Your Law of demand diagram ib images are ready. Law of demand diagram ib are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Law of demand diagram ib files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for law of demand diagram ib pictures information linked to the law of demand diagram ib keyword, you have visit the ideal site. Our site always gives you suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Law Of Demand Diagram Ib. The Law of Demand. Using diagrams explain how total revenue will change if. These points are then graphed and the line connecting them is the demand curve D. Give a general example and demonstrate it through a Price v Quantity Demanded diagram.
 Pin On Uni Life From pinterest.com
Pin On Uni Life From pinterest.com
Supply The law of supply. The law of demand is explained to explain how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. This diagram illustrates a very important concept in IB economics which you have to understand and be able to clearly explain. The Law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant. Unit Consumed Teaching Suggestion. It helps to explain the downward-sloping demand curve.
States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus.
States that as the price of a product rises the quantity supplied of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. Price rises but costs do not change. The law refers to the direction in which quantity demanded. If the price of solar power falls and the price of oil and coal stay the same the demand for solar power will rise. In other words when the price of any product increases then its demand will fall and when its price decreases. Unit Consumed Teaching Suggestion.
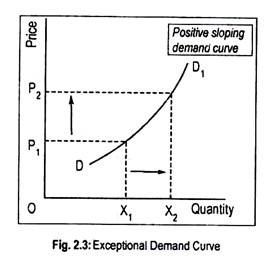 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Opens a modal Change in expected future prices and demand. The law of demand is explained to explain how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. Define demand as the willingness and ability of a consumer to pay a certain price for a good or service at a specific period in time. Demand is elastic and price decreases iii. These points are then graphed and the line connecting them is the demand curve D.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Opens a modal Price of related products and demand. Effective demand is the amount of a good people are willing to buy at given prices over a given period of time backed by the ability to pay. Buyers and sellers come together to carry out an economic transaction. Diagrams the key to getting high and full marks in your IB Paper 1 and Paper 2. We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
There is an inverse or negative association between price and. Opens a modal Price of related products and demand. States that as the price of a product rises the quantity supplied of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. Supply The law of supply. Market demand as the sum of individual demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself. We substitute solar power for coal power. Demand is inelastic and price decreases v. Explain the meaning of law of demand where ceteris paribus as price increases the quantity demanded of a product falls. Demand is inelastic and price increases iv.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
Outline the concept of income elasticity of demand understanding that it involves responsiveness of demand and hence a shifting demand curve to a change in income. YED percentage change in quantity demanded divided by percentage change in income. As you know we love to use economic models to depict the theory in a more simplistic way of course holding certain variables constant ceteris paribus so. It helps to explain the downward-sloping demand curve. By referring to the concept of excess supply and using a diagram analyse the effects of improved technology and the falling prices of inputs on the increasing affordability of food in many markets.
 Source: ibeconomist.com
Source: ibeconomist.com
The law of demand is explained to explain how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. Figure 11 - A demand curve. As more of a variable factor of production is added to a fixed factor of production the additional to total output will eventually begin to decline. Price rises but costs do not change. Using diagrams explain how total revenue will change if.
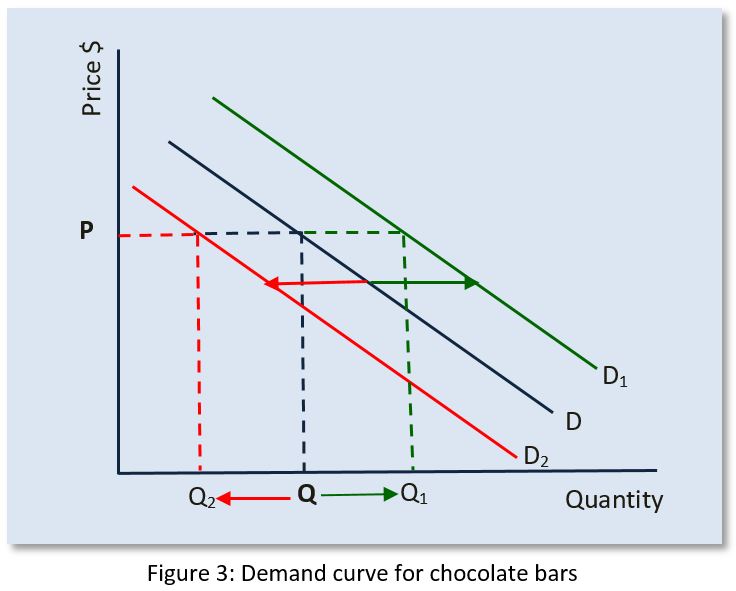 Source: ibdeconomics.com
Source: ibdeconomics.com
Begin lesson with a quick starter by tempting a student with. The Law of Demand. When the price of an individual good falls demand rises the law of demand. If only one determinant is explained a maximum of level 2 6 marks may be awarded. The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Opens a modal Price of related products and demand. Demand is inelastic and price increases iv. Law of Demand Definition. The law of demand is explained to explain how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. A micro example demand curves working for an individual market.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself. If the price of solar power falls and the price of oil and coal stay the same the demand for solar power will rise. A demand schedule is determined and from this a demand curve is modeled. The downward slope of the demand curve again illustrates the law of demandthe inverse relationship between prices and quantity demanded. These points are then graphed and the line connecting them is the demand curve D.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Demand is elastic and price increases vii. The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period. Demand is inelastic and price increases iv. - as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded increases ceteris paribus vice versa changes in price. Demand is elastic and price increases ii.
 Source: ibeconomist.com
Source: ibeconomist.com
Demand is inelastic and price decreases v. Demand is elastic and price increases ii. Diagrams the key to getting high and full marks in your IB Paper 1 and Paper 2. IB Economics notes on 13 Supply. When the price of an individual good falls demand rises the law of demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A Demand Curve for Gasoline. Thus it expresses an inverse relation between price and demand. The downward slope of the demand curve again illustrates the law of demandthe inverse relationship between prices and quantity demanded. Explain the determinants of PED including the number and closeness of substitutes the degree of necessity time and the proportion of income spent on the good. States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
A micro example demand curves working for an individual market. The law of supply. Producer surplus Refers to the difference between the price received by firms for selling their good and the lowest price they are willing to accept to produce the good. Demand is perfectly inelastic and price increases vi. Explain the determinants of PED including the number and closeness of substitutes the degree of necessity time and the proportion of income spent on the good.
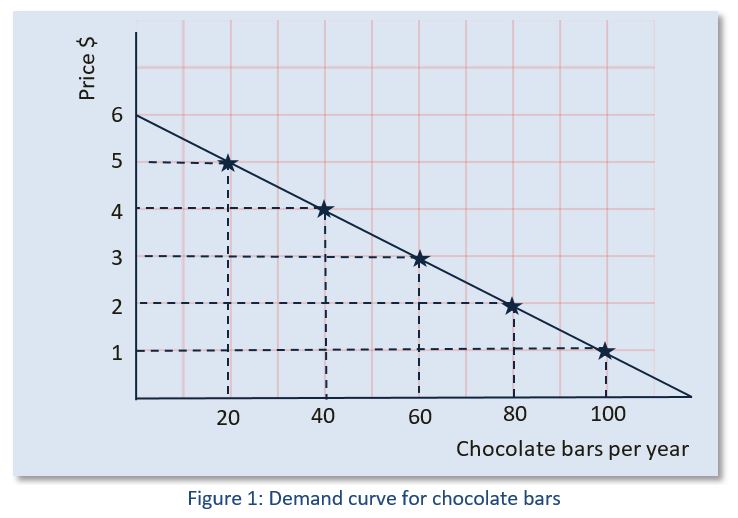 Source: ibdeconomics.com
Source: ibdeconomics.com
Buyers and sellers come together to carry out an economic transaction. Explain the law of demand and use diagrams and examples to distinguish between shifts of the demand curve and movements along the demand curve. A micro example demand curves working for an individual market. It is called the law of diminishing marginal returns. The law refers to the direction in which quantity demanded.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility can be stated as the more a specific product consumer obtain the less they will want more units of the same product. Explain using diagrams and PED values the concepts of price elastic demand price inelastic demand unit elastic demand perfectly elastic demand and perfectly inelastic demand. In other words when the price of any product increases then its demand will fall and when its price decreases. If only two determinants are explained a maximum of level 3 8 marks may be awarded.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Market demand as the sum of individual demand. Demand is inelastic and price increases iv. Consumer demand is central to IB Economics and microeconomics. These points are then graphed and the line connecting them is the demand curve D. Outline the concept of income elasticity of demand understanding that it involves responsiveness of demand and hence a shifting demand curve to a change in income.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Demand is elastic and price increases ii. As you know we love to use economic models to depict the theory in a more simplistic way of course holding certain variables constant ceteris paribus so. If only one determinant is explained a maximum of level 2 6 marks may be awarded. The law of demand expresses a relationship between the quantity demanded and its price. Explain the determinants of PED including the number and closeness of substitutes the degree of necessity time and the proportion of income spent on the good.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Opens a modal Price of related products and demand. The law of demand expresses a relationship between the quantity demanded and its price. Opens a modal Price of related products and demand. Demand is elastic and price decreases iii. It may be defined in Marshalls words as the amount demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title law of demand diagram ib by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






