Your Kinked demand model economics discussion images are available. Kinked demand model economics discussion are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Kinked demand model economics discussion files here. Get all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for kinked demand model economics discussion pictures information linked to the kinked demand model economics discussion topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Kinked Demand Model Economics Discussion. International Journal of Industrial Organization 6 1988 373-384. ECONOMICS WEEK 3 DISCUSSION 2 2ND POST How do economists explain the KINKED demand curve model found under an. The kinked demand curve revisited Debapriya Sen Department of Economics University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla CA 92093-0508 USA Received 12 November 2003. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price.
 Kinked Demand Curve Model Of Oligopoly With Diagram From economicsdiscussion.net
Kinked Demand Curve Model Of Oligopoly With Diagram From economicsdiscussion.net
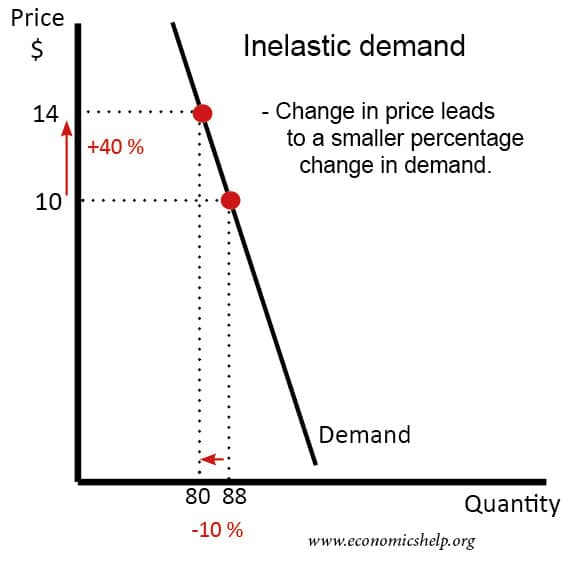
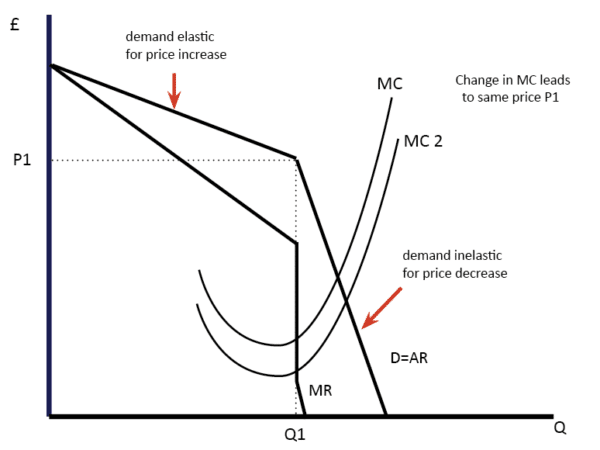
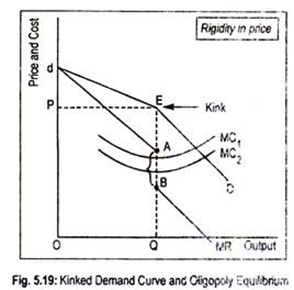
This causes the demand for goods produced by the firm attempting the price increase to fall. The firms mostly make efforts to operate in non price competition for increasing their respective shares of the market and their profit. It predicts that prices should be more likely to change if they have recently changed and that prices should be more flexible in markets where customers can more easily compare prices. North-Holland THE KINKED DEMAND CURVE A Game-Theoretic Approach V. The graph shows how price rigidity occurs. The kinked demand curve model provides one possible explanation of the stickiness or rigidity inflexibility or rigidly inflexibility of oligopoly prices.
The kinked demand curve revisited Debapriya Sen Department of Economics University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla CA 92093-0508 USA Received 12 November 2003.
The kinked demand curve revisited Debapriya Sen Department of Economics University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla CA 92093-0508 USA Received 12 November 2003. Introduction The Sweezy model of oligopoly appeared in 19391 It was concluded by Stigler in 1947 that the empirical evidence reveals neither price experiences that would lead oligopolists to believe in the. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. Kaushik and William L. The two that are most frequently discussed however are the kinkeddemand theory and the cartel theory. Let us consider the effect on quantity demanded of a reduction in the price of a commodity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
However these strategies are dominated and perfect equilibrium is unique at the minimum optimal common price. According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. Any changes in marginal cost result in the same. Sweezy uses kinked demand curve to describe price rigidity in oligopoly market structure.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
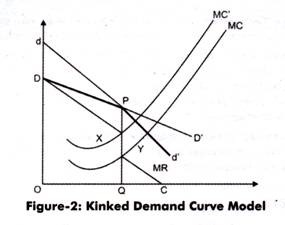
The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. For linear demand curves MR has the same y-intercept and two times the slope resulting in two different sections for the MR curve when demand has a kink. In the kinked demand curve model MR is discontinuous due to the asymmetric nature of the demand curve. The two that are most frequently discussed however are the kinkeddemand theory and the cartel theory. The kinked demand curve model was developed by Paul Sweezy 1939.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Kaushik and William L. The kinked-demand theory can be tested against menu-cost models in micro data. This causes the demand for goods produced by the firm attempting the price increase to fall. The kinked demand curve model was developed by Paul Sweezy 1939. First other firms will follow a price cut and second they will not follow a price rise.

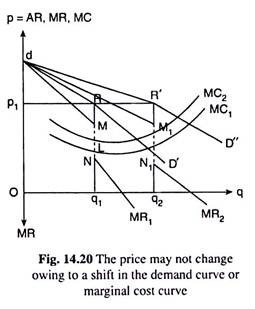
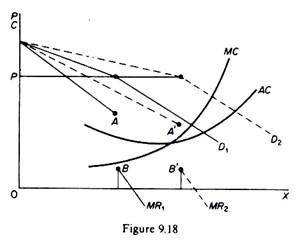
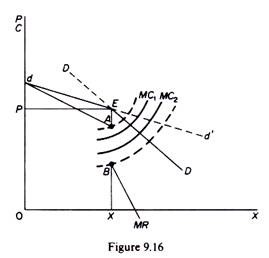
Any changes in marginal cost result in the same. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. View ECONOMICS WEEK 3 DISCUSSION 2 2ND POST from ECON 310 at DeVry University Chicago. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations. The kinkeddemand theory is illustrated in Figure and applies to oligopolistic markets where each firm sells a differentiated product.
 Source: educatech.in
Source: educatech.in
The kinked demand curve hypothesis was put forward independently by Paul M. ECONOMICS WEEK 3 DISCUSSION 2 2ND POST How do economists explain the KINKED demand curve model found under an. If a seller increases the price of his product the rival sellers will not follow him so that the first seller loses a considerable amount of sales. The kinked demand curve hypothesis was put forward independently by Paul M. The kinked-demand curve model as an operational oligopoly model was presented by P.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
It predicts that prices should be more likely to change if they have recently changed and that prices should be more flexible in markets where customers can more easily compare prices. It should be noted that although the kinked-demand curve appears in Chamberlins analysis of both the large group and the small group he does not use it explicitly as a tool of analysis of the behaviour of the firm. In the oligopoly model under discussion the properties of the kinked demand curve as well as its significance are especially discussed. 7 The kinked demand curve analysis is based on two assumptions. Since an oligopolist is not aware of the demand curve economists have designed various price-output models based on the behavior pattern of other firms in the industry.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
If a seller increases the price of his product the rival sellers will not follow him so that the first seller loses a considerable amount of sales. North-Holland THE KINKED DEMAND CURVE A Game-Theoretic Approach V. The kinked demand curve model was developed by Paul Sweezy 1939. The kink in the demand curve stems from the asymmetric behavioural pattern of sellers. The kinked-demand curve can explain the stickiness of prices in a situation of changing costs and of high rivalry.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The kinkeddemand theory is illustrated in Figure and applies to oligopolistic markets where each firm sells a differentiated product. Analysis of the Kinked Demand Curve Model. For linear demand curves MR has the same y-intercept and two times the slope resulting in two different sections for the MR curve when demand has a kink. The graph shows how price rigidity occurs. It should be noted that although the kinked-demand curve appears in Chamberlins analysis of both the large group and the small group he does not use it explicitly as a tool of analysis of the behaviour of the firm.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The kinked demand curve model was developed by Paul Sweezy 1939. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. TEXTBOOK DEPARTURES FROM THE ORIGINAL SWEEZY MODEL by Surendra K. First other firms will follow a price cut and second they will not follow a price rise. Stigler has shown on empirical evidence that in an inflationary period the rise in output prices is not confined only to.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The kinked demand model postulates that when a firm increases it price its competitors do not change their prices. Any changes in marginal cost result in the same. This is as usual shown by the demand curve for the firms product. The kinked demand curve hypothesis was put forward independently by Paul M. The graph shows how price rigidity occurs.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
ECONOMICS WEEK 3 DISCUSSION 2 2ND POST How do economists explain the KINKED demand curve model found under an. Therefore to understand the kinked demand curve model it is important to note the reactions of rival organizations on the price changes made by. In the kinked demand curve model MR is discontinuous due to the asymmetric nature of the demand curve. The firms mostly make efforts to operate in non price competition for increasing their respective shares of the market and their profit. The kinked demand curve model was developed by Paul Sweezy 1939.
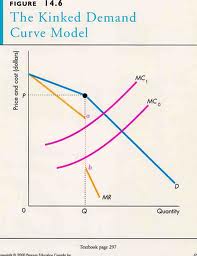 Source: assignmentpoint.com
Source: assignmentpoint.com
For linear demand curves MR has the same y-intercept and two times the slope resulting in two different sections for the MR curve when demand has a kink. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. It is for explaining price and output under oligopoly with product differentiation that economists often use the kinked demand curve hypothesis. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. Analysis of the Kinked Demand Curve Model.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The kinkeddemand theory is illustrated in Figure and applies to oligopolistic markets where each firm sells a differentiated product. Sweezy uses kinked demand curve to describe price rigidity in oligopoly market structure. North-Holland THE KINKED DEMAND CURVE A Game-Theoretic Approach V.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The kinkeddemand theory is illustrated in Figure and applies to oligopolistic markets where each firm sells a differentiated product. The two that are most frequently discussed however are the kinkeddemand theory and the cartel theory. The kinked demand curve hypothesis was put forward independently by Paul M. The kinked-demand theory can be tested against menu-cost models in micro data. The kinked demand curve model provides one possible explanation of the stickiness or rigidity inflexibility or rigidly inflexibility of oligopoly prices.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
North-Holland THE KINKED DEMAND CURVE A Game-Theoretic Approach V. BHASKAR University College London WCIE 6BT UK Final version received August 1987 In a simple model of duopoly firms price moves are modelled as an extensive form game where firms can respond to undercutting. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. The kinked-demand curve model as an operational oligopoly model was presented by P. According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The two that are most frequently discussed however are the kinkeddemand theory and the cartel theory. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. It is for explaining price and output under oligopoly with product differentiation that economists often use the kinked demand curve hypothesis. The kinked demand curve model was developed by Paul Sweezy 1939. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price.
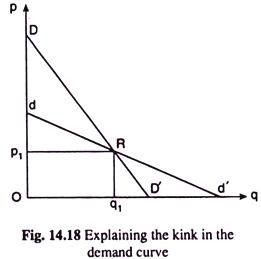 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The two that are most frequently discussed however are the kinkeddemand theory and the cartel theory. Kaushik and William L. It is for explaining price and output under oligopoly with product differentiation that economists often use the kinked demand curve hypothesis. The kinked-demand curve can explain the stickiness of prices in a situation of changing costs and of high rivalry. When firms are not too dissimilar kinked demand strategies enforcing an arbitrary price may be Nash equilibria.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Kinked Demand Curve In an oligopolistic market firms cannot have a fixed demand curve since it keeps changing as competitors change the prices quantity of output. THE KINKED-DEMAND MODEL OF OLIGOPOLY. The kinked demand curve revisited Debapriya Sen Department of Economics University of California San Diego 9500 Gilman Drive La Jolla CA 92093-0508 USA Received 12 November 2003. Accepted 5 January 2004 Available online 14 April 2004 Abstract In a Stackelberg oligopoly with cost asymmetry and possibility of entry the Stackelberg leader faces a kinked demand. Therefore to understand the kinked demand curve model it is important to note the reactions of rival organizations on the price changes made by.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title kinked demand model economics discussion by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.