Your Kinked demand curve theory marginal revenue images are available. Kinked demand curve theory marginal revenue are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Kinked demand curve theory marginal revenue files here. Get all free vectors.
If you’re looking for kinked demand curve theory marginal revenue images information linked to the kinked demand curve theory marginal revenue interest, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
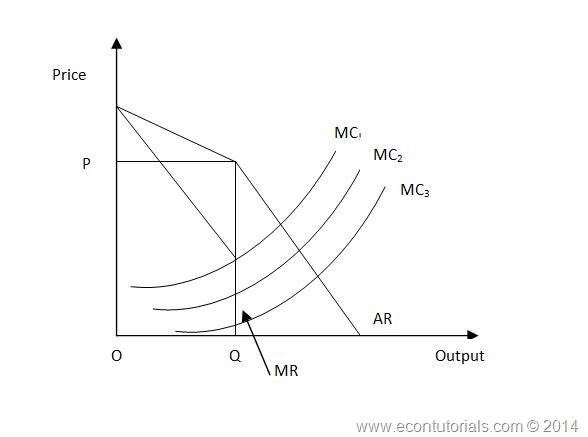
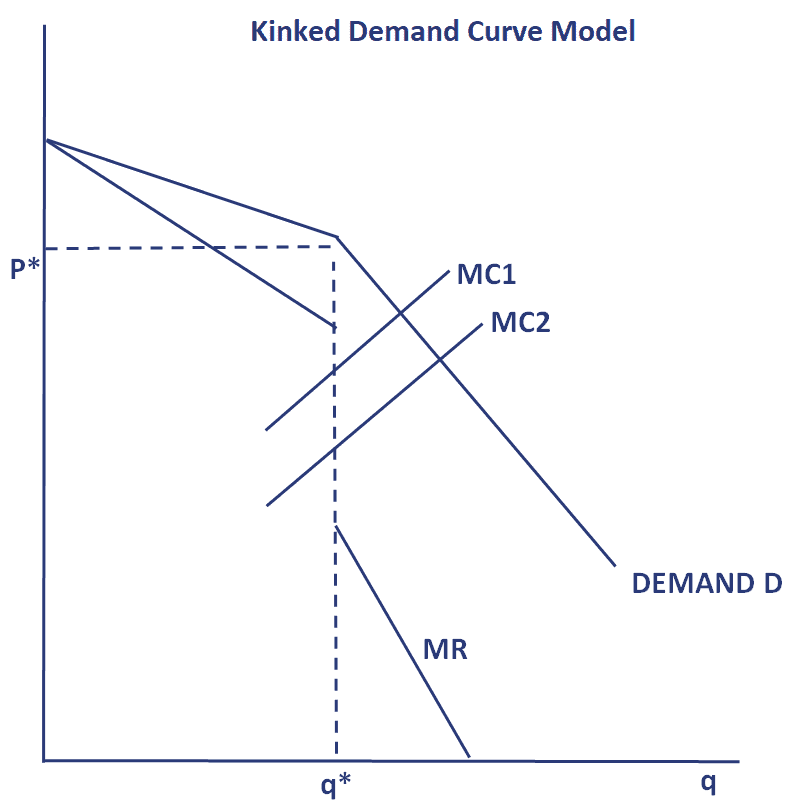
Kinked Demand Curve Theory Marginal Revenue. Raise price and raise ouputE. B will be horizontal. For the demand curve DX above the kink the marginal revenue is given by MR 1. Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve.

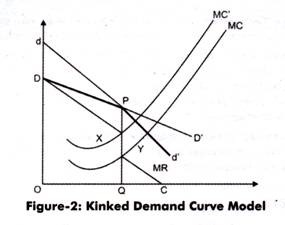
That is at the kink or the profit maximizing price. The graph also shows two possible marginal cost curves MCI and MC2. This means price and output will be shown by a point. Suppose that the marginal cost curve passes through the gap in the marginal revenue curve. Analysis of the Kinked Demand Curve Model. Assume that an oligopolist has a kinked demand curve.
The profit-maximizing level of output occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and the profit- maximizing price is the maximum price consumers will pay for that level of output.
According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product. Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. Suppose that the marginal cost curve passes through the gap in the marginal revenue curve. For a perfectly competitive firm the marginal revenue curve is a horizontal or perfectly elastic line. The Kinked demand curve suggests firms have little incentive to increase or decrease prices. Marginal Revenue Curve The Pepsi marginal revenue curve associated with the kinked-demand curve contains three distinct segments see Figure 7.
 Source: econfix.wordpress.com
Source: econfix.wordpress.com
An increase in marginal cost that remains within the gap of the marginal revenue curve of a kinked demand oligopolist willA. This results in significant price rigidity in an oligopoly. The profit-maximizing level of output occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and the profit- maximizing price is the maximum price consumers will pay for that level of output. That is at the kink or the profit maximizing price. Raise price and decrease outputC.

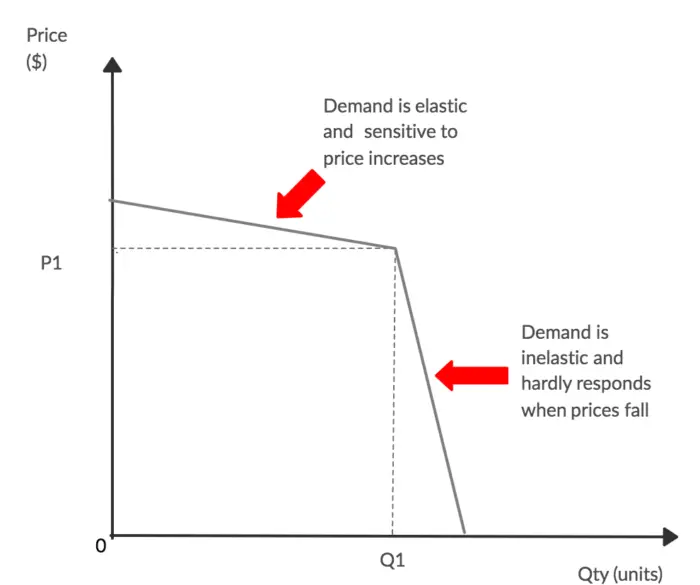
This is illustrated in Fig. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. B will be horizontal. For the demand curve DX above the kink the marginal revenue is given by MR 1. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices.
 Source: amosweb.com
Source: amosweb.com
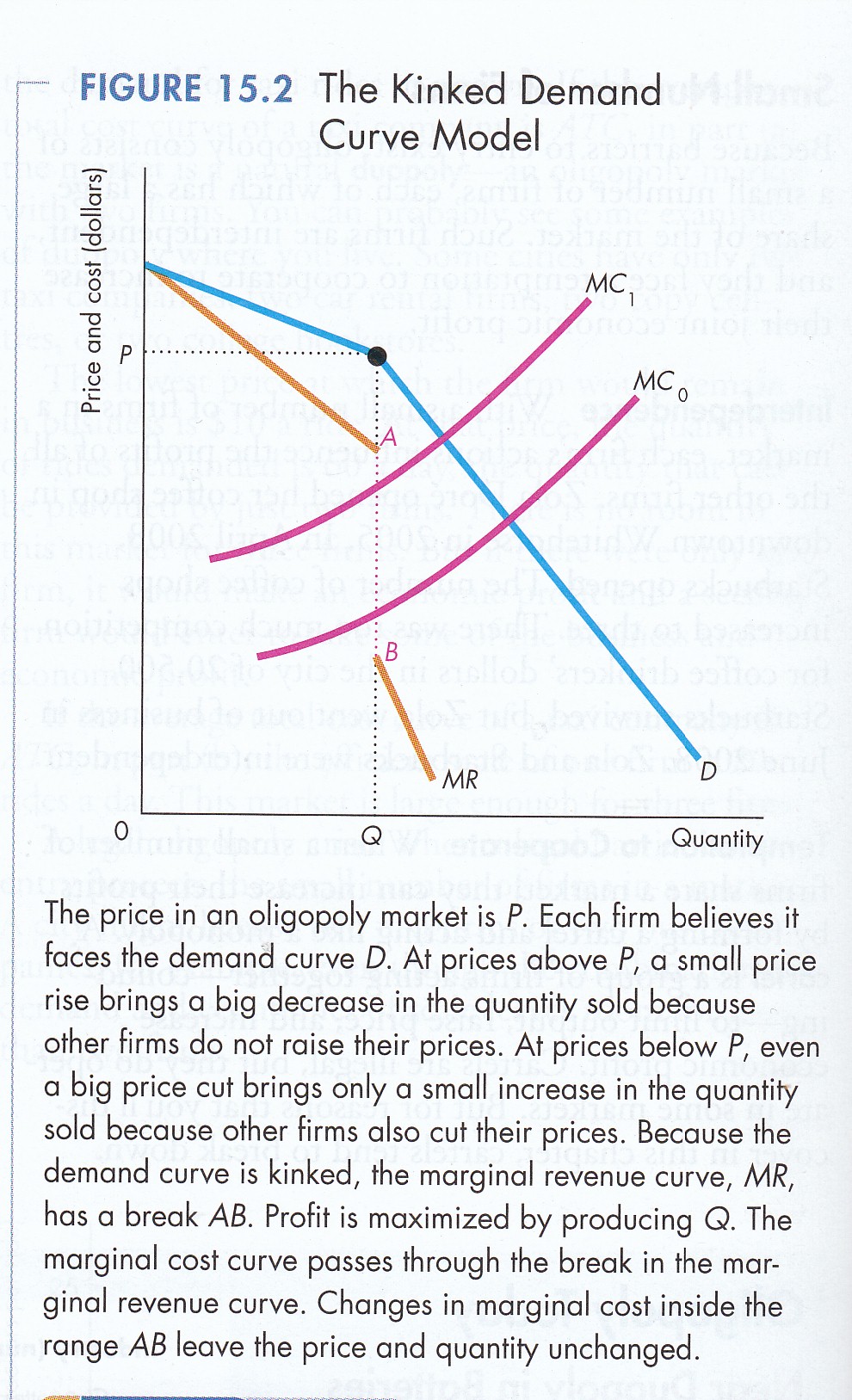
At high prices the firm faces the relatively elastic market demand curve labeled MD 1 in Figure. Corresponding to MD 1 is the marginal revenue curve labeled MR 1. This results in significant price rigidity in an oligopoly. Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations.
 Source: es.slideshare.net
Source: es.slideshare.net
The Kinked demand curve suggests firms have little incentive to increase or decrease prices. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations. Raise price and decrease outputC. Analysis of the Kinked Demand Curve Model. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve.
 Source: pdfprof.com
Source: pdfprof.com
B will be horizontal. For a perfectly competitive firm the marginal revenue curve is a horizontal or perfectly elastic line. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. Lower price and lower outputB. C will always be zero at.
 Source: biznewske.com
Source: biznewske.com
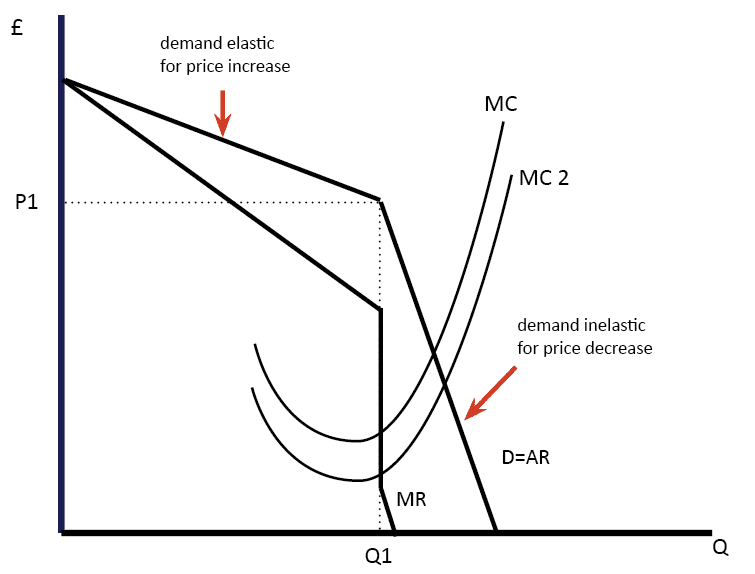
The implication is that even as an oligopolists costs rise and fall in the short-run its level of output and price tends to remain stable. Kinked demand curves and traditional demand curves are similar in that they are both downward-sloping. Because the demand curve has a kink and the marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve the marginal revenue curve would have a gap where the two segments of the demand curve meet. Likewise the kinked demand curve theory explains that even when the demand conditions change the price may remain stable. What is the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly.
 Source: econtutorials.com
Source: econtutorials.com
Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. They are distinguished by a hypothesized convex bend with a discontinuity at the bendkink. Profit is maximized at the same price and quantity combination as long as the marginal cost curve crosses the marginal. Raise price and raise ouputE. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Due to the kinked nature of the demand curve an output range exists in the marginal revenue curve is vertical such that any change in marginal cost do not impact the profit-maximizing output level and. On the lower part of the curve. B will be horizontal. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices. They are distinguished by a hypothesized concave bend with a discontinuity at the bend - the kink Therefore the first derivative point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve.
 Source: personal.psu.edu
Source: personal.psu.edu
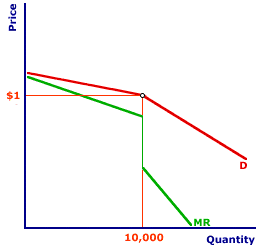
On the lower part of the curve. Lower price and lower outputB. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The top portion of the marginal revenue corresponds to the elastic demand generated by price increases above 1 and for quantities less than 10000 cans. On the lower part of the curve.
 Source: compilerpress.ca
Source: compilerpress.ca
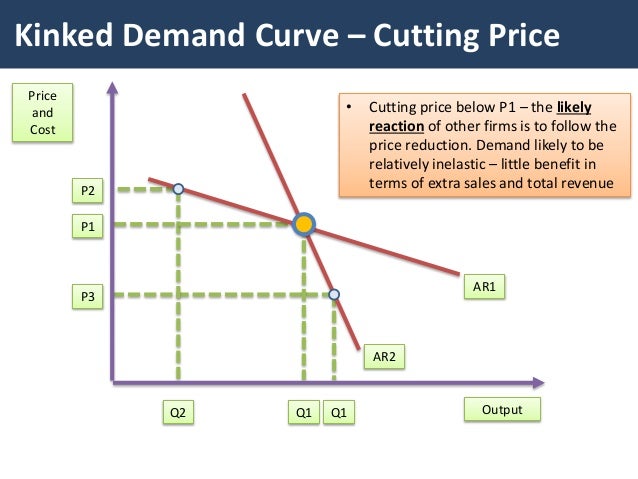
This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. On the upper part of the curve. Lower price and lower outputB.
 Source: myeconomics.info
Source: myeconomics.info
In contrast with the standard Cournot or Bertrand models the theory rep-. Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. Associated with the demand curve is a marginal revenue curve. Kinked demand curves are similar to traditional demand curves as they are downward-sloping. The profit-maximizing level of output occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and the profit- maximizing price is the maximum price consumers will pay for that level of output.
 Source: macrobank.blogspot.com
Source: macrobank.blogspot.com
The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. They are distinguished by a hypothesized convex bend with a discontinuity at the bendkink. Similarly the CD portion of the MR curve is derived from the less elastic portion of. In contrast with the standard Cournot or Bertrand models the theory rep-. This is illustrated in Fig.

The graph also shows two possible marginal cost curves MCI and MC2. Due to the kinked nature of the demand curve an output range exists in the marginal revenue curve is vertical such that any change in marginal cost do not impact the profit-maximizing output level and. For the demand curve DX above the kink the marginal revenue is given by MR 1. Assume Happylands marginal cost is represented by. This is illustrated in Fig.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
On the lower part of the curve. They are distinguished by a hypothesized convex bend with a discontinuity at the bendkink. Kinked demand curves and traditional demand curves are similar in that they are both downward-sloping. Likewise the kinked demand curve theory explains that even when the demand conditions change the price may remain stable. Along with this kinked demand curve comes a kinked marginal revenue curve with a vertical section.
 Source: pdfprof.com
Source: pdfprof.com
Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve. On the upper part of the curve. An increase in marginal cost that remains within the gap of the marginal revenue curve of a kinked demand oligopolist willA. Associated with the demand curve is a marginal revenue curve. Marginal Revenue Curve The Pepsi marginal revenue curve associated with the kinked-demand curve contains three distinct segments see Figure 7.
 Source: breakingdownfinance.com
Source: breakingdownfinance.com
A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. Marginal Revenue Curve The Pepsi marginal revenue curve associated with the kinked-demand curve contains three distinct segments see Figure 7. The top portion of the marginal revenue corresponds to the elastic demand generated by price increases above 1 and for quantities less than 10000 cans.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Kinked demand curves are similar to traditional demand curves as they are downward-sloping. In the oligopoly model under discussion the properties of the kinked demand curve as well as its significance are especially discussed. This is illustrated in Fig. For the demand curve DX above the kink the marginal revenue is given by MR 1. Thus the first derivative at that point is undefined and leads to a jump discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The graph also shows two possible marginal cost curves MCI and MC2. Assume Happylands marginal cost is represented by. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. Likewise the kinked demand curve theory explains that even when the demand conditions change the price may remain stable. According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title kinked demand curve theory marginal revenue by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






