Your Ib economics definition demand and supply images are available in this site. Ib economics definition demand and supply are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Ib economics definition demand and supply files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for ib economics definition demand and supply pictures information connected with to the ib economics definition demand and supply topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Ib Economics Definition Demand And Supply. Describe consumption investment government spending net exports as components of Aggregate Demand. Unit 91 - Aggregate Demand. Demand and supply Market. It is important to note that price is not a determinate of demand because the definition of demand is of course the quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to purchase in a given time at a given price.
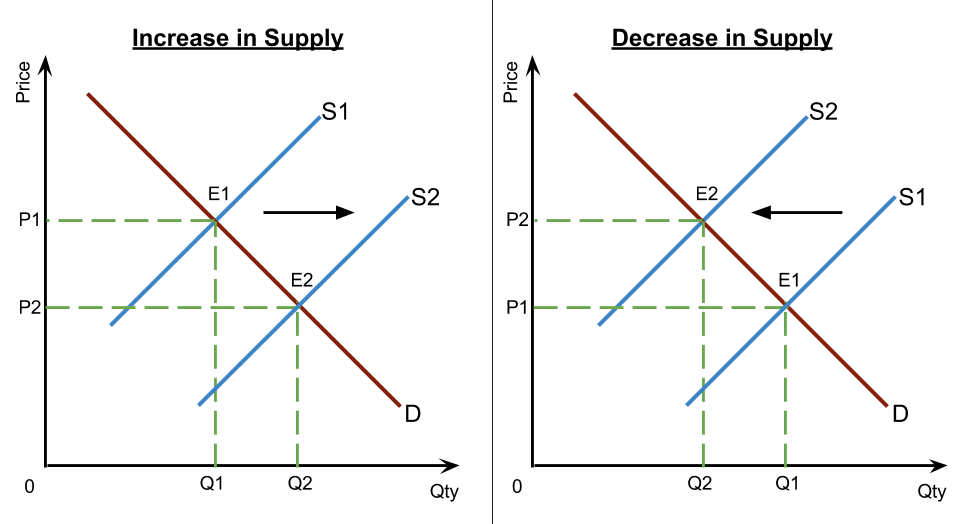 Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 1 Competitive Markets Demand And Supply From adarshibeconomics.blogspot.com
Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 1 Competitive Markets Demand And Supply From adarshibeconomics.blogspot.com
Describe consumption investment government spending net exports as components of Aggregate Demand. The law of demand explains how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. Means of production are privately held by individuals and firms. Finally the business cycle which is a recurring pattern of. Free market economy market economy An economy where there is minimal government intervention. Distinguish between the microeconomic concept of demand for a product the macroeconomic concept of Aggregate Demand.
Is the total amount of goods and services that producers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period.
22 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply. The law of supply. Microeconomics 11 Competitive Markets. Aggregate Demand and Supply Macroeconomics Study Guide Macroeconomics is split into 5 main units. Price rises but costs do not change. Consumer demand is central to IB Economics and microeconomics.
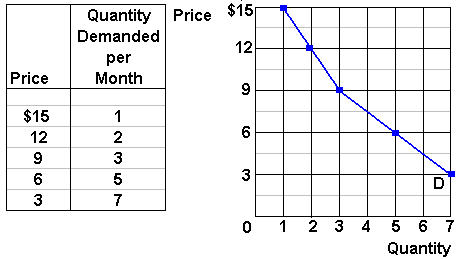 Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
As the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. Aggregate demand and Aggregate Supply. Microeconomics 11 Competitive Markets. IB Economics Revision video about the basics of the laws of demand and supplyThank you for watchingIf there is any topic that you would be interested in u. Finally the business cycle which is a recurring pattern of.
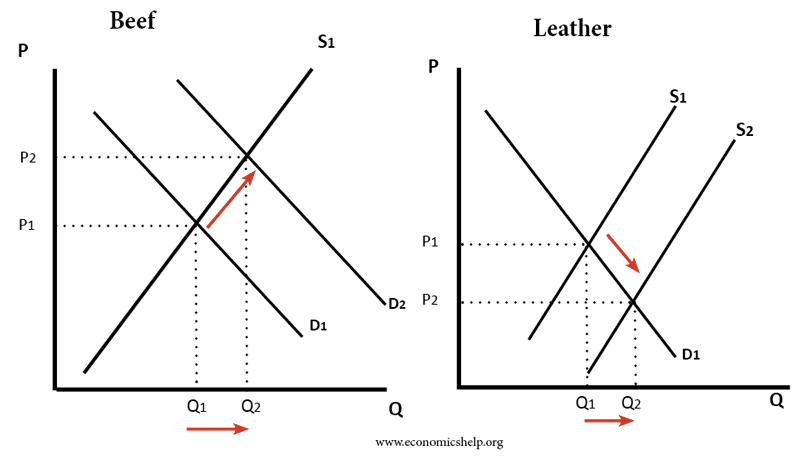 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Consumer demand is central to IB Economics and microeconomics. The market demand gives the total quantity demanded by all consumers. Supply The law of supply. Demand and supply Market. Means of production are privately held by individuals and firms.
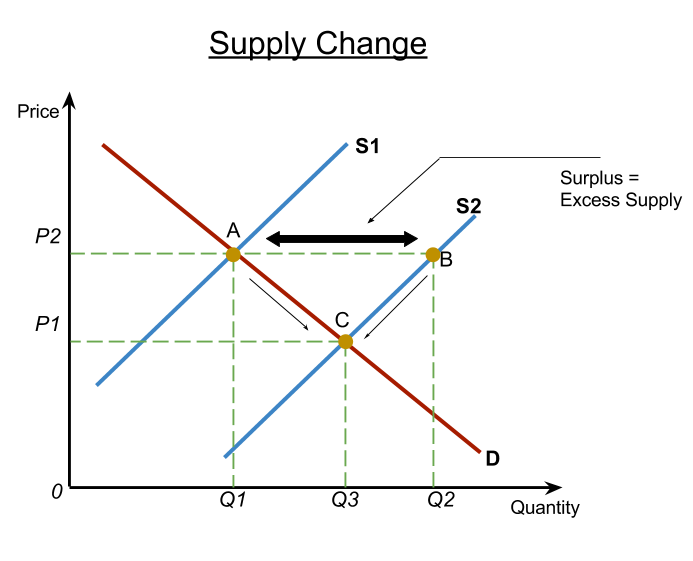 Source: adarshibeconomics.blogspot.com
Source: adarshibeconomics.blogspot.com
The state determines how much to produce howhow many to produce and for whom to produce. Consumer demand is central to IB Economics and microeconomics. Demand and supply Market. Unit 91 - Aggregate Demand. The willingness and ability of the consumer to consume a good or service in a given amount of time.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Free market economy market economy An economy where there is minimal government intervention. A demand schedule is determined and from this a demand curve is modeled. Is the means for allocating resources through supply and demand in a market arriving at an equilibrium price. We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself. The law of demand is explained to explain how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product.
 Source: ar.pinterest.com
Source: ar.pinterest.com
Aggregate demand consists of Consumption C Investment I Government spending G Exports X and Imports M AD C I G X M Definition. Instead determinants include income levels the popularity of the product and the availability and popularity price of available substitutes and. Aggregate demand consists of Consumption C Investment I Government spending G Exports X and Imports M AD C I G X M Definition. Level of Economic Activity ADAS Macroeconomic Objectives Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy and Supply-Side Policies. We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Planned economy command economy Means of production are owned by the state. Aggregate demand consists of Consumption C Investment I Government spending G Exports X and Imports M AD C I G X M Definition. Price rises but costs do not change. Prices act as a signal to firms and consumer to adjust their economic behaviour. The law of demand is explained to explain how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself. Providing clear and inviting instruction and guidance this Companion will support students through their IB Economics course. Demand and supply determine what how and for whom in production. Construct an Aggregate Demand curve. Demand and supply determine how much to produce howhow many to produce and for whom to produce.
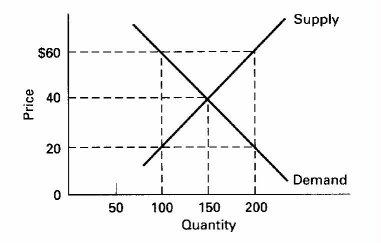 Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
The law of demand explains how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. Demand and supply determine how much to produce howhow many to produce and for whom to produce. A demand schedule is determined and from this a demand curve is. Means of production are privately held by individuals and firms. Level of Economic Activity ADAS Macroeconomic Objectives Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy and Supply-Side Policies.
 Source: adarshibeconomics.blogspot.com
Source: adarshibeconomics.blogspot.com
Aggregate demand and Aggregate Supply. Is the total amount of goods and services that producers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period. Aggregate demand In microeconomics demand only represents the demand for one product or service in a particular market whereas aggregate demand in macroeconomics is the total demand for goods and services in a period of time at a given price level. Demand and supply Market. Demand and supply determine what how and for whom in production.
 Source: markedbyteachers.com
Source: markedbyteachers.com
Demand and supply Market. This section of the IB Economics course examines economic activity by modeling the the circular flow model before turning attention to how economys total output and income can be measured. Demand and supply determine what how and for whom in production. Providing clear and inviting instruction and guidance this Companion will support students through their IB Economics course. The use of P and Q on the axes is sufficient for a demand and supply diagram.
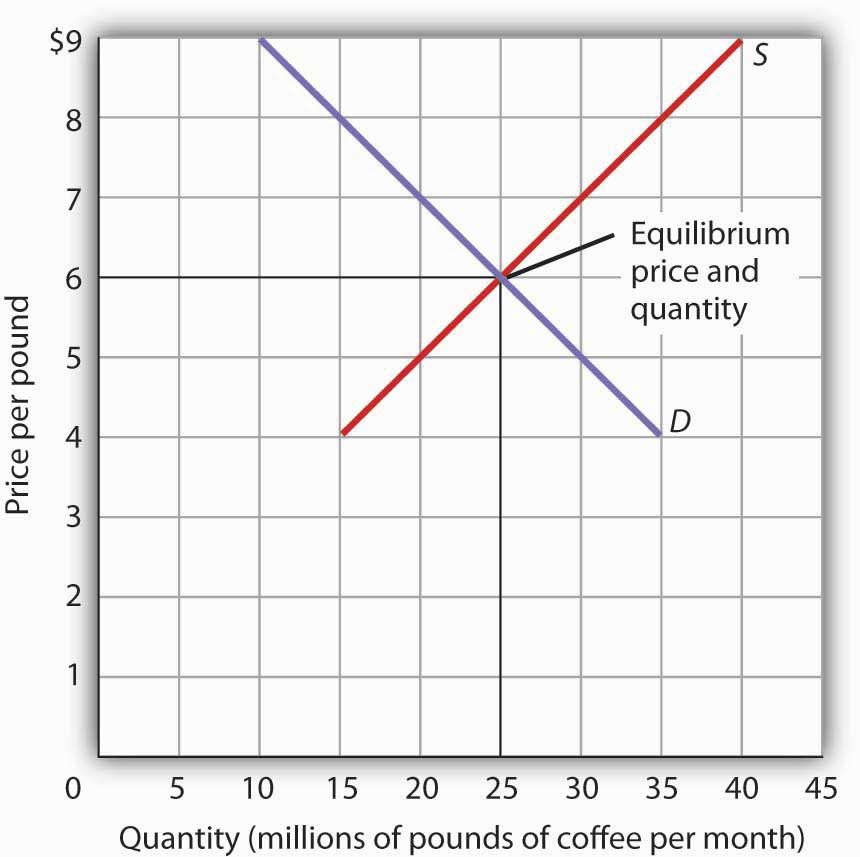 Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Planned economy command economy Means of production are owned by the state. Describe consumption investment government spending net exports as components of Aggregate Demand. Aggregate demand In microeconomics demand only represents the demand for one product or service in a particular market whereas aggregate demand in macroeconomics is the total demand for goods and services in a period of time at a given price level. Price rises but costs do not change. Supply The law of supply.
 Source: markedbyteachers.com
Source: markedbyteachers.com
Growth in output and income are considered. Free market economy market economy An economy where there is minimal government intervention. Planned economy command economy Means of production are owned by the state. IB Economics notes and questions helpful. An organization or arrangement through which goods and services are exchanged – do not have to physically meet – markets can be local bikes in Eugene national cars in China or.
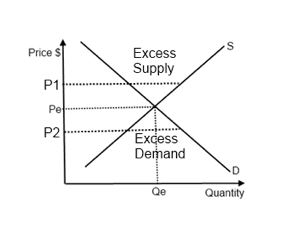 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
Tariff causes the world supply curve to shift upwards or the tariff causes the price to rise creating government revenue 1 with the amount referenced to the diagram 2. IB Points to Understand for both SL and HL unless otherwise noted Price elasticity of demand and its determinants. This section of the IB Economics course examines economic activity by modeling the the circular flow model before turning attention to how economys total output and income can be measured. Level of Economic Activity ADAS Macroeconomic Objectives Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy and Supply-Side Policies. We start with an introduction to competitive markets before moving on to the concept of demand itself.
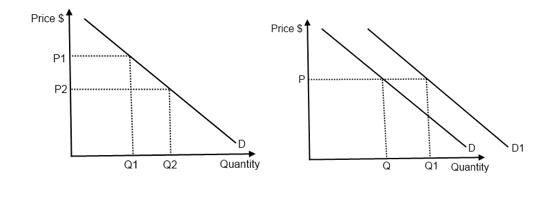 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
Consumer demand is central to IB Economics and microeconomics. IB Economics Revision video about the basics of the laws of demand and supplyThank you for watchingIf there is any topic that you would be interested in u. Microeconomics 11 Competitive Markets. The willingness and ability of the consumer to consume a good or service in a given amount of time. Construct an Aggregate Demand curve.
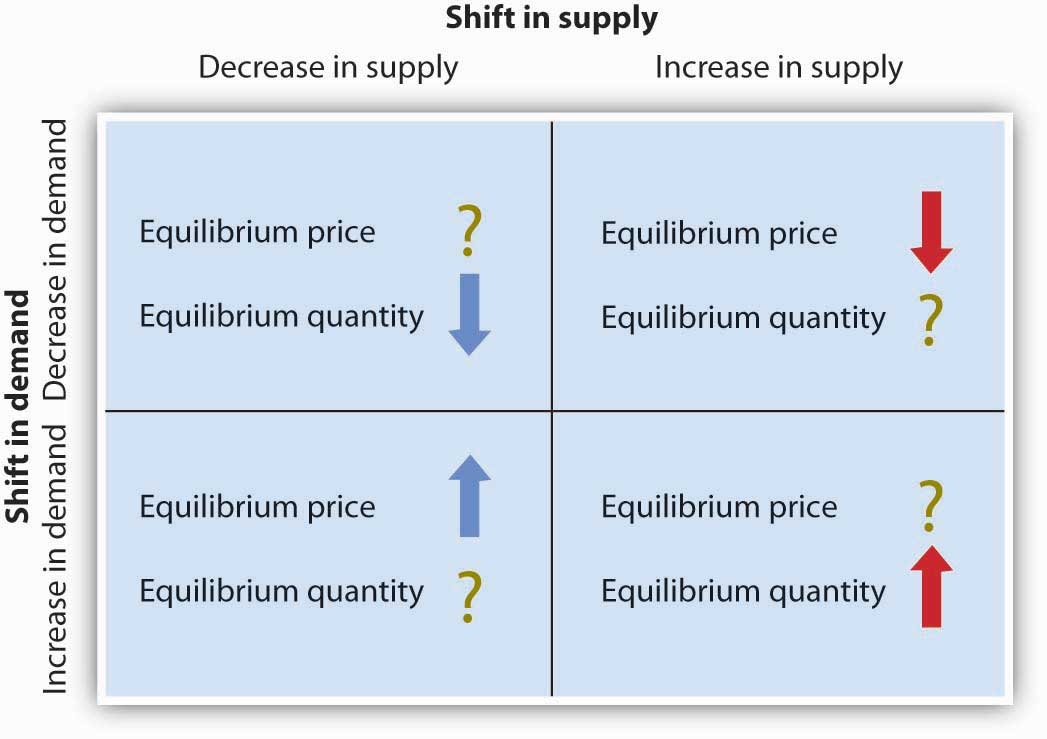 Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
The law of demand explains how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. Finally the business cycle which is a recurring pattern of. The state determines how much to produce howhow many to produce and for whom to produce. Prices act as a signal to firms and consumer to adjust their economic behaviour. Planned economy command economy an economy where the means of production are collectively owned except labour.
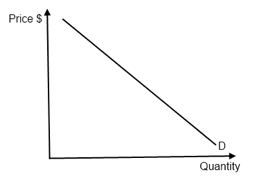 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
Construct an Aggregate Demand curve. Level of Economic Activity ADAS Macroeconomic Objectives Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy and Supply-Side Policies. Providing clear and inviting instruction and guidance this Companion will support students through their IB Economics course. Price rises but costs do not change. Unit 91 - Aggregate Demand.
 Source: cz.pinterest.com
Source: cz.pinterest.com
The market demand gives the total quantity demanded by all consumers. Aggregate demand is the total demand for goods and services in an economy at different price levels. Planned economy command economy Means of production are owned by the state. Is the total amount of goods and services that producers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period. Explain why the AD curve is negative sloping.
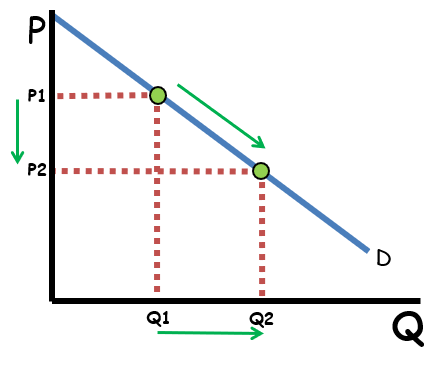 Source: reviewecon.com
Source: reviewecon.com
The law of demand explains how consumers behave in relation to price changes of a product. Describe consumption investment government spending net exports as components of Aggregate Demand. Construct an Aggregate Demand curve. Explain why the AD curve is negative sloping. Unit 91 - Aggregate Demand.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title ib economics definition demand and supply by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






