Your Price elasticity of demand in pure monopoly images are available in this site. Price elasticity of demand in pure monopoly are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Price elasticity of demand in pure monopoly files here. Get all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for price elasticity of demand in pure monopoly images information linked to the price elasticity of demand in pure monopoly topic, you have visit the right blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
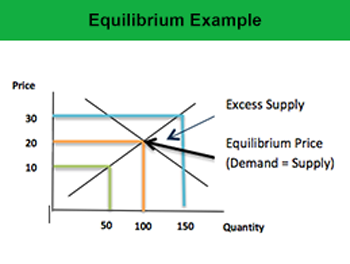
Price Elasticity Of Demand In Pure Monopoly. Unit Elastic MR 0 R unchanged. Given the assumptions of large numbers and homogeneous product the demand curve in pure competition is perfectly elastic showing that the firm is a price-taker. This demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in Figure 104. Price should then be set so that.
 Chapter 3 Monopoly And Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets From kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Chapter 3 Monopoly And Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets From kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
The price elasticity of demand is the most important determinant of market power due to the pricing rule. This does not change the revenue. Elasticity of Demand in Market A 2. If demand is unit elastic then 1 price cut increase the quantity sold by 1. Unit Elastic MR 0 R unchanged. 102 The Monopoly Model Principles of Economics Discover The Best Tip Excel wwwumnedu Excel.
It determines its own price.
The efficiency loss under perfect price discrimination is larger than under either pure monopoly or ordinary price discrimination. Elasticity of Demand in Market A 2. Explore our Catalog Join for free and get. If the demand is inelastic then marginal revenue is negative. Jan 09 2022 13Suppose the demand function for a good is expressed as Q 100 - 4p. It selects from its demand curve the price that corresponds to the quantity the firm has chosen to produce in order to earn the maximum profit possible.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Likewise is a monopoly perfectly inelastic. Elasticity of Demand in Market A 2. Price should then be set so that. Likewise is a monopoly perfectly inelastic. There are three major sources of monopoly power.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
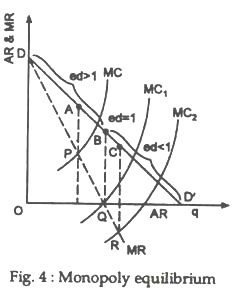
Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient. Pure or Absolute Monopoly exists when a Single Firm is the Sole Producer for a Product. The Price Elasticity of demand is inversely related to excess capacity in the monopolistic competitive market Discuss Before we even dwell and discuss on the abovementioned topic it would vital for us to understand and define what Price Elasticity of Demand Excess Capacity and Monopolistic Competitive Market are all about from the economic perspective. What does the demand curve for the purely monopolistic firm look like. A monopoly does not take the market price as given.
 Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Suppose the demand curve facing a monopoly firm is given by Equation 101 where Q is the quantity demanded per unit of time and P is the price per unit. The monopolists pricing rule as a function of the elasticity of demand for its product is. Monopoly Price and Its Relationship to Elasticity of Demand. 102 The Monopoly Model Principles of Economics Discover The Best Tip Excel wwwumnedu Excel. In monopoly the demand of the firm is also the demand of the industry and hence is negatively sloping.

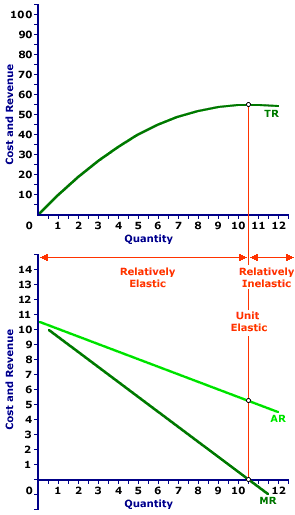
This does not change the revenue. As the price elasticity rises marginal revenue gets closer to price. Elasticity of Demand in Market A 2. It may be noted that a profit-making monopolist always operates on the elastic part of the demand curve. 1 day ago Suppose the demand curve facing a monopoly firm is given by Equation 101 where Q is the quantity demanded per unit of time and P is the price per unit.
 Source: amosweb.com
Source: amosweb.com
What does the demand curve for the purely monopolistic firm look like. Significance of Elasticity of Demand at Equilibrium under Monopoly. If the demand is inelastic then marginal revenue is negative. If the demand is inelastic then marginal revenue is negative. Elasticity of Demand in Market B 5.

Likewise is a monopoly perfectly inelastic. What is the primary reason that pure monopolies develop. Given the assumptions of large numbers and homogeneous product the demand curve in pure competition is perfectly elastic showing that the firm is a price-taker. P MC 1 2 2MC Therefore if MC rises by 25 percent price then price will also rise by 25 percent. The efficiency loss under perfect price discrimination is larger than under either pure monopoly or ordinary price discrimination.
 Source: ar.pinterest.com
Source: ar.pinterest.com
What is the primary reason that pure monopolies develop. Professor of Economics and Public Policy. If the demand is inelastic then marginal revenue is negative. However it would seem to make sense that the elasticity of supply is lower for a monopolist because if for example there is an increase in demand leading to higher prices the additional output produced by a competitive firm would be higher than a monopolist as the monopolist would tend to restrict output to. The Price Elasticity of demand is inversely related to excess capacity in the monopolistic competitive market Discuss Before we even dwell and discuss on the abovementioned topic it would vital for us to understand and define what Price Elasticity of Demand Excess Capacity and Monopolistic Competitive Market are all about from the economic perspective.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Price Elasticity of Demand 1. In monopoly the demand of the firm is also the demand of the industry and hence is negatively sloping. In the case of monopoly entry by potential rivals is prohibitively difficult. L P MCP 1E d. The higher the price elasticity of demand in absolute value for a product by a particular group of individuals the lower will be the price set by a.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
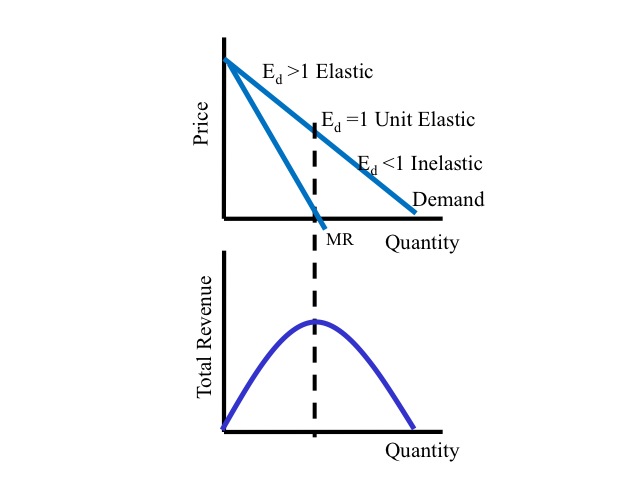
The price elasticity of demand is the most important determinant of market power due to the pricing rule. If the good currently sells for 10 then the price elasticity of demand equals A-15. If demand is unit elastic then marginal revenue is zero. P - MC P - 1 E d or alternatively P MC 1 1 E d In this example E d -20 so 1E d -12. The price elasticity of the demand curve facing a monopoly firm determines if the marginal revenue received by the monopoly is positive elastic demand or negative inelastic demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Monopoly Price and Its Relationship to Elasticity of Demand 827. Q 10 P Q 10 P. Market Power If the monopoly faces a very. This demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in Figure 104. Since elasticity of demand is negative in most cases the second expression on the right-hand side is negative which means that marginal revenue is less than price P.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The principle of price elasticity of demand is important to. How are pure monopolies able to remain in existence in the long run. The higher the price elasticity of demand in absolute value for a product by a particular group of individuals the lower will be the price set by a. There are three major sources of monopoly power. P - MC P - 1 E d or alternatively P MC 1 1 E d In this example E d -20 so 1E d -12.

What is the primary reason that pure monopolies develop. The price elasticity of the demand curve facing a monopoly firm determines if the marginal revenue received by the monopoly is positive elastic demand or negative inelastic demand. What does the demand curve for the purely monopolistic firm look like. Try the Course for Free. The principle of price elasticity of demand is important to.
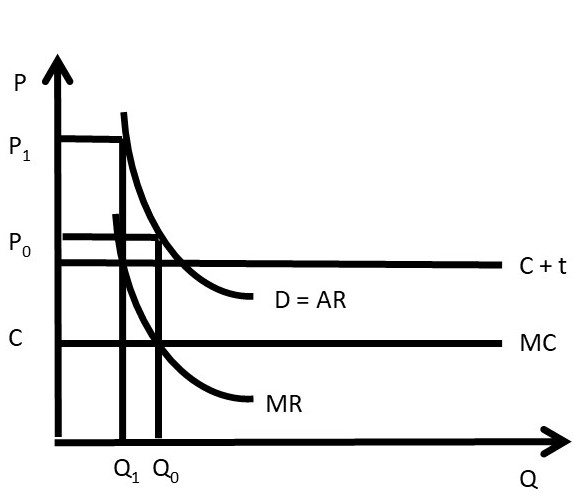 Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient. In monopoly the demand of the firm is also the demand of the industry and hence is negatively sloping. If the demand is inelastic then marginal revenue is negative. Flexible Online Learning at Your Own Pace. The price elasticity of demand is the most important determinant of market power due to the pricing rule.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The reason is that if it is on the elastic part of its demand AR curve price cut will lead to an increase in its total revenue and marginal revenue will be positive. Elasticity of Demand in Market B 5. This demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in Figure 104. As the price elasticity rises marginal revenue gets closer to price. Try the Course for Free.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
There are three major sources of monopoly power. This demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in Figure 104. If the good currently sells for 10 then the price elasticity of demand equals A-15. Elasticity of Demand in Market A 2. Since elasticity of demand is negative in most cases the second expression on the right-hand side is negative which means that marginal revenue is less than price P.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
P - MC P - 1 E d or alternatively P MC 1 1 E d In this example E d -20 so 1E d -12. A pure monopoly occurs when a company lacks competition and is the only seller in a market providing certain goods andor services. The price elasticity of the demand curve facing a monopoly firm determines if the marginal revenue received by the monopoly is positive elastic demand or negative inelastic demand. However it would seem to make sense that the elasticity of supply is lower for a monopolist because if for example there is an increase in demand leading to higher prices the additional output produced by a competitive firm would be higher than a monopolist as the monopolist would tend to restrict output to. Since elasticity of demand is negative in most cases the second expression on the right-hand side is negative which means that marginal revenue is less than price P.
 Source: courses.byui.edu
Source: courses.byui.edu
How are pure monopolies able to remain in existence in the long run. If demand is unit elastic then marginal revenue is zero. Given the assumptions of large numbers and homogeneous product the demand curve in pure competition is perfectly elastic showing that the firm is a price-taker. In the case of monopoly entry by potential rivals is prohibitively difficult. If demand is unit elastic then 1 price cut increase the quantity sold by 1.
 Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
102 The Monopoly Model Principles of Economics Discover The Best Tip Excel wwwumnedu Excel. Price Elasticity of Demand 1. Pure or Absolute Monopoly exists when a Single Firm is the Sole Producer for a Product. Build your Career in Data Science Web Development Marketing More. It determines its own price.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title price elasticity of demand in pure monopoly by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.