Your Point price elasticity of demand example problems images are ready. Point price elasticity of demand example problems are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Point price elasticity of demand example problems files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for point price elasticity of demand example problems images information connected with to the point price elasticity of demand example problems interest, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
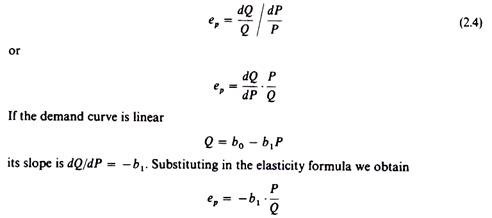
Point Price Elasticity Of Demand Example Problems. Noting that dqdp 10 we get ǫ p qp dq dp p 500 10p 10 p p50. QD 5000 50PX. The price of the product is 50. Since the change in demand is smaller than the change in price we can conclude that demand is relatively inelastic.
 Point Elasticity Of Demand From economicsonline.co.uk
Point Elasticity Of Demand From economicsonline.co.uk
EC101 DD EE Manove Elasticity of DemandWhy percentages. 50200 025. Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 108 1082 100 2 9 100 222 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100 10 8 10 8 2. Therefore a one percent increase in price will result in a 1 percent decrease in quantity demanded. How to find the point price elasticity of demand with the following demand function. When price increases from Re.
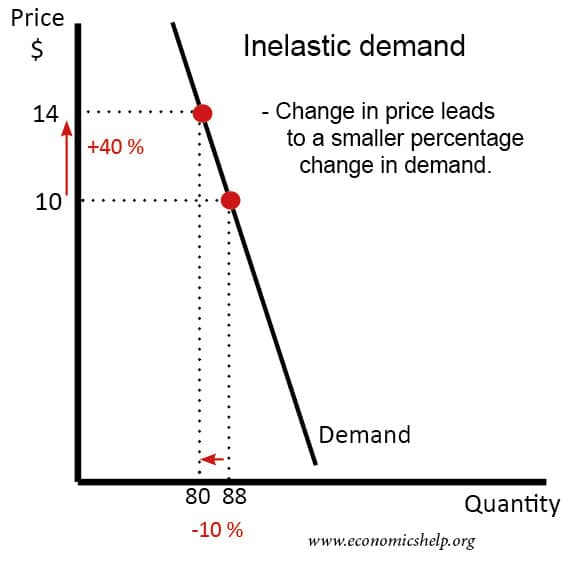
This means that for every 1 increase in price there is a 05 decrease in demand.
The Problem with Price Elasticity. Demand is elastic inelastic or unit elastic. One is given below. Point price elasticity works by finding the exact e. Price Elasticity of Demand Example. E -100062800 -214 Sometimes you may be required to solve for quantity or price and are given a point price elasticity of demand measureIn this case you need to backwards solve by rearranging the point price elasticity of demand formula to.
 Source: learncbse.in
Source: learncbse.in
From the midpoint formula we know that. The slope is the rate of change in units along the curve or the riserun change in y over the change in x. The price elasticity of demand in this situation would be 05 or 05. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for this price change and calculate whether total revenue from the car park rises or falls. Given Q 0 4000 bottles Q 1 5000 bottles P 0 350 and P 1 250.
 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Using our result from a we get ǫ 30 30 50 15. Price elasticity of demand refers to how much a price change will cause a change in the quantity demanded. To calculate price elasticity of demand you use the formula from above. Price Elasticity of Demand Example. We know that QP in this problem is -400 and we need to find the point price elasticity of demand at a price of 10 and at a price of 8.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
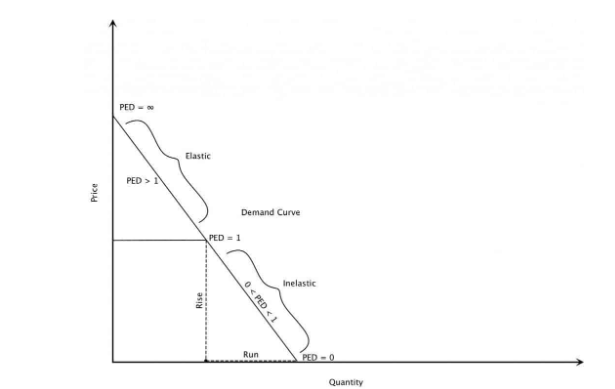
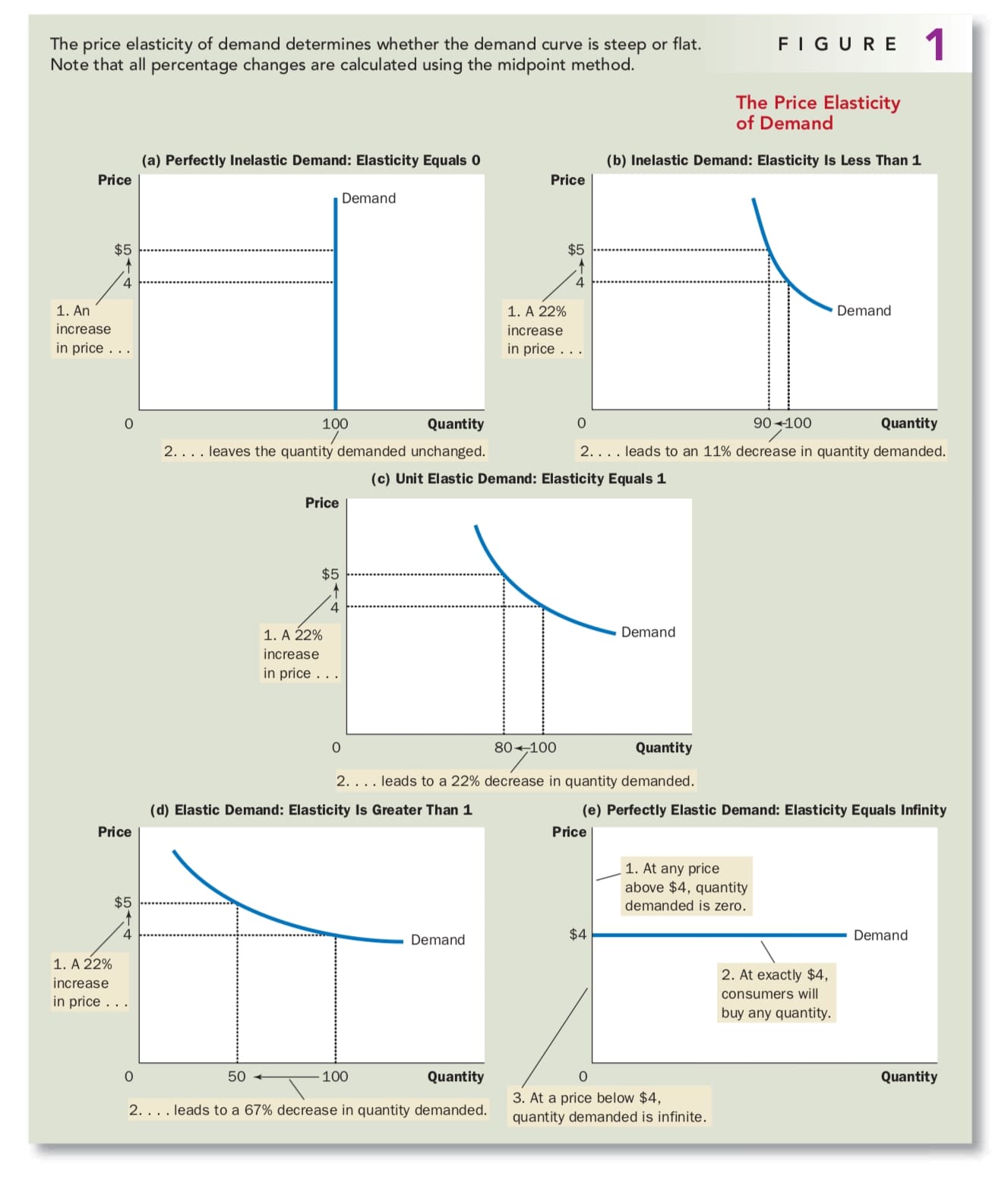
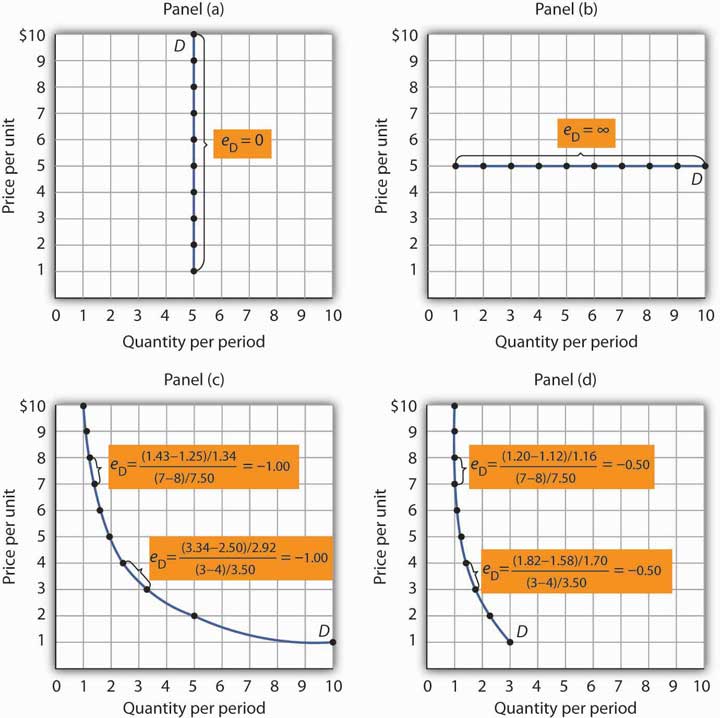
One is given below. Given Q 0 4000 bottles Q 1 5000 bottles P 0 350 and P 1 250. 50200 025. Empirical estimates of demand often show curves like those in Panels c and d that have the same elasticity at every point on the curve. At a price of ten we demand 0 of the good so the measure is undefined.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
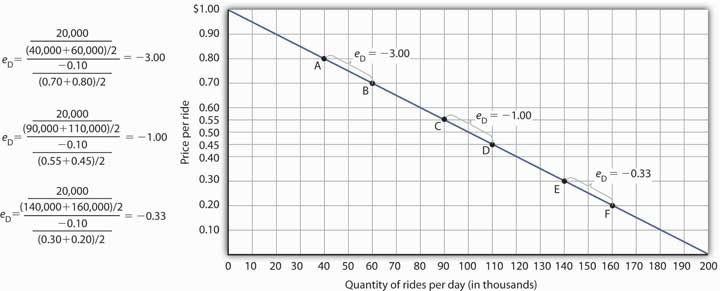
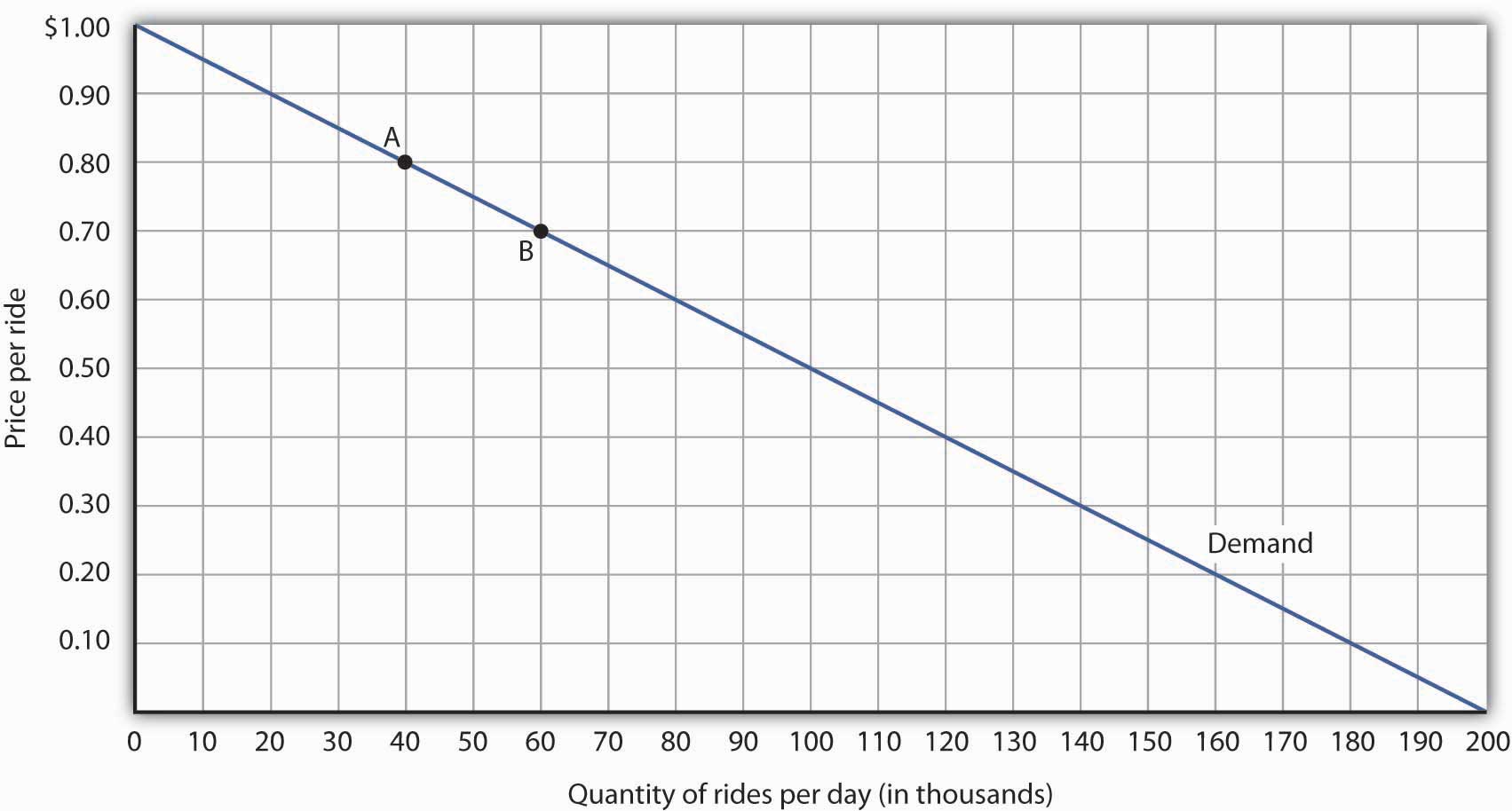
For example in Figure 1 each point shown on the demand curve price drops by 10 and the number of units demanded increases by 200. Therefore a one percent increase in price will result in a 1 percent decrease in quantity demanded. Point price elasticity works by finding the exact e. Elasticity of demand Proportionate change in quantity demandedProportionate change in price. For each of the following cases calculate the point price elasticity of demand and state whether.
 Source: global.oup.com
Source: global.oup.com
50200 025. Elasticity of demand Proportionate change in quantity demandedProportionate change in price. Divide the percentage change in quantity by the percentage change in price. Change in Quantity 40 - 5050 -020 -20 Change in Price 600 - 400400 050 50. EC101 DD EE Manove Elasticity of DemandWhy percentages.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
The demand curve in Panel c has price elasticity of demand equal to 100 throughout its range. 105 proportionate increase is 5. Now that you have all the values you need to solve for price elasticity of demand simply plug them into the original formula to answer. 50200 025. Change in Quantity 40 - 5050 -020 -20 Change in Price 600 - 400400 050 50.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
B A decrease in total revenue. Empirical estimates of demand often show curves like those in Panels c and d that have the same elasticity at every point on the curve. Also Q 530 500. Demand is price inelastic Total revenue. B A decrease in total revenue.
 Source: 52coding.com.cn
Source: 52coding.com.cn
From the midpoint formula we know that. When the price is 50 the elasticity of demand is -1. Change in Quantity 40 - 5050 -020 -20 Change in Price 600 - 400400 050 50. One is given below. To find the elasticity of demand we need to divide the percent change in quantity by the percent change in price.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Elasticity of demand around a price of Re. Noting that dqdp 10 we get ǫ p qp dq dp p 500 10p 10 p p50. 105 proportionate decrease in quantity demanded ie from 2000 to 1800 is of 10. Q 4000 400P. Assume that a business firm sells a product at the price of 450.
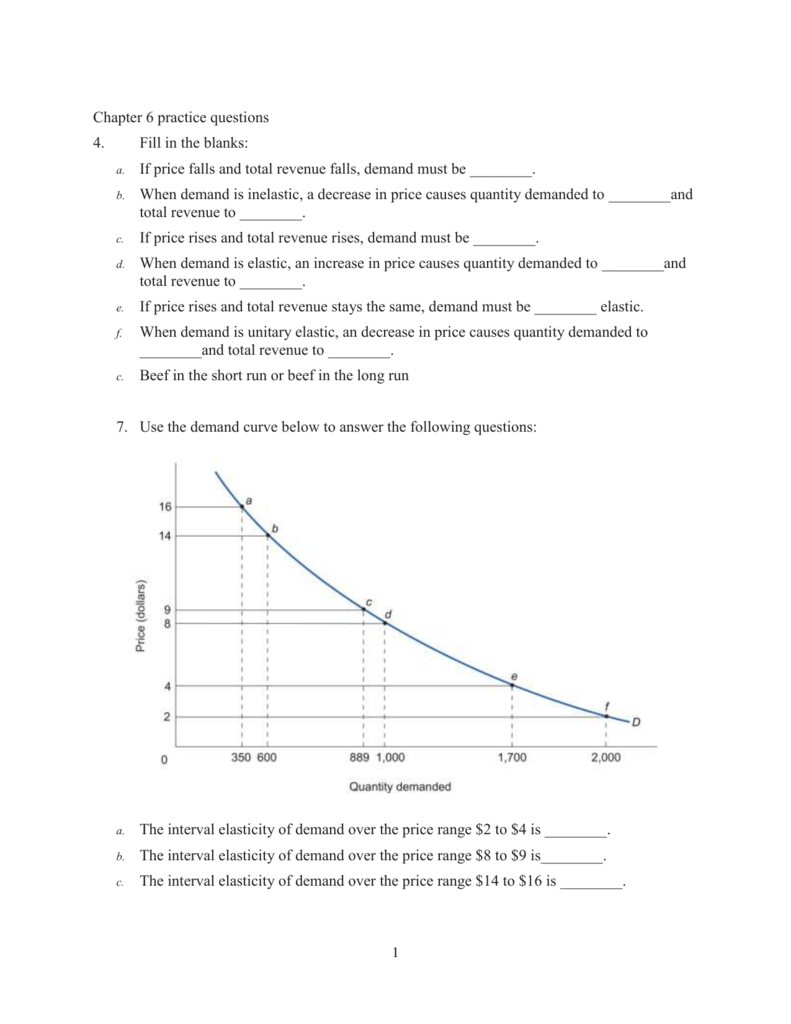 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Most people working in finance retail or pricing will likely have encountered the term price elasticity of demand PED at. Price Elasticity of Demand 5000 4000 5000 4000 250 350 250 350 Price Elasticity. The demand curve in Panel c has price elasticity of demand equal to 100 throughout its range. Example 1 Suppose the demand curve for oPads is given by q 500 10p. The slope is the rate of change in units along the curve or the riserun change in y over the change in x.
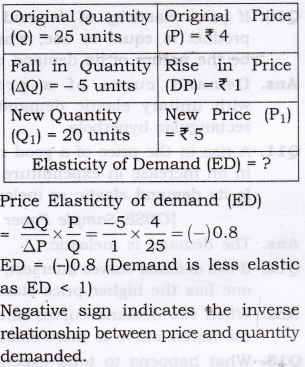 Source: learncbse.in
Source: learncbse.in
Demand is price inelastic Total revenue. QD 5000 50PX. So the slope is 10200 along the entire demand curve and does not change. At a price of ten we demand 0 of the good so the measure is undefined. 3 per day revenue 3 x 1200 3600.
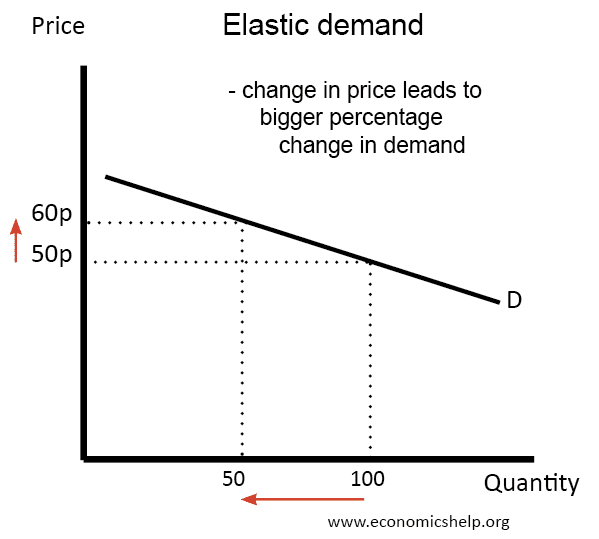 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 108 1082 100 2 9 100 222 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100 10 8 10 8 2. Change in Quantity 40 - 5050 -020 -20 Change in Price 600 - 400400 050 50. B What is the price elasticity of demand when the price is 30. Consequently the demand for the product is raised from 25000 units to 35000 units. Eco point price elasticity of demand problems.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Using our result from a we get ǫ 30 30 50 15. Price Elasticity of Demand 5000 4000 5000 4000 250 350 250 350 Price Elasticity. In Panel d the price elasticity of demand is equal to 050 throughout its range. This value is multiplied by 100 and ends with a percentage change rate of 25. Price Elasticity of Demand Example.
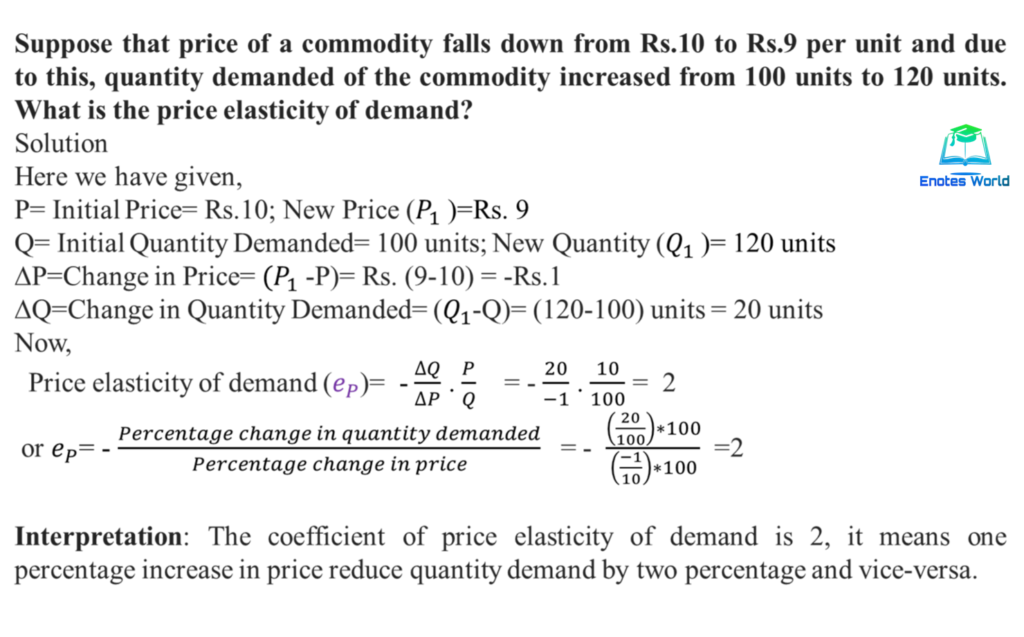 Source: enotesworld.com
Source: enotesworld.com
To calculate price elasticity of demand you use the formula from above. QD 5000 50PX. Lets assume that if cost of a trip changes from 2 P0 to 3 P1 passenger demand per day falls from 05 million Q0 to 04 million Q1. In Panel d the price elasticity of demand is equal to 050 throughout its range. Most people working in finance retail or pricing will likely have encountered the term price elasticity of demand PED at.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
In Panel d the price elasticity of demand is equal to 050 throughout its range. So the slope is 10200 along the entire demand curve and does not change. For example consider the demand schedule for a hypothetical product. Also Q 530 500. Point price elasticity works by finding the exact e.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
To find the elasticity of demand we need to divide the percent change in quantity by the percent change in price. Also Q 530 500. This value is multiplied by 100 and ends with a percentage change rate of 25. Using our result from a we get ǫ 30 30 50 15. Price Elasticity of Demand percent change in quantity percent change in price Price Elasticity of Demand percent change in quantity percent change in price.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
How to find the point price elasticity of demand with the following demand function. Point price elasticity works by finding the exact e. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for this price change and calculate whether total revenue from the car park rises or falls. The price elasticity of demand in this situation would be 05 or 05. The demand curve is given by.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
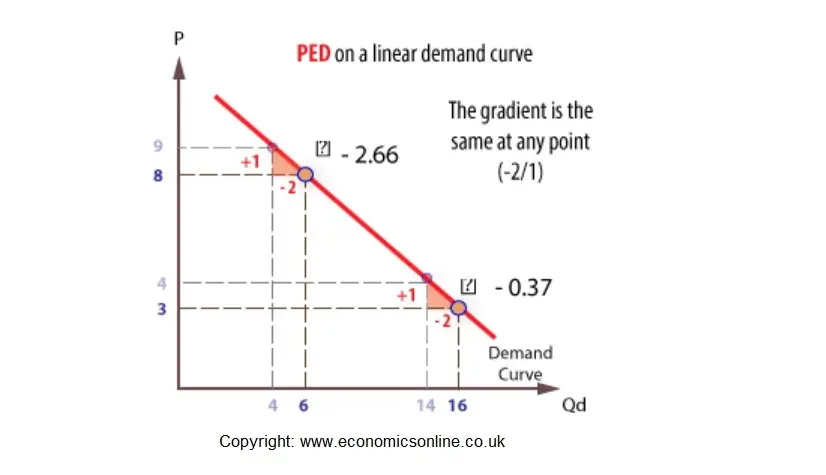
We can now calculate the point elasticity at point To find the gradient we have taken the nearest point at When calculating the elasticity of demand for all goods with a downward sloping demand curve you should get a negative value. In Panel d the price elasticity of demand is equal to 050 throughout its range. Also Q 530 500. Since the change in demand is smaller than the change in price we can conclude that demand is relatively inelastic. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for this price change and calculate whether total revenue from the car park rises or falls.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title point price elasticity of demand example problems by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.