Your Midpoint formula for cross elasticity of demand images are ready. Midpoint formula for cross elasticity of demand are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Midpoint formula for cross elasticity of demand files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for midpoint formula for cross elasticity of demand images information linked to the midpoint formula for cross elasticity of demand keyword, you have come to the right site. Our website frequently gives you hints for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
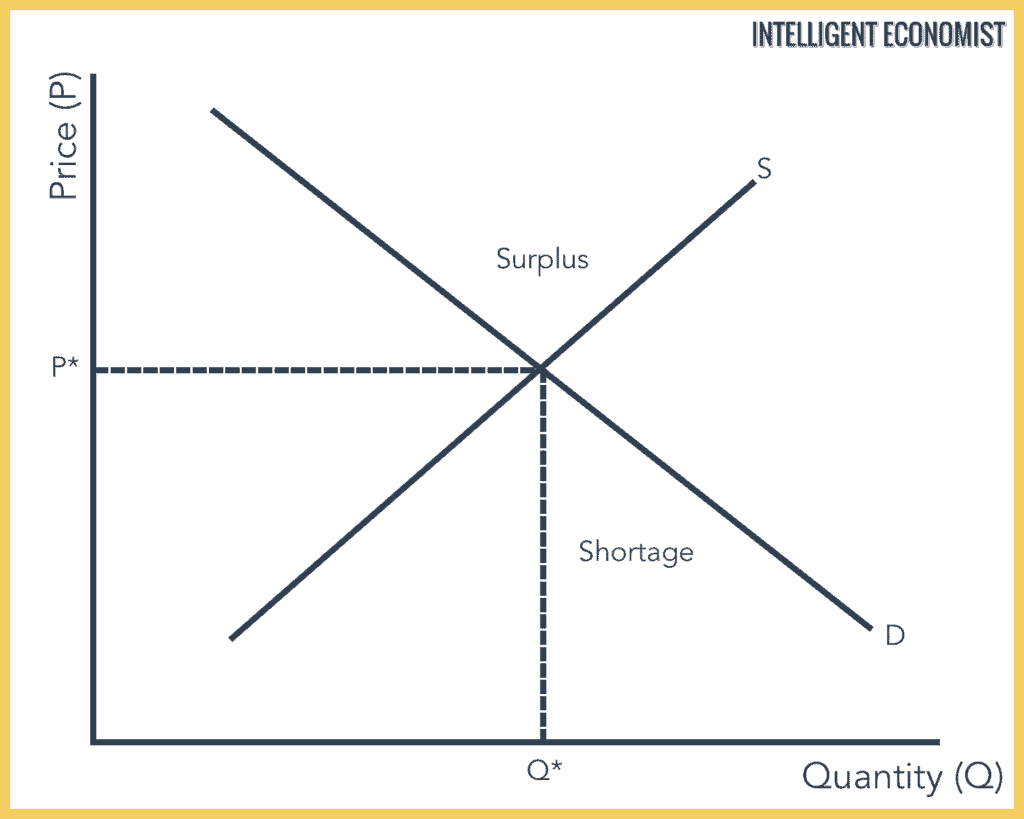
Midpoint Formula For Cross Elasticity Of Demand. In such a case cross elasticity will be calculated as. Elasticity midpoint formula. If XED 0 then the products are complements of each other. All we need to do at this point is divide the percentage change in quantity demanded we calculate above by the.
 Calculating Price Elasticities Using The Midpoint Formula Economics 2 0 Demo From courses.lumenlearning.com
Calculating Price Elasticities Using The Midpoint Formula Economics 2 0 Demo From courses.lumenlearning.com
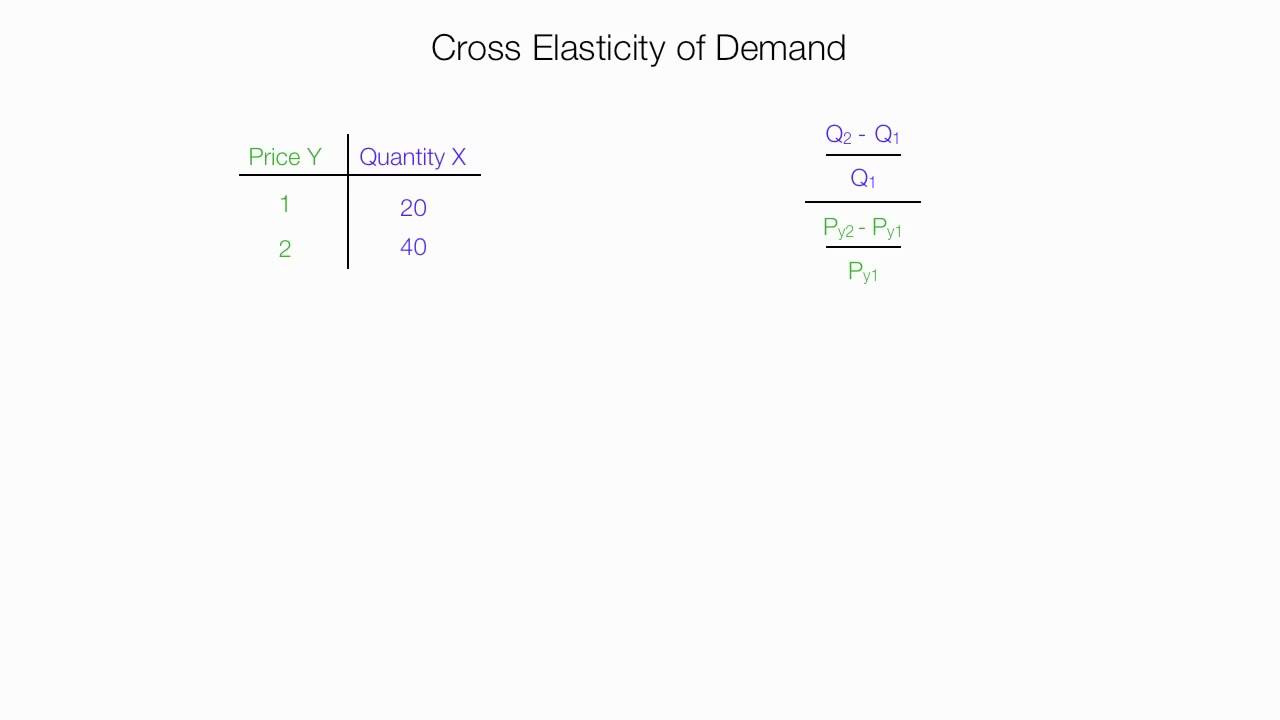
With the midpoint method elasticity is much easier to calculate because the formula reflects the average percentage change of price and quantity. This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. All we need to do at this point is divide the percentage change in quantity demanded we calculate above by the. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Q1X Q0X Q1X Q0X P1Y P0Y P1Y P0Y where Q 0X Initial demanded quantity Demanded Quantity Quantity demanded is the quantity of a. For example if the price of butter is increased from 20 to 25 the demand for bread is decreased from 200 units to 125 units. In the formula below Q reflects quantity and P indicates price.
The midpoint elasticity formula for calculating the response of changes in B to changes in A is given as.
We set up the equation in the following manner ending price minus initial price divided by average price using the midpoint formula divided by ending quantity minus initial quantity divided by average quantity discussion of elasticity problems and discussion of elastic vs inelastic. The quantity sold will go from 100 units to 25 units. A decrease of 75 units 100 - 25 75. If we had to buy the air that we breath the irreplaceable aspect of air and our utter dependence would would create an inelastic relationship. For example if the price of butter is increased from 20 to 25 the demand for bread is decreased from 200 units to 125 units. If the factor is equal to 1 the percentage change in price is identical to the percentage change in quantity.
 Source: essayprop.com
Source: essayprop.com
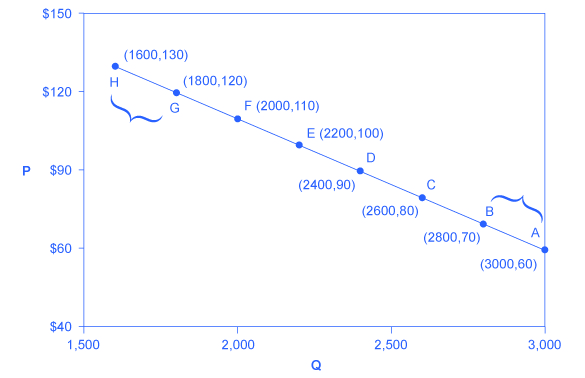
This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. Price Elasticity of Demandpercent change in quantitypercent change in price Price Elasticity of Demand percent change in quantity percent change in price. The quantity sold will go from 100 units to 25 units. The formula looks a lot more complicated than it is.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The price change is exactly the same as in the example above so that percentage change is still 50. To do this we use the following formula. With the midpoint method elasticity is much easier to calculate because the formula reflects the average percentage change of price and quantity. All we need to do at this point is divide the percentage change in quantity demanded we calculate above by the. If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
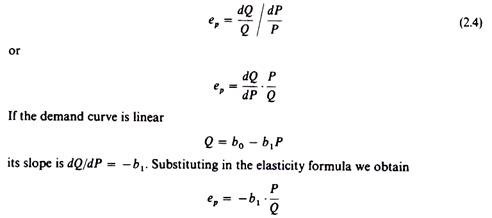
Calculate the price elasticity of demand you get. Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100. With the midpoint method elasticity is much easier to calculate because the formula reflects the average percentage change of price and quantity. Compute the elasticity of demand for the given demand function Dp and determine whether the demand is elastic inelastic or of unit elasticity at the indicated price p. The second term is the percentage change in variable A.
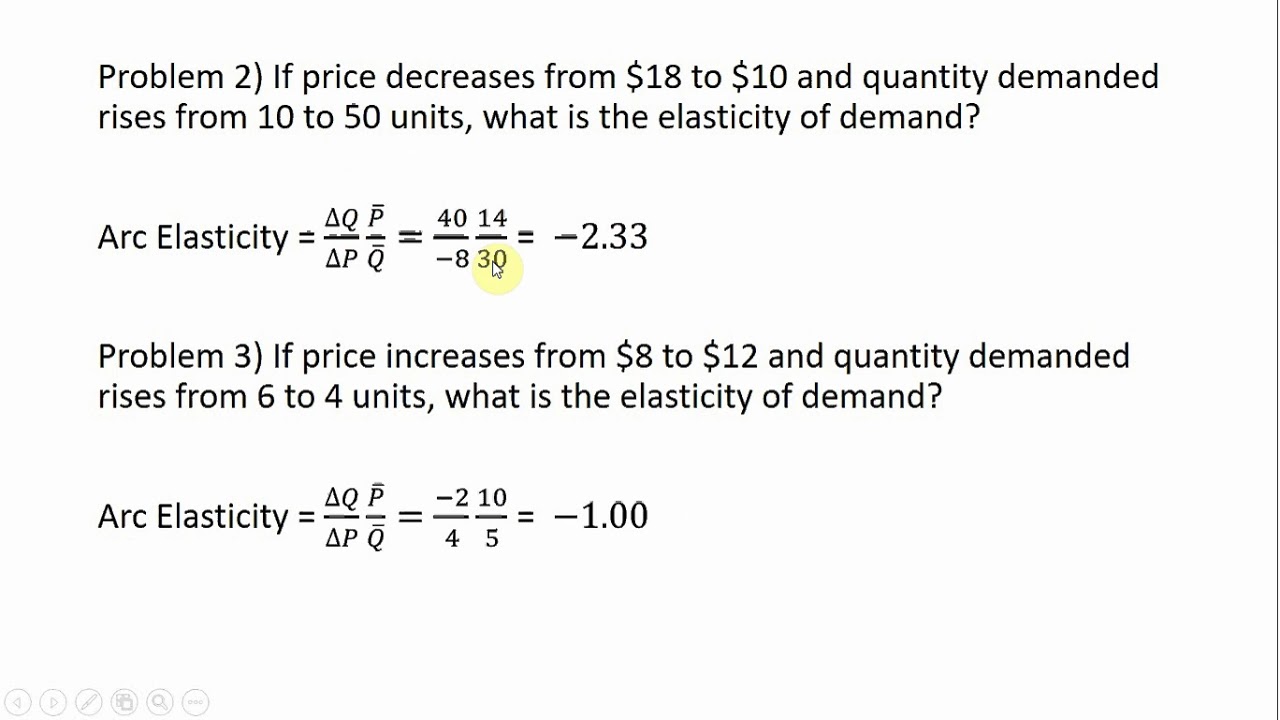 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
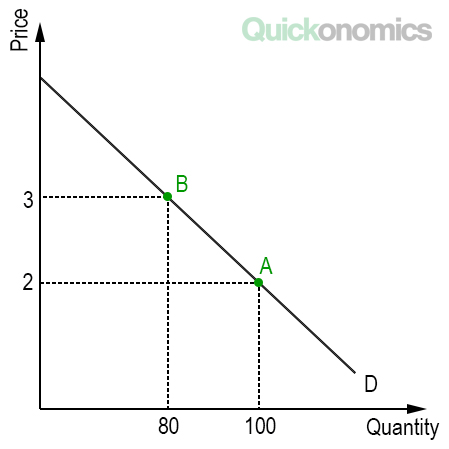
The formula for calculating elasticity is. We set up the equation in the following manner ending price minus initial price divided by average price using the midpoint formula divided by ending quantity minus initial quantity divided by average quantity discussion of elasticity problems and discussion of elastic vs inelastic. This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. The Midpoint Method To calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price. With the percentage changes calculated with the midpoint method we can now compute a distinct price elasticity of demand between points A and B.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100. The midpoint elasticity formula is a common method of calculating elasticity especially the price elasticity of demand price elasticity of supply income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand. This would be a change from the beginning units sold of 100 of 75100 or 75. With the midpoint method elasticity is much easier to calculate because the formula reflects the average percentage change of price and quantity. If playback doesnt begin shortly try.
 Source: www2.palomar.edu
Source: www2.palomar.edu
The midpoint elasticity formula for calculating the response of changes in B to changes in A is given as. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Q1X Q0X Q1X Q0X P1Y P0Y P1Y P0Y where Q 0X Initial demanded quantity Demanded Quantity Quantity demanded is the quantity of a. Price Elasticity of Demandpercent change in quantitypercent change in price Price Elasticity of Demand percent change in quantity percent change in price. The quantity sold will go from 100 units to 25 units. Calculate the price elasticity of demand you get.
 Source: quickonomics.com
Source: quickonomics.com
This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. Own-price elasticity of supply can be calculated using mid-point and point-slope formula in the same way as for e P D. A decrease of 75 units 100 - 25 75. In the formula below Q reflects quantity and P indicates price. To do this we use the following formula.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The formula looks a lot more complicated than it is. This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. The Midpoint Method To calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price. Midpoint elasticity B2 - B1 B2 B12 A2 - A1 A2 A12 The first term on the right-hand side of the equation is the percentage change in variable B. With the percentage changes calculated with the midpoint method we can now compute a distinct price elasticity of demand between points A and B.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
To do this we use the following formula. Cross-price elasticity of demand e XP D Whereas the own-price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity to a goods own price cross-price elasticity of demand shows us how quantity demand responds to changes in the price of. With the percentage changes calculated with the midpoint method we can now compute a distinct price elasticity of demand between points A and B. Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. In such a case cross elasticity will be calculated as.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A decrease of 75 units 100 - 25 75. Midpoint elasticity B2 - B1 B2 B12 A2 - A1 A2 A12 The first term on the right-hand side of the equation is the percentage change in variable B. The midpoint formula will give the same value whether moving from the higher price to the lower price or from the lower price to the higher price. The Mid point forumula for Price Elasticity of Demand. The second term is the percentage change in variable A.
 Source: quickonomics.com
Source: quickonomics.com
In complementary goods cross elasticity of goods is negative. Cross-price elasticity of demand e XP D Whereas the own-price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity to a goods own price cross-price elasticity of demand shows us how quantity demand responds to changes in the price of. The Mid point forumula for Price Elasticity of Demand. The Midpoint Method To calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price. The formula looks a lot more complicated than it is.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The Midpoint Method To calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price. If XED 0 then the products are complements of each other. We set up the equation in the following manner ending price minus initial price divided by average price using the midpoint formula divided by ending quantity minus initial quantity divided by average quantity discussion of elasticity problems and discussion of elastic vs inelastic. This formula is most often used at the introductory level of economic instruction. The second term is the percentage change in variable A.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Calculate the price elasticity of demand you get. Cross-price elasticity of demand e XP D Whereas the own-price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity to a goods own price cross-price elasticity of demand shows us how quantity demand responds to changes in the price of. Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. Calculate the price elasticity of demand you get. The Mid point forumula for Price Elasticity of Demand.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The cross-price elasticity of demand is computed similarly. P ED Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 P 2 P 1 P 2 P 12 Percent Change in Quantity Percent Change in Price P E D Q 2 - Q 1. This is called the midpoint method for elasticity and is represented by the following equations. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Q1X Q0X Q1X Q0X P1Y P0Y P1Y P0Y where Q 0X Initial demanded quantity Demanded Quantity Quantity demanded is the quantity of a. LatexdisplaystyletextCross-Price Elasticity of Demandfractextpercent change in quantity of sprockets demandedtextpercent change in price of widgetslatex The initial quantity of sprockets demanded is 9 and the subsequent quantity demanded is 10 Q1 9 Q2 10.
 Source: penpoin.com
Source: penpoin.com
This is called the midpoint method for elasticity and is represented by the following equations. Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100. The formula for calculating elasticity is. LatexdisplaystyletextCross-Price Elasticity of Demandfractextpercent change in quantity of sprockets demandedtextpercent change in price of widgetslatex The initial quantity of sprockets demanded is 9 and the subsequent quantity demanded is 10 Q1 9 Q2 10. If XED 0 then the products are complements of each other.
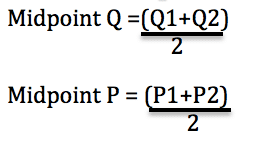 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Cross price elasticity of demand XED QXQX PYPY Where QX Quantity of product X PY Price of the product Change in the quantity demandedprice From this formula the following can be deduced. The midpoint formula will give the same value whether moving from the higher price to the lower price or from the lower price to the higher price. Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. A decrease of 75 units 100 - 25 75. The formula for calculating elasticity is.
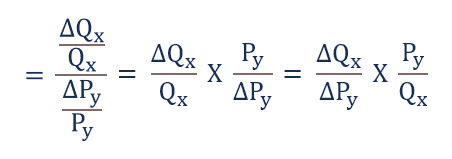 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
If the factor is equal to 1 the percentage change in price is identical to the percentage change in quantity. Elasticity midpoint formula. This would be a change from the beginning units sold of 100 of 75100 or 75. The formula looks a lot more complicated than it is. Cross price elasticity of demand XED QXQX PYPY Where QX Quantity of product X PY Price of the product Change in the quantity demandedprice From this formula the following can be deduced.
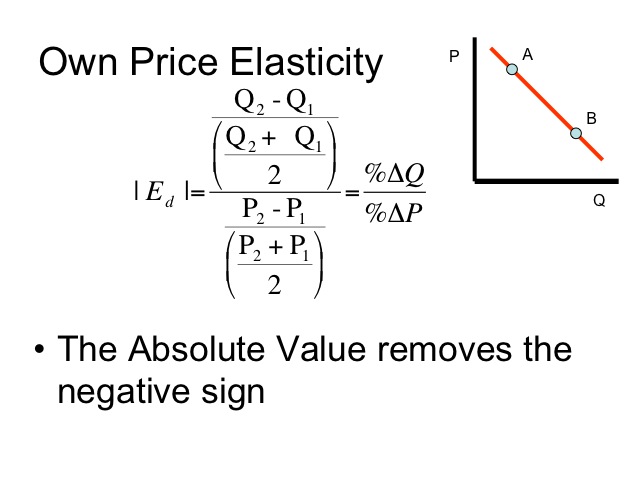 Source: courses.byui.edu
Source: courses.byui.edu
If the factor is equal to 1 the percentage change in price is identical to the percentage change in quantity. The formula for Midpoint Method of Price Elasticity of Demand is. To do this we use the following formula. Percent change in quantity Q2 Q1 Q2 Q12 100 percent change in quantity Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 100. We set up the equation in the following manner ending price minus initial price divided by average price using the midpoint formula divided by ending quantity minus initial quantity divided by average quantity discussion of elasticity problems and discussion of elastic vs inelastic.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title midpoint formula for cross elasticity of demand by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.