Your How to figure out cross elasticity images are available in this site. How to figure out cross elasticity are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the How to figure out cross elasticity files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for how to figure out cross elasticity images information connected with to the how to figure out cross elasticity keyword, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
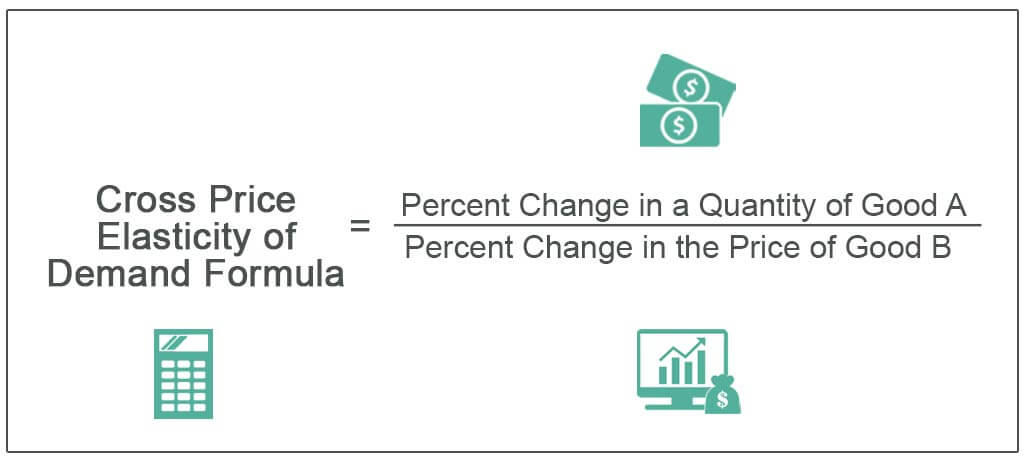
How To Figure Out Cross Elasticity. Cross-price elasticity is a ratio that represents the rate of change between. Were going from one good to another. Given Q 0X 4000 bottles Q 1X 3000 bottles P 0Y 350 and P 1Y 250 Therefore the cross price elasticity of demand. The percent change in the price of widgets is the same as above or -286.
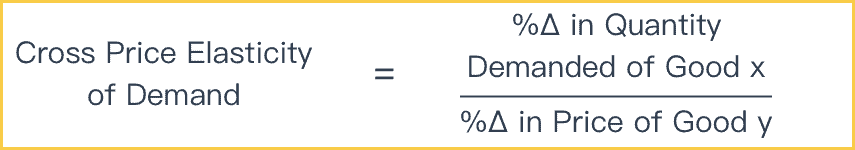 Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Intelligent Economist From intelligenteconomist.com
Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Intelligent Economist From intelligenteconomist.com
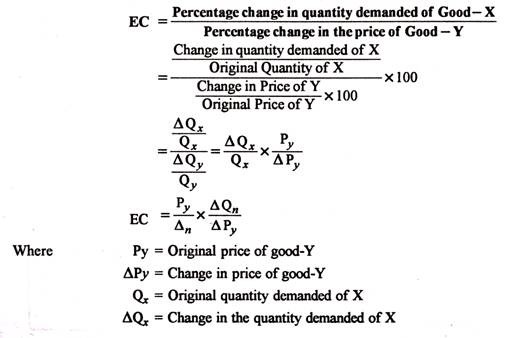
ΔQd x Δ Q x d the percentage change in quantity demanded. CPE cookies ΔQΔP cookies P cookies Q We know from our regression that ΔQΔP cookies is the coefficient of Price of Cookies -871. And so you do the math. Assume that the quantity demanded for detergent cakes has increased from 500 units to 600 units with an increase in the price of detergent powder from 150 to 200. Given Q 0X 4000 bottles Q 1X 3000 bottles P 0Y 350 and P 1Y 250 Therefore the cross price elasticity of demand. To calculate Cross Price Elasticity of Demand we are essentially looking for how the price of cookies impacts the sales of eggs.
So you have a very high cross elasticity of demand.
So we use the formula. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and substitutes into the other input buying more of it. You can calculate the cross elasticity demand by taking the percentage change in quantity demanded of the one good and then dividing it by the percentage change in the price of the other good and if the number that you get is positive then that means that the two goods are substitutes and if the number you get is negative then it means that the two goods are. Thus we calculate elasticity using. Given Q 0X 4000 bottles Q 1X 3000 bottles P 0Y 350 and P 1Y 250 Therefore the cross price elasticity of demand. Includes the calculation of percent change.
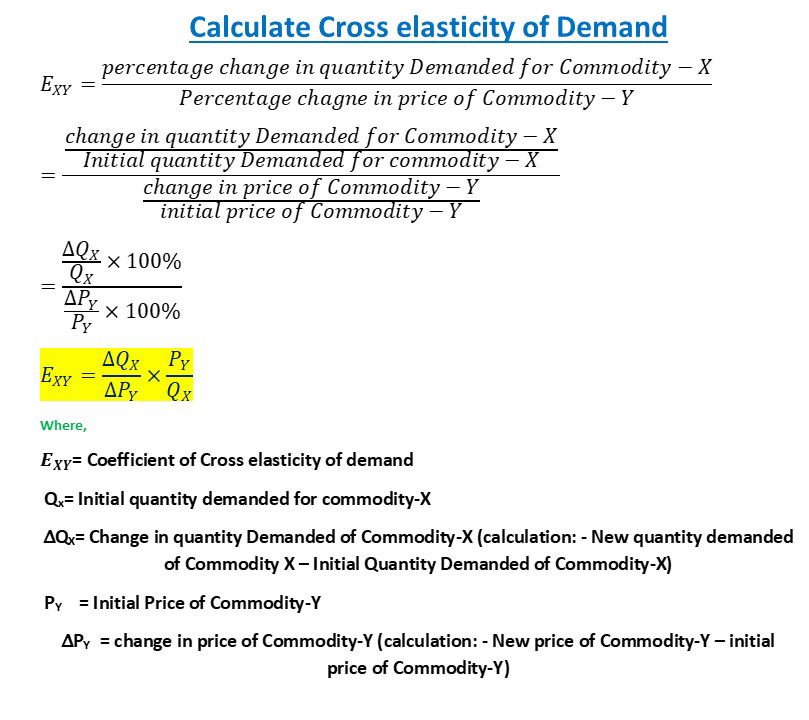 Source: ezilearning.com
Source: ezilearning.com
For cross-price elasticity this means. The percent change in the price of widgets is the same as above or -286. Calculate the cross elasticity of demand between two products. Ed px ΔQd x ΔP x E p x d Δ Q x d Δ P x. CPE cookies ΔQΔP cookies P cookies Q We know from our regression that ΔQΔP cookies is the coefficient of Price of Cookies -871.
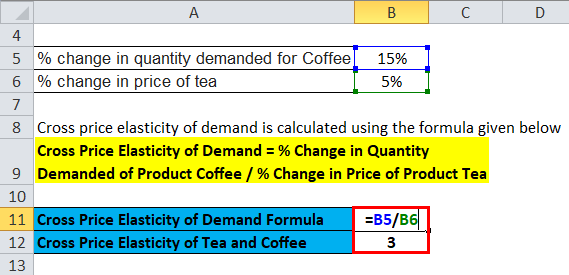 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
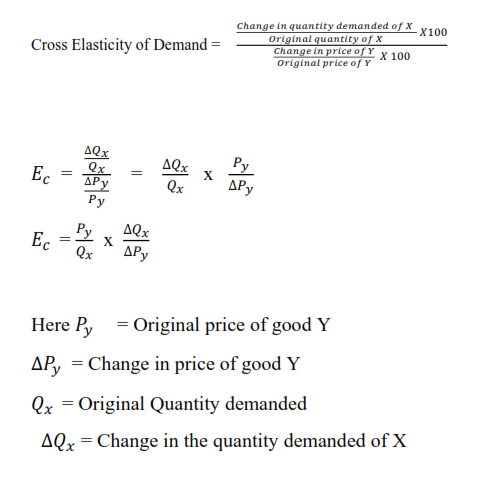
The percent change in the price of widgets is the same as above or -286. CPE cookies ΔQΔP cookies P cookies Q We know from our regression that ΔQΔP cookies is the coefficient of Price of Cookies -871. Cross Price Elasticity Formulaoriginal new price of product A original new quantity of product B change in quantitychange in price. Let us understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand with the help of an example. Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand in the case.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Ed px ΔQd x ΔP x E p x d Δ Q x d Δ P x. Let us understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand with the help of an example. Also called cross-price elasticity of demand this measurement is calculated by taking the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good and dividing it by the percentage change in the. Were going from one good to another. We identified it from well-behaved source.
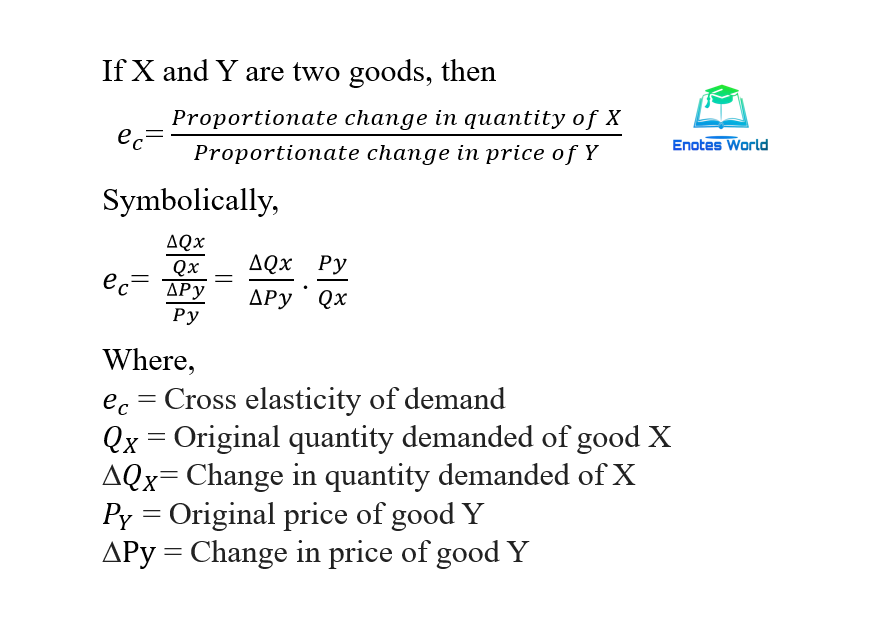 Source: enotesworld.com
Source: enotesworld.com
A complement will have a negative cross-price elasticity since if the change in price is positive the change in quantity will be negative and vice-versa. So if you have 67 divided by 5 you get to roughly 134. η p1 Q 1 P 2 Cross-Price elasticity. If negative – then this means the two inputs are complements. You can calculate the cross elasticity demand by taking the percentage change in quantity demanded of the one good and then dividing it by the percentage change in the price of the other good and if the number that you get is positive then that means that the two goods are substitutes and if the number you get is negative then it means that the two goods are.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
η p1 Q 1 P 2 Where P2 is the price of the substitute good. If negative – then this means the two inputs are complements. Let us understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand with the help of an example. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and substitutes into the other input buying more of it. So lets just say for simplicity roughly 5.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
And so you do the math. Its submitted by dispensation in the best field. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and substitutes into the other input buying more of it. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and also buys less of the other input. And so you do the math.
 Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Source: wallstreetmojo.com
A complement will have a negative cross-price elasticity since if the change in price is positive the change in quantity will be negative and vice-versa. Also called cross-price elasticity of demand this measurement is calculated by taking the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good and dividing it by the percentage change in the. Its submitted by dispensation in the best field. That is the case in our demand equation of Q 3000 - 4P 5ln P. Cross-price elasticity of demand dQ dP PQ In order to use this equation we must have quantity alone on the left-hand side and the right-hand side be some function of the other firms price.

Includes the calculation of percent change. Also called cross-price elasticity of demand this measurement is calculated by taking the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good and dividing it by the percentage change in the. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and substitutes into the other input buying more of it. η p1 Q 1 P 2 Where P2 is the price of the substitute good. For cross-price elasticity this means.
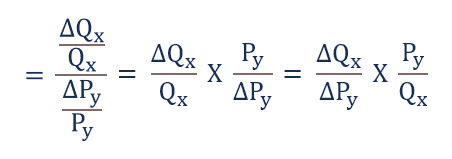 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Ed px ΔQd x ΔP x E p x d Δ Q x d Δ P x. Thats why we call it cross elasticity. Were going from one good to another. We use the standard economics formula for calculating cross elasticity of demand relative to price. Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand 105 percent 286 percent 037 Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand 105 percent 286 percent 037.
 Source: simplynotes.in
Source: simplynotes.in
Let us understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand with the help of an example. If the price of a complement rises our demand will fall if the price of a substitute rises our demand will rise. Cross-price elasticity of demand dQ dP PQ In order to use this equation we must have quantity alone on the left-hand side and the right-hand side be some function of the other firms price. Because the cross-price elasticity is negative we can conclude that widgets and sprockets are complementary. Also called cross-price elasticity of demand this measurement is calculated by taking the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good and dividing it by the percentage change in the.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
To calculate Cross Price Elasticity of Demand we are essentially looking for how the price of cookies impacts the sales of eggs. Because the cross-price elasticity is negative we can conclude that widgets and sprockets are complementary. So this is approximately 134. η p1 Q 1 P 2 Cross-Price elasticity. CPE cookies ΔQΔP cookies P cookies Q We know from our regression that ΔQΔP cookies is the coefficient of Price of Cookies -871.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
So if you have 67 divided by 5 you get to roughly 134. Let us understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand with the help of an example. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and substitutes into the other input buying more of it. If the price of a complement rises our demand will fall if the price of a substitute rises our demand will rise. Thus we differentiate with respect to P and get.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
If negative – then this means the two inputs are complements. So if you have 67 divided by 5 you get to roughly 134. So this is approximately 134. If the price of a complement rises our demand will fall if the price of a substitute rises our demand will rise. Thats why we call it cross elasticity.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
That is the case in our demand equation of Q 3000 - 4P 5ln P. Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand in the case. ΔQd x Δ Q x d the percentage change in quantity demanded. Cross price elasticity XED change in demand of product A change of price of product B where products A and B are different offerings. A complement will have a negative cross-price elasticity since if the change in price is positive the change in quantity will be negative and vice-versa.
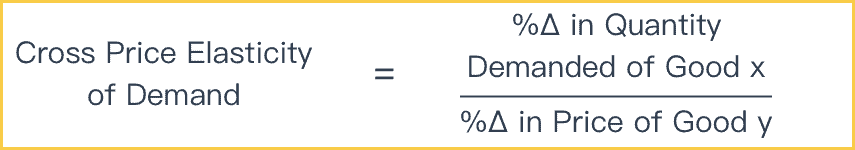 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Ed px ΔQd x ΔP x E p x d Δ Q x d Δ P x. So this is approximately 134. For cross-price elasticity this means. So you have a very high cross elasticity of demand. CPE cookies ΔQΔP cookies P cookies Q We know from our regression that ΔQΔP cookies is the coefficient of Price of Cookies -871.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
So if you have 67 divided by 5 you get to roughly 134. ΔP x Δ P x the percentage change in price. So lets just say for simplicity roughly 5. Price elasticity is measured in percentage changes in each of the variables. Cross-price elasticity is a ratio that represents the rate of change between.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
CPE cookies ΔQΔP cookies P cookies Q We know from our regression that ΔQΔP cookies is the coefficient of Price of Cookies -871. We use the standard economics formula for calculating cross elasticity of demand relative to price. Thats why we call it cross elasticity. ΔP x Δ P x the percentage change in price. So lets just say for simplicity roughly 5.
 Source: enotesworld.com
Source: enotesworld.com
To calculate Cross Price Elasticity of Demand we are essentially looking for how the price of cookies impacts the sales of eggs. Thus we differentiate with respect to P and get. ΔP x Δ P x the percentage change in price. If the pricewage of one increases the firm buys less of it and also buys less of the other input. That is the case in our demand equation of Q 3000 - 4P 5ln P.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title how to figure out cross elasticity by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






