Your Negative demand side shock images are available in this site. Negative demand side shock are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Negative demand side shock files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for negative demand side shock pictures information connected with to the negative demand side shock topic, you have visit the right blog. Our site frequently provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Negative Demand Side Shock. The recession of 1974-75 was caused by adverse supply shocks primarily the Oil Crisis which occurred when the Arab members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries OPEC embargoed petroleum exports driving up the price of oil. Moreover supply-side shocks may induce additional demand effects if as is likely consumers and investors are forward looking. A demand-side shock could be an event which causes fall in aggregate demand such as global recession fall in bank lending or fall in wages of workers. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment.
 The Asad Model Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Policy From slidetodoc.com
The Asad Model Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Policy From slidetodoc.com
Negative demand effects causing actual output to fall. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment. We have learned much about the causes and consequences of financial crises following the 20082009 Great Recession Reinhart and Rogoff 2009 2011 Schularick and Taylor 2012. Entertainment restaurants and hotels experience very large supply and demand shocks with the demand shock dominating. A real-life example of this occurred in the 1970s. I think that the hypothesis.
Either shock will have an effect on the prices of the product or service.
A permanent fall in potential. Shocks directly affecting exports or imports such as the economic collapse of a trading partner. Negative real shocks are more complicated than shocks to aggregate demand. One demand side effect and one less known supply side effect. The new level of output iClick to select The new price level CR cannot be determined will be higher will be lower. The new price level _____ lower.

People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. We have learned much about the causes and consequences of financial crises following the 20082009 Great Recession Reinhart and Rogoff 2009 2011 Schularick and Taylor 2012. These demand effects will be larger the more permanent the shock is deemed to be. A Temporary Adverse Supply Shock continued A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve. Additionally as service sector workers lose their jobs and income they stop purchasing all kinds of goods such as cars and appliances which can also be thought of as a sectoral demand shock.

Evidence based on a new dataset of two centuries of financial crises and trade suggests financial crises are clearly negative shocks to demand. A permanent fall in potential. External help eg. Additionally as service sector workers lose their jobs and income they stop purchasing all kinds of goods such as cars and appliances which can also be thought of as a sectoral demand shock. Faster recovery at a lower price level than allowing short-run aggregate supply to adjust on its own.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Moreover supply-side shocks may induce additional demand effects if as is likely consumers and investors are forward looking. A temporary adverse supply shock has no direct effect on the demand for or. Evidence based on a new dataset of two centuries of financial crises and trade suggests financial crises are clearly negative shocks to demand. Faster recovery but it will cause even greater inflation. One demand side effect and one less known supply side effect.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Nearly a decade of zero or negative real rates suggest that their effects could be much more limited than previously believed. Examples of negative demand shocks include. In our last video we looked at inflationary and recessionary gaps in the ADAS model. Shocks directly affecting exports or imports such as the economic collapse of a trading partner. These demand effects will be larger the more permanent the shock is deemed to be.

Faster recovery but it will cause even greater inflation. Health unsurprisingly experiences an overall increase in demand for its output. These results are important. The new level of output iClick to select The new price level CR cannot be determined will be higher will be lower. Tax rates which also affect consumer and investment spending.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
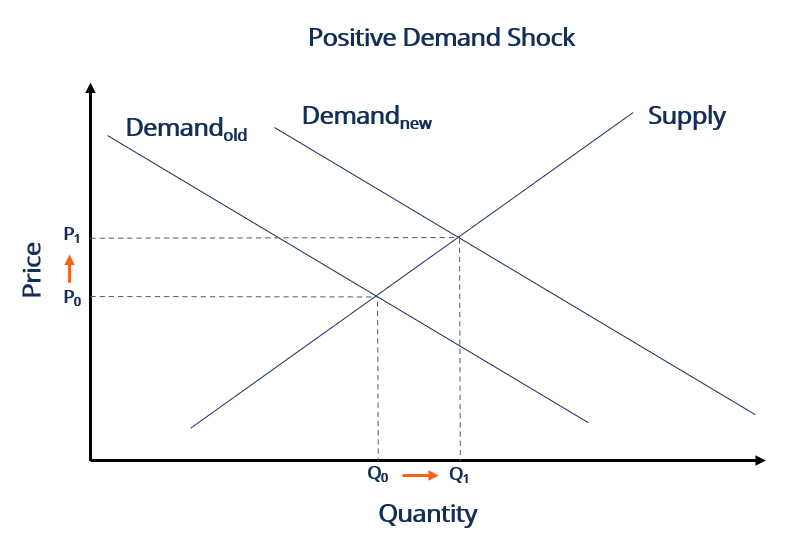
A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. TheFE line shifts left. The labour supply is unaffected. Other demand side shocks affect planned spending indirectly such as changes in. These results are important.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
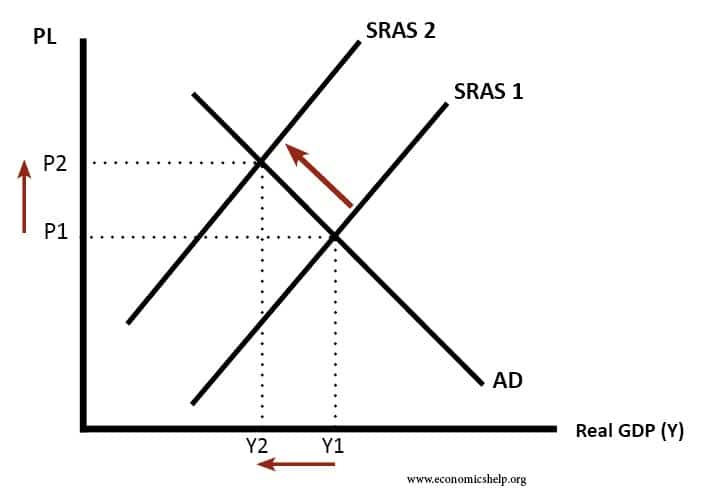
As dire as they may be supply shock recessions are partly an efficient. Slower recovery if they misjudge their own spending. We have learned much about the causes and consequences of financial crises following the 20082009 Great Recession Reinhart and Rogoff 2009 2011 Schularick and Taylor 2012. Shocks directly affecting exports or imports such as the economic collapse of a trading partner. For example the imposition of an embargo on trade in oil would cause an adverse supply shock since oil is.
 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
A demand-side shock could be an event which causes fall in aggregate demand such as global recession fall in bank lending or fall in wages of workers. Health unsurprisingly experiences an overall increase in demand for its output. For example the imposition of an embargo on trade in oil would cause an adverse supply shock since oil is. As dire as they may be supply shock recessions are partly an efficient. These cause less quantity of goods to be consumed and those consumers still in the market pay a lower price for the good.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
A Temporary Adverse Supply Shock continued A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve. A permanent fall in potential. One demand side effect and one less known supply side effect. A temporary adverse supply shock has no direct effect on the demand for or. Examples of negative demand shocks include.
 Source: bfi.uchicago.edu
Source: bfi.uchicago.edu
Tax rates which also affect consumer and investment spending. The new level of output will be ____. Interest rates which affect both consumer and investment spending. The new level of output iClick to select The new price level CR cannot be determined will be higher will be lower. Accept bailout from IMF EU often requiring conditions such as structural adjustment Dealing with Demand Side Shocks.
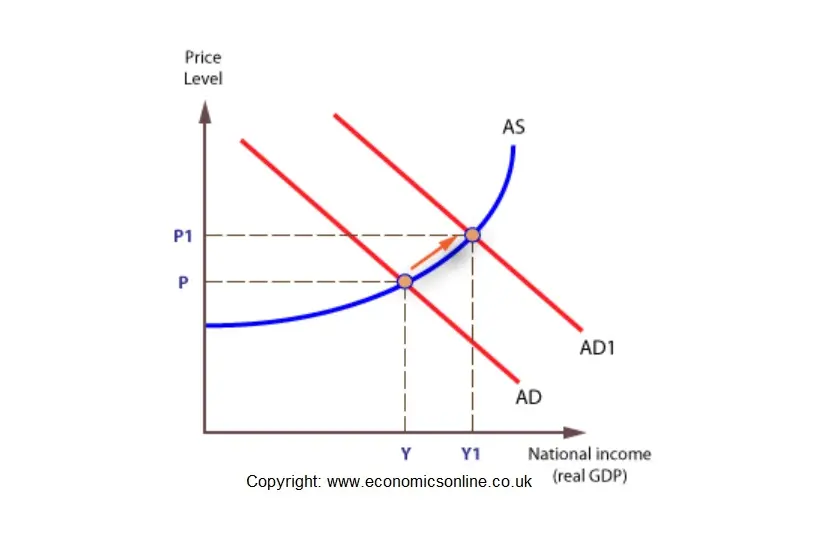 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
In our last video we looked at inflationary and recessionary gaps in the ADAS model. Examples of negative demand shocks include. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. Additionally as service sector workers lose their jobs and income they stop purchasing all kinds of goods such as cars and appliances which can also be thought of as a sectoral demand shock. I think that the hypothesis.
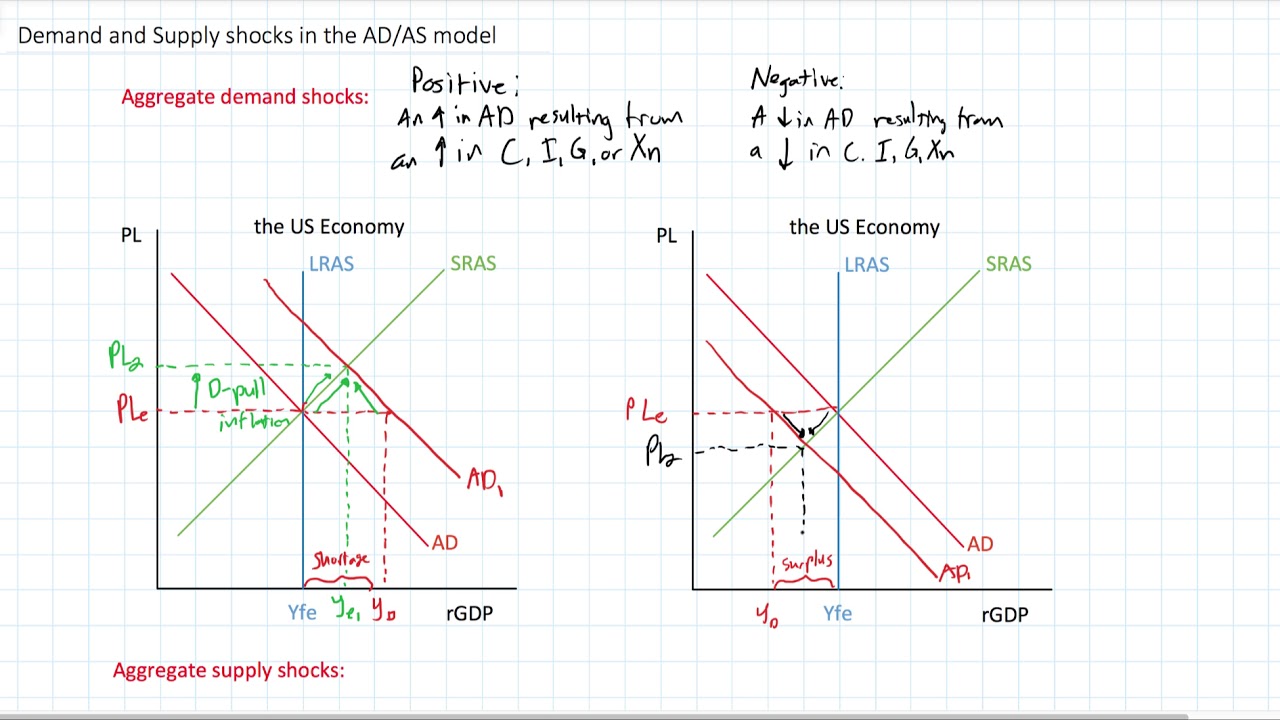 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Either shock will have an effect on the prices of the product or service. Demand shocks new keynesian model and supply effects of monetary policy. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment. Other demand side shocks affect planned spending indirectly such as changes in. A Temporary Adverse Supply Shock continued A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve.
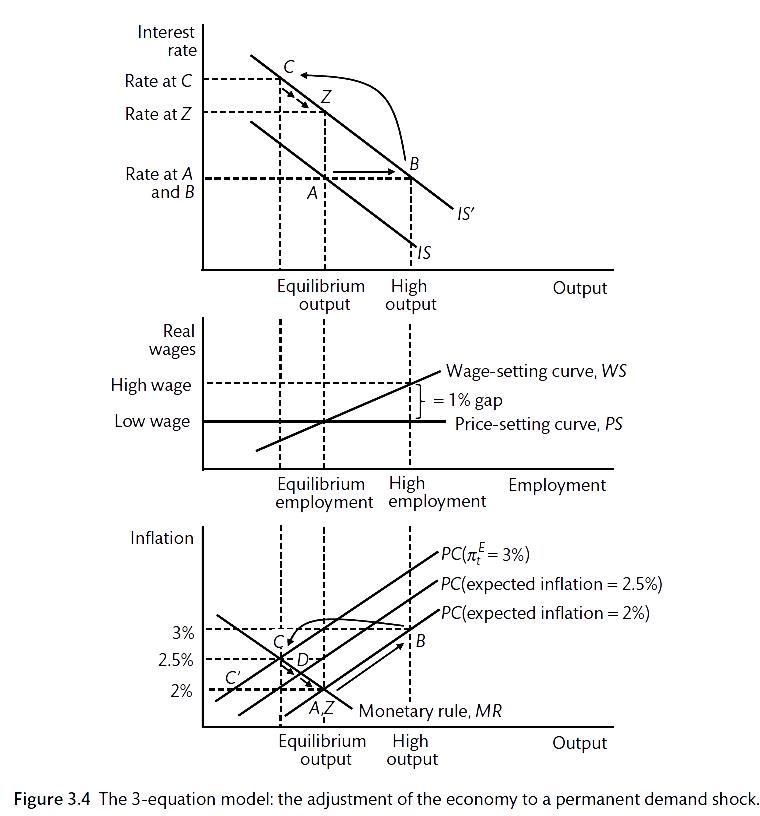 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
The labour supply is unaffected. Negative demand effects causing actual output to fall. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment. Slower recovery if they misjudge their own spending. A real-life example of this occurred in the 1970s.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The labour supply is unaffected. Faster recovery but it will cause even greater inflation. Health unsurprisingly experiences an overall increase in demand for its output. Either shock will have an effect on the prices of the product or service. A permanent fall in potential.
 Source: tutor2u.net
Source: tutor2u.net
The new level of output will be ____. At the occupation level we show that high-wage occupations are relatively immune from adverse supply- and demand-side shocks while low-wage occupations are much more vulnerable. A temporary adverse supply shock has no direct effect on the demand for or. Examples of negative demand shocks include. A Temporary Adverse Supply Shock continued A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve.

For example the imposition of an embargo on trade in oil would cause an adverse supply shock since oil is. TheFE line shifts left. A Temporary Adverse Supply Shock continued A temporary adverse supply shock is a movement along the IS curve not a shift of the IS curve. A permanent fall in potential. The new price level _____ lower.
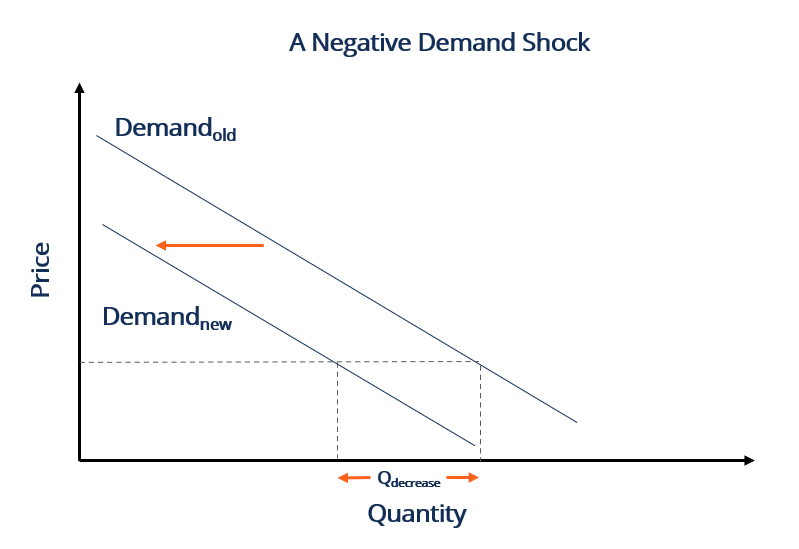 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
A temporary adverse supply shock has no direct effect on the demand for or. The new price level _____ lower. TheFE line shifts left. Faster recovery but it will cause even greater inflation. If a negative demand-side shock and a temporary e supply-side shock occur simultaneously what will be the short-run effects on price level and outpur.
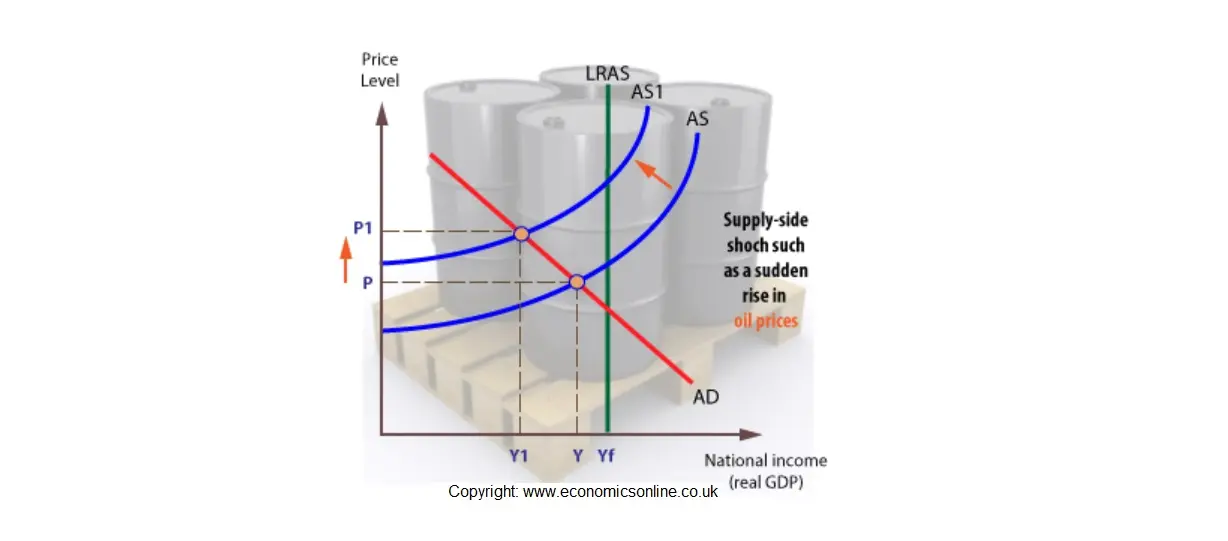 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
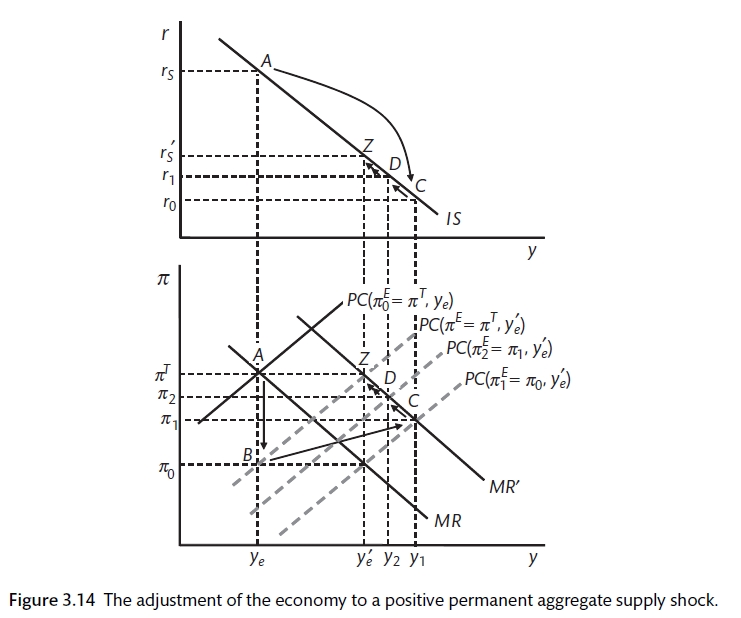
Interest rates which affect both consumer and investment spending. Faster recovery but it will cause even greater inflation. If a negative demand side shock and a temporary negative supply side shock occur simultaneously what will be the short run effects on price level and output. Accept bailout from IMF EU often requiring conditions such as structural adjustment Dealing with Demand Side Shocks. In the short run an economy-wide negative supply shock will shift the aggregate supply curve leftward decreasing the output and increasing the price level.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title negative demand side shock by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.