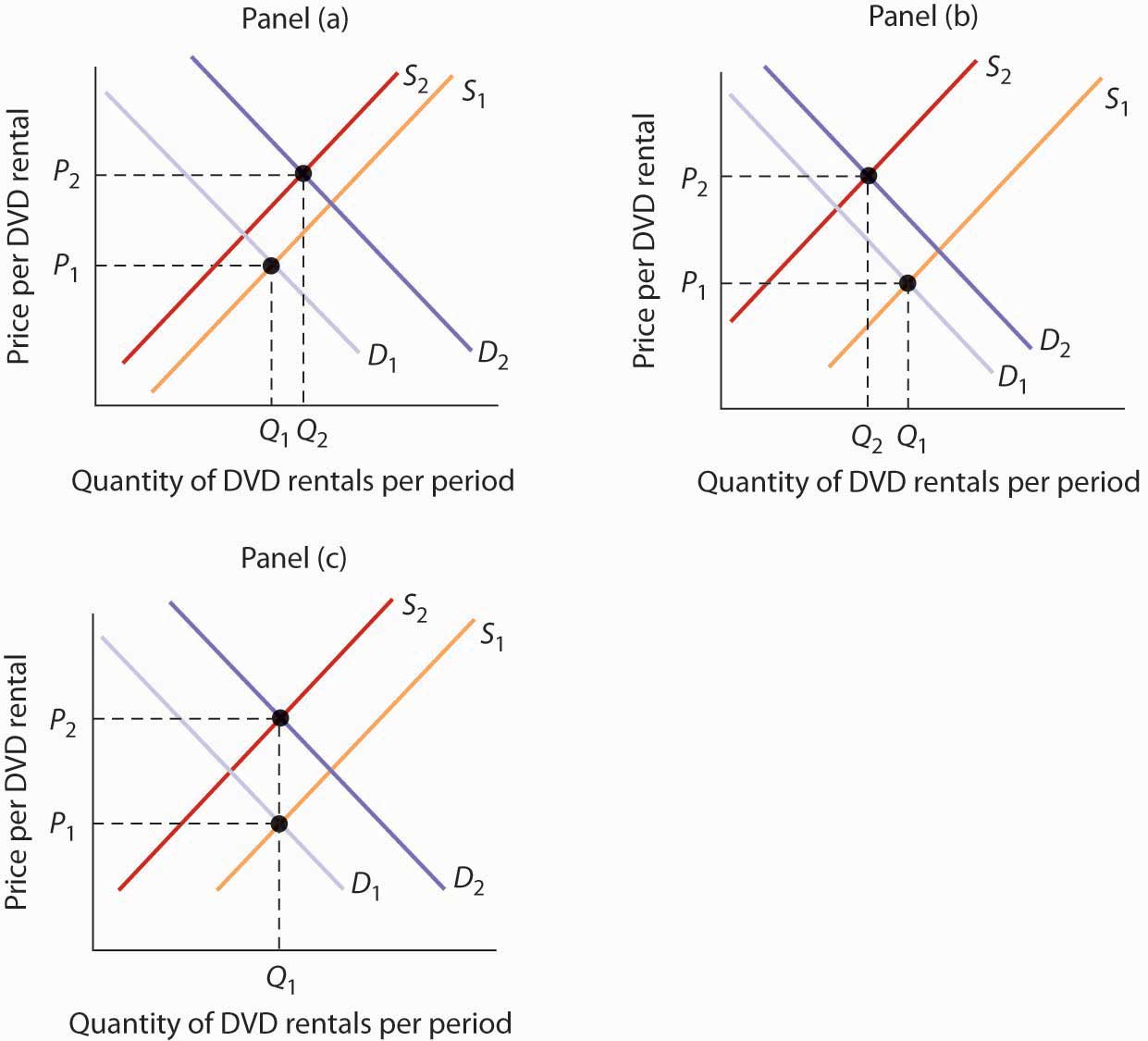
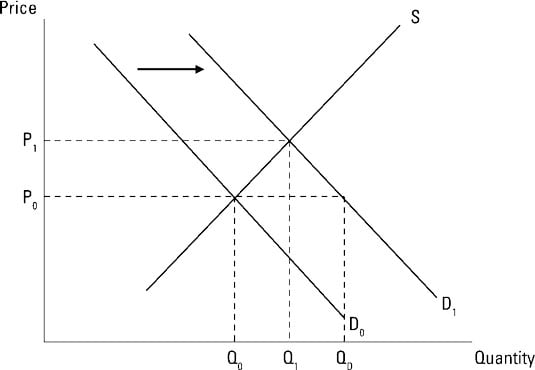
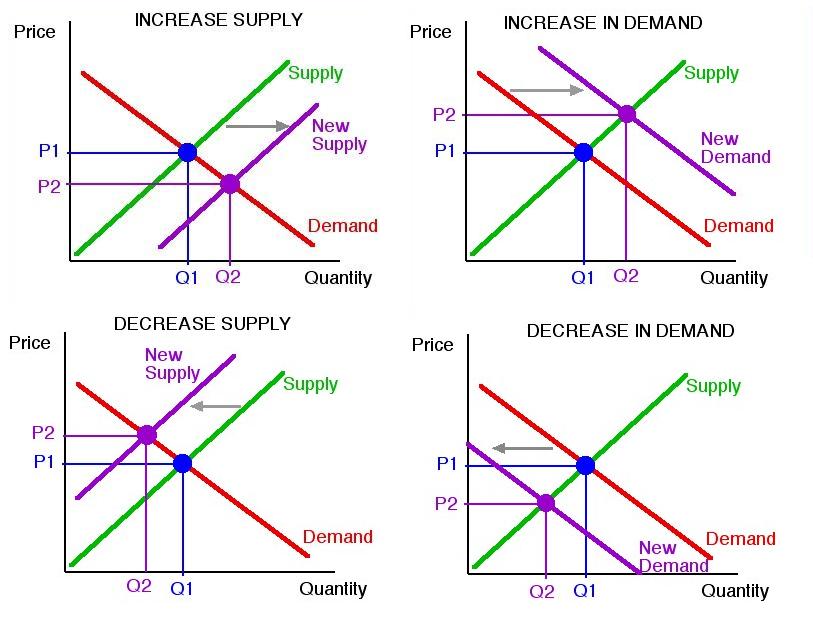
Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. Q2 instead of Q1 are offered at the given price OP. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US. Note that the two exchange rates are inverses. Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2.
Q2 instead of Q1 are offered at the given price OP.
Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve. The amount of the shift and the elasticity of. Because of an increase in supply there is a shift at the given price OP from A1 on supply curve S1 to A2 on supply curve S2. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.
 Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. The amount of the shift and the elasticity of. Price stability Two forces contribute to the size of a price change. Currency for each Mexican peso and a total volume of 85 billion pesos.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
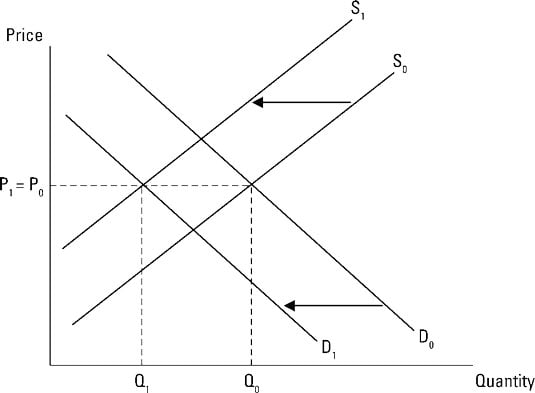
Note that the two exchange rates are inverses. Currency for each Mexican peso and a total volume of 85 billion pesos. In Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply a reduction in supply is shown as a shift of the supply curve to the left. Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve. Because of an increase in supply there is a shift at the given price OP from A1 on supply curve S1 to A2 on supply curve S2.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
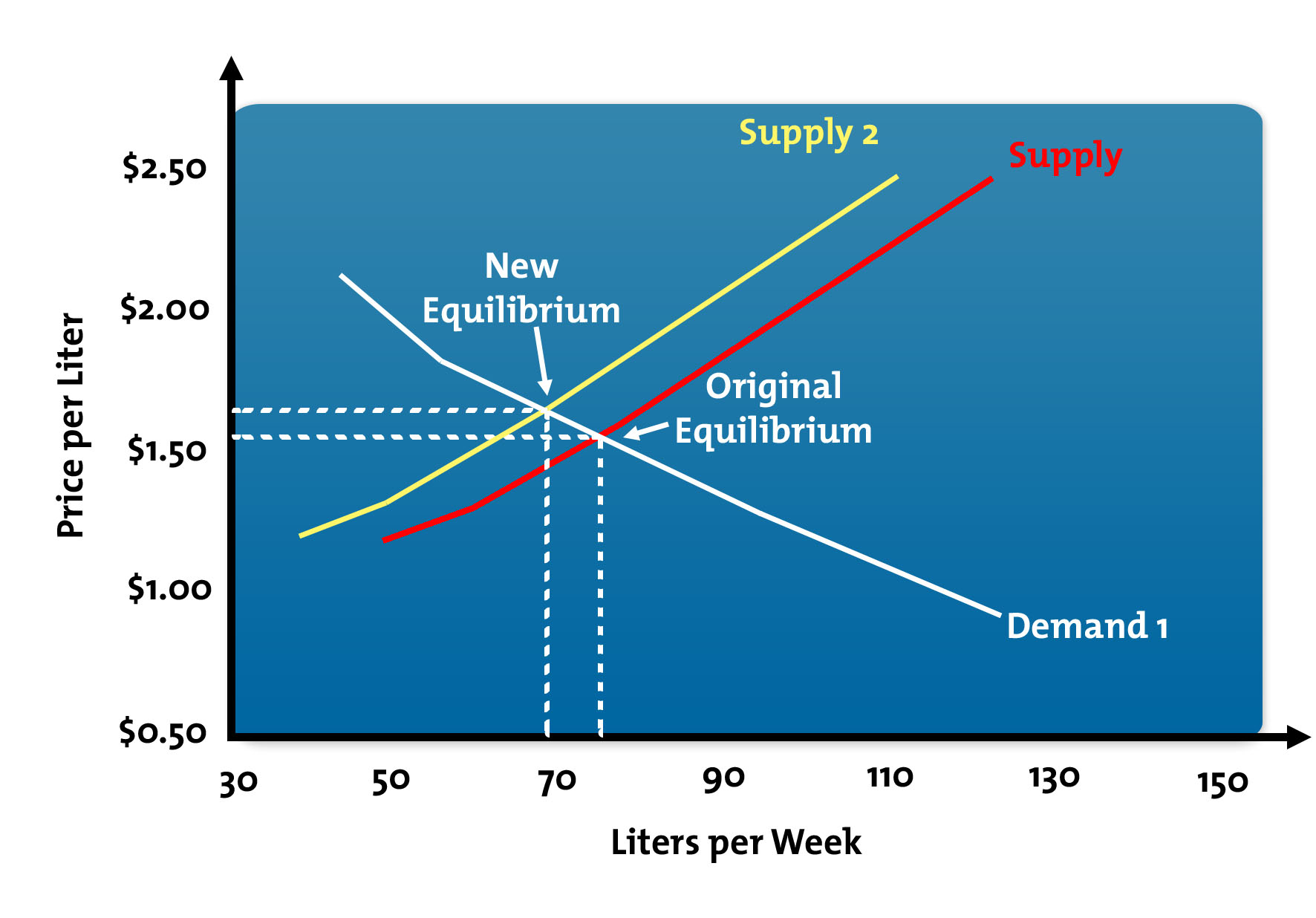
Note that the two exchange rates are inverses. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US. Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
In microeconomics the supply curve is an economic model that represents the relationship between quantity and price of a product which the supplier is willing to supply at a given point of time and is an upward sloping curve where the price of the product is represented along the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis. Q2 instead of Q1 are offered at the given price OP. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. At this point large quantities ie. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
At this point large quantities ie. Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. Note that the two exchange rates are inverses. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. Currency for each Mexican peso and a total volume of 85 billion pesos. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. At this point large quantities ie.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. At this point large quantities ie. Price stability Two forces contribute to the size of a price change. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.
 Source: ygraph.com
Source: ygraph.com
Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. At this point large quantities ie. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US.
 Source: mindtools.com
Source: mindtools.com
In microeconomics the supply curve is an economic model that represents the relationship between quantity and price of a product which the supplier is willing to supply at a given point of time and is an upward sloping curve where the price of the product is represented along the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US. At this point large quantities ie. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. Because of an increase in supply there is a shift at the given price OP from A1 on supply curve S1 to A2 on supply curve S2.

At this point large quantities ie. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. 10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso or 0. Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. Currency for each Mexican peso and a total volume of 85 billion pesos. Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve. The amount of the shift and the elasticity of.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Q2 instead of Q1 are offered at the given price OP. Q2 instead of Q1 are offered at the given price OP. The amount of the shift and the elasticity of. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US. 10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso or 0.
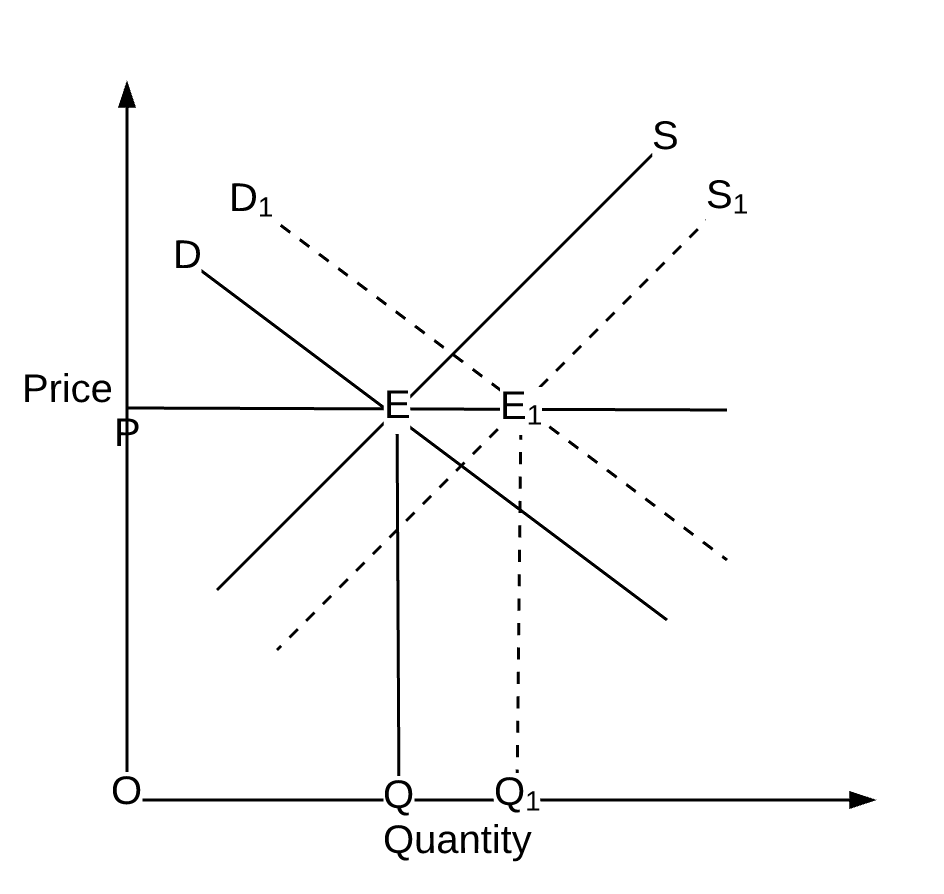 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US.
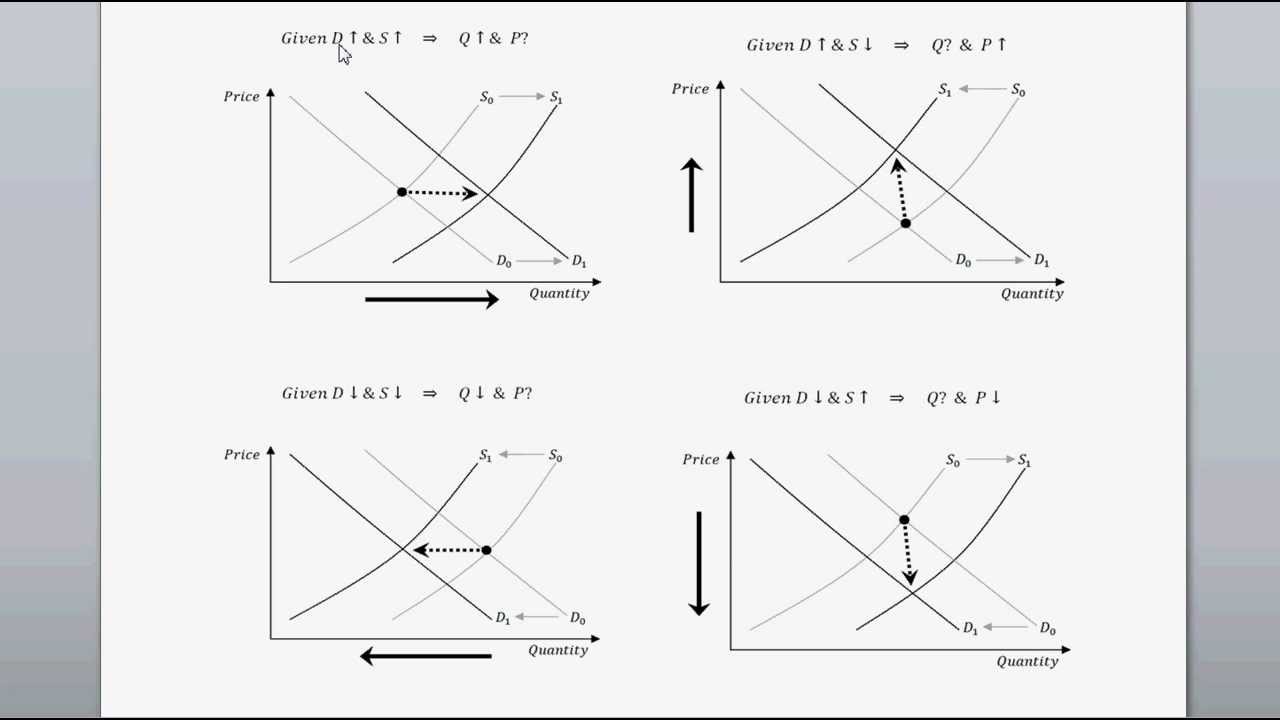 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In microeconomics the supply curve is an economic model that represents the relationship between quantity and price of a product which the supplier is willing to supply at a given point of time and is an upward sloping curve where the price of the product is represented along the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis. 10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso or 0. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.
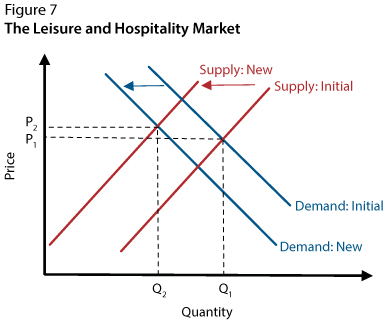 Source: research.stlouisfed.org
Source: research.stlouisfed.org
The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. At this point large quantities ie. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US.

The amount of the shift and the elasticity of. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. Use graphs to explain how changes in money demand or money supply are related to changes in the bond market in interest rates in aggregate demand and in real. Note that the two exchange rates are inverses. 10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso or 0.
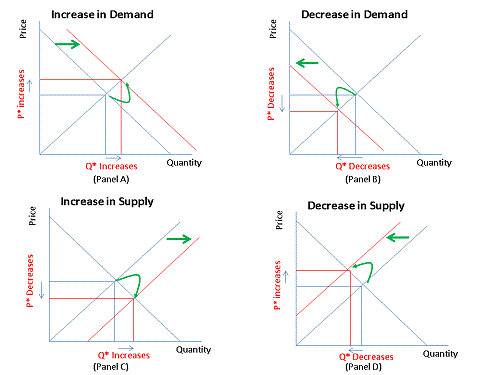 Source: graduatetutor.com
Source: graduatetutor.com
10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso or 0. 10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso or 0. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2. In Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply a reduction in supply is shown as a shift of the supply curve to the left. Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Draw a money demand curve and explain how changes in other variables may lead to shifts in the money demand curve. In microeconomics the supply curve is an economic model that represents the relationship between quantity and price of a product which the supplier is willing to supply at a given point of time and is an upward sloping curve where the price of the product is represented along the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis. The demand curve D for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve S of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point E which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in US. When demand shifts from D1 to D2 on a more vertical supply curve inelastic supply almost all the adjustment to a new equilibrium takes place in the change in price. In Figure an increase in supply in indicated by the shift of the supply curve from S1 to S2.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title supply and demand curve shifts table by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.