Your Kinked demand curve theory explains images are available in this site. Kinked demand curve theory explains are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Kinked demand curve theory explains files here. Download all free images.
If you’re looking for kinked demand curve theory explains pictures information related to the kinked demand curve theory explains topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
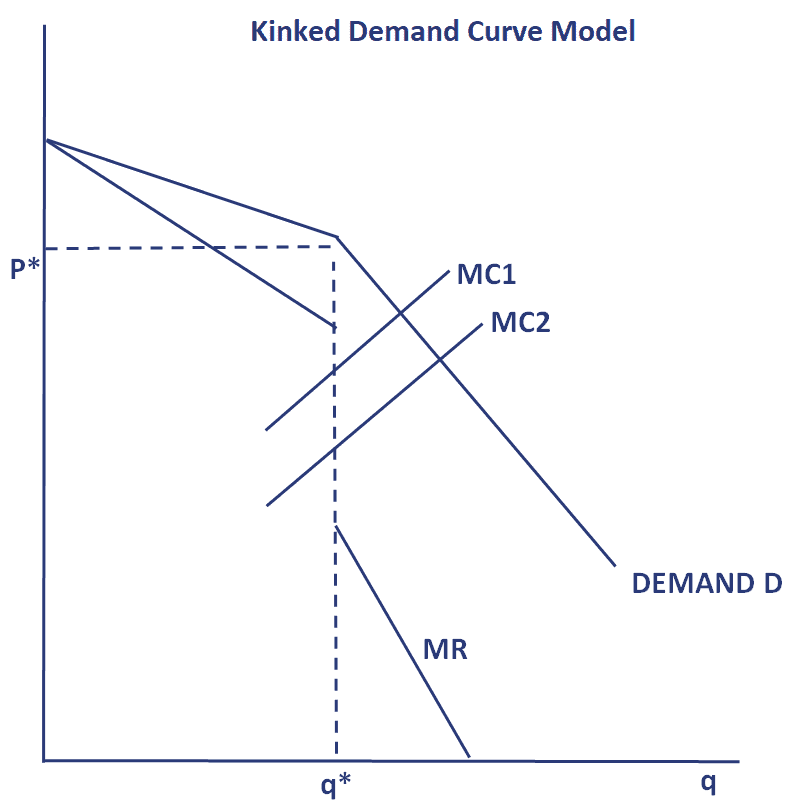
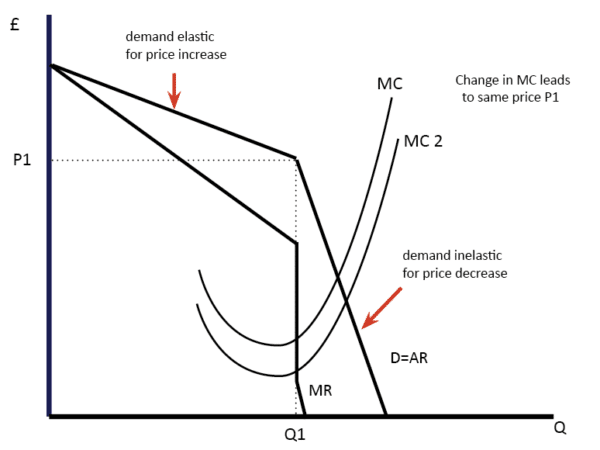
Kinked Demand Curve Theory Explains. The Kinked Demand Curve is a theory regarding oligopoly and monopolistic competition that explains price rigidity and price stickiness. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations.

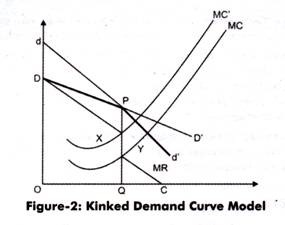
Evaluate the reasons why firms may. The two segments joins in a corner called kink. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices. And MR 2 of MR and two different parts of the MR curve.
Then it is shown that the equilibrium price is attained at a kink of the demand curve of the leader implying rigidity of price.
Kinked demand was an initial attempt to explain sticky prices. Explain the behaviour of firms in this market structure. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The segment above the prevailing price level is highly elastic. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. It is comprised of two segments one which is more elastic which results if a firm increases its price and the other that is less elastic which results if a firm decreases its prices.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. The segment above the prevailing price level is highly elastic. According to the kinked demand curve hypothesis the demand curve facing an oligopolist has a kink at the level of the prevailing price. The model explains why oligopoly prices are stable. Then it is shown that the equilibrium price is attained at a kink of the demand curve of the leader implying rigidity of price.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
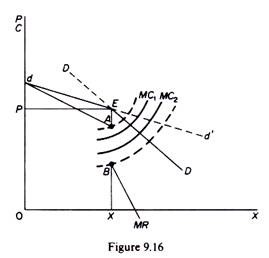
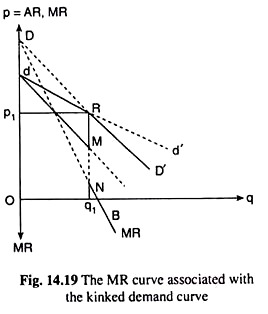
The Kinked Demand Curve is a theory regarding oligopoly and monopolistic competition that explains price rigidity and price stickiness. It was originally formulated as a theory of price rigidity. But it fails to explain how the industry-wide price was established in the first place. Explaining the kinked demand curve. That is at the point of kink R on the demand curve dRD or at q q 1 we have two different values e 1 and e 2 of e and that is why at q q 1 we obtain two different values MR.
 Source: breakingdownfinance.com
Source: breakingdownfinance.com
The kink is formed at the prevailing price level because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic. Criticisms of the Kinked Demand Curve Model. Then it is shown that the equilibrium price is attained at a kink of the demand curve of the leader implying rigidity of price. The kink is formed at the prevailing price level because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic. 1419 numerical coefficient e of price- elasticity of demand is.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
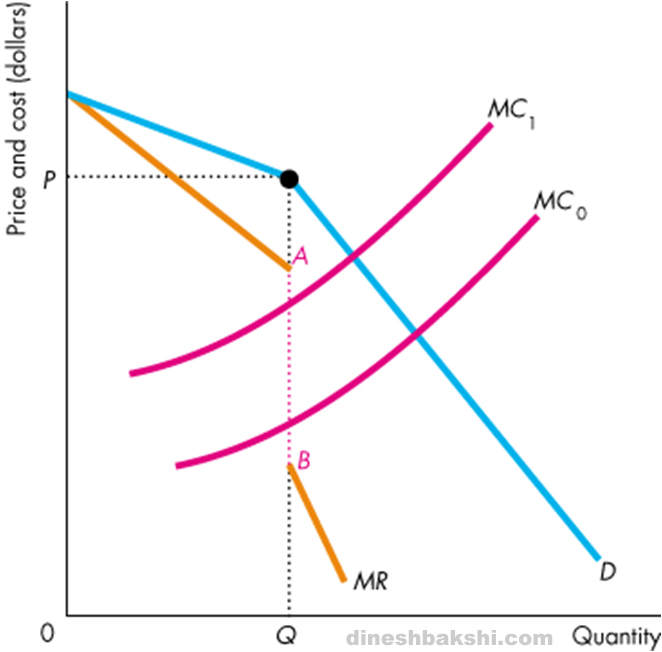
This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. Kinked Demand Curve The MR Curve Price and Cost Output AR1 The marginal revenue curve is always twice as steep as average revenue There will be two marginal revenues curves if AR is kinked We find a vertical intersection at quantity Q1. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. 1419 numerical coefficient e of price- elasticity of demand is. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M.
 Source: pdfprof.com
Source: pdfprof.com
Hall and Hitch 1939 has been one of the staples of oligopoly theory. This means that the behavior of one company is expected to impact the behavior of the other companies in the market. That is at the point of kink R on the demand curve dRD or at q q 1 we have two different values e 1 and e 2 of e and that is why at q q 1 we obtain two different values MR. Kinked demand curves have in common with traditional demand curve that they are downward-sloping. The Kinked Demand Curve Model of Oligopoly Pricing.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Explaining the kinked demand curve. Firms dont want to cut prices because they will start a price war where they dont gain market share but do get lower prices and lower revenue. Then it is shown that the equilibrium price is attained at a kink of the demand curve of the leader implying rigidity of price. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. The example of the kinked-demand theory shows that what is true for menu-cost models needs not be trueofallmodelsofstate-dependentpricing.
 Source: es.slideshare.net
Source: es.slideshare.net
Criticisms of the Kinked Demand Curve Model. According to the kinked demand curve hypothesis the demand curve facing an oligopolist has a kink at the level of the prevailing price. Hall and Hitch 1939 has been one of the staples of oligopoly theory. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. It was originally formulated as a theory of price rigidity.

They are distinguished by a hypothesized convex bend with a discontinuity at the bend - the kink. A kinked demand curve in any subgame-perfect equilibrium. The two segments joins in a corner called kink. Criticisms of the Kinked Demand Curve Model. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases.
 Source: msrblog.com
Source: msrblog.com
This means that the behavior of one company is expected to impact the behavior of the other companies in the market. A rm conjectures that its rivals will match its price if it reduces. Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations. Kinked Demand Curve The MR Curve Price and Cost Output AR1 The marginal revenue curve is always twice as steep as average revenue There will be two marginal revenues curves if AR is kinked We find a vertical intersection at quantity Q1. This means that the behavior of one company is expected to impact the behavior of the other companies in the market.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The model explains why oligopoly prices are stable. The model of the kinked demand curve suggests prices will be stable. Students should be able to. The kinked demand curve model for oligopoly markets is based on the assumption that companies within the market are interdependent. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
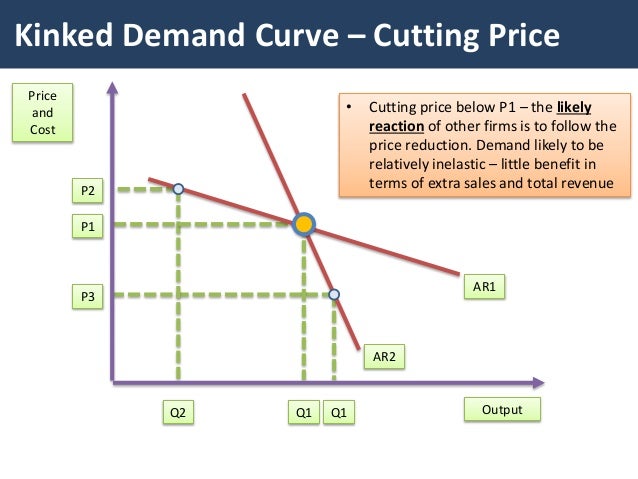
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. This point requires a. The model of the kinked demand curve suggests prices will be stable. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases.

The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. In our previous lesson on oligopoly we showed how payoff matrices and game theory could be used to analyze the strategic interdependent behavior of two firms when deciding the price they would charge. The kinked demand curve model for oligopoly markets is based on the assumption that companies within the market are interdependent. But it fails to explain how the industry-wide price was established in the first place. Understand the characteristics of this market structure with particular reference to the interdependence of firms.
 Source: studyres.com
Source: studyres.com
The market demand curve that each oligopolist faces is determined by the output and price decisions of the other firms in the oligopoly. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. The segment below the prevailing price level is inelastic. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Explaining the kinked demand curve. Explain reasons for collusive and non-collusive behaviour. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. Explain the behaviour of firms in this market structure. The kinked demand curve model for oligopoly markets is based on the assumption that companies within the market are interdependent.
 Source: econfix.wordpress.com
Source: econfix.wordpress.com
Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. This kink exists because of two reasons. The Kinked Demand Curve is a theory regarding oligopoly and monopolistic competition that explains price rigidity and price stickiness. In this lesson we take a graphical approach to oligopoly and seek to explain why prices. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices.
 Source: myeconomics.info
Source: myeconomics.info
This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. The two segments joins in a corner called kink. Explaining the kinked demand curve. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations. This means that the behavior of one company is expected to impact the behavior of the other companies in the market.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Understand the characteristics of this market structure with particular reference to the interdependence of firms. Explain the behaviour of firms in this market structure. This means that the behavior of one company is expected to impact the behavior of the other companies in the market. As we know at any point R p 1 q 1 on the firms demand curve in Fig. A kinked demand curve in any subgame-perfect equilibrium.
 Source: dineshbakshi.com
Source: dineshbakshi.com
This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. Firms dont want to cut prices because they will start a price war where they dont gain market share but do get lower prices and lower revenue. And MR 2 of MR and two different parts of the MR curve. Bhaskar University College London March 15 2007 The kinked demand curve Sweezy 1939.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title kinked demand curve theory explains by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






