Your How does tax affect supply and demand images are ready in this website. How does tax affect supply and demand are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the How does tax affect supply and demand files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for how does tax affect supply and demand pictures information related to the how does tax affect supply and demand topic, you have come to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
How Does Tax Affect Supply And Demand. Any tax on a business will affect its supply. This video goes over some brief examples showing how a tax on sellers and then a tax on consumers will affect the efficient equilibrium in a supply and deman. The tax paid by the. This is why it really doesnt matter who pays the tax workers or firms because the end result will be the same.
 The Impact Of Subsidies From sanandres.esc.edu.ar
The Impact Of Subsidies From sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. This would then cause an outward shift of aggregate demand ADCIGX-M. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Industry output would be n 0 q 2. This would have the same result as a tax on suppliers resulting in hire wages paid but lower wages received. 2136 if price rises from P 0 to P 2 each of the firms would be eager to produce q 2 units instead of q 0.
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.
In the graph above the total tax paid by the producer and the consumer is equal to P 0 P 2. In this case the tax will primarily affect the amount of supply leading to increased sales costs and reduced supply at any level and also transmission of the supply curve to t he left and up and. Now we should express the price P without taxation through the new price level P_1 when the. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. Industry output would be n 0 q 2. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. In the case of an indirect tax we need to modify our function of supply since the tax is collected from the sellers the demand function will not change. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. In the graph above the total tax paid by the producer and the consumer is equal to P 0 P 2. Taxes increase the costs of producing and selling items which the business may pass on to the consumer in the form of higher prices.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. If you want help developing the intuition–or see some examples– of how taxes affect the supply and demand of goods and services potentially the labor. Those factors influence employment and household income which then impact consumer spending and investment. In this case the tax will primarily affect the amount of supply leading to increased sales costs and reduced supply at any level and also transmission of the supply curve to t he left and up and. If price rises by more than the amount of the tax there will be excess supply.
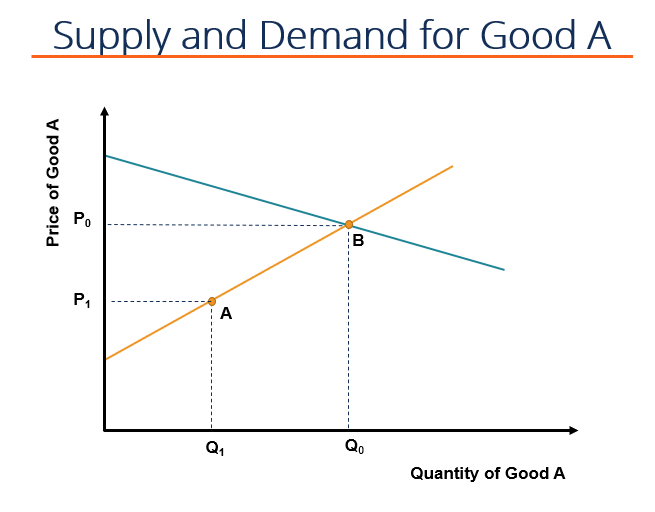 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
A fall in corporation tax will increase the post-tax profits of businesses In theory this will increase funds available to fund capital investment eg. When demand happens to be price inelastic and supply is price elastic the majority of the tax burden falls upon the consumer. Does taxes increase aggregate demand. In this case the tax will primarily affect the amount of supply leading to increased sales costs and reduced supply at any level and also transmission of the supply curve to t he left and up and. This would then cause an outward shift of aggregate demand ADCIGX-M.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The relative effect on buyers and sellers is known as the incidence of the tax. In the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply a tax rate increase will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in aggregate expenditures induced by. Fiscal policy affects aggregate demand through changes in government spending and taxation. The effect of the tax cut on the short-run aggregate supply SRAS curve depends on which model you use. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic.

In this case the tax will primarily affect the amount of supply leading to increased sales costs and reduced supply at any level and also transmission of the supply curve to t he left and up and. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. In the graph above the total tax paid by the producer and the consumer is equal to P 0 P 2.

In some cases a tax may cause a decrease in demand of products consumed primarily by individual consumers and an increase in demand of products consumed primarily by firms or government. If price rises by more than the amount of the tax there will be excess supply. Does taxes increase aggregate demand. In some cases a government may impose a tax on a certain goodsuch as tobacco or alcoholwith the specific intention of reducing the quantity that is consumed. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic.
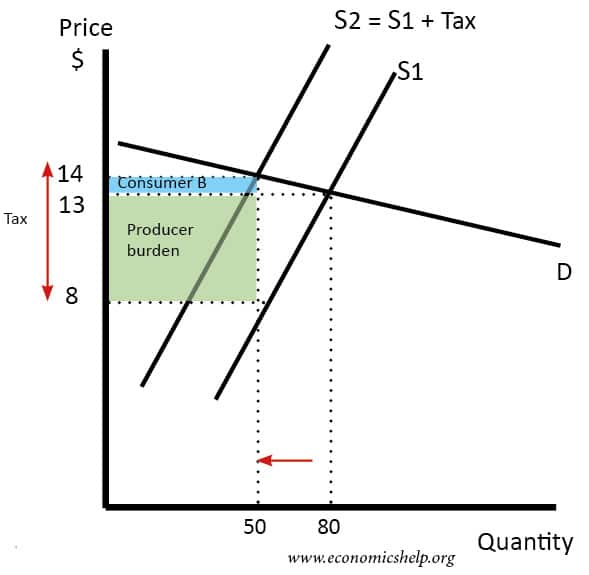 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. A fall in corporation tax will increase the post-tax profits of businesses In theory this will increase funds available to fund capital investment eg. In this case the tax will primarily affect the amount of supply leading to increased sales costs and reduced supply at any level and also transmission of the supply curve to t he left and up and. If price rises by more than the amount of the tax there will be excess supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The tax paid by the. In some cases a government may impose a tax on a certain goodsuch as tobacco or alcoholwith the specific intention of reducing the quantity that is consumed. In new plant factories and technologies. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic. A fall in corporation tax will increase the post-tax profits of businesses In theory this will increase funds available to fund capital investment eg.
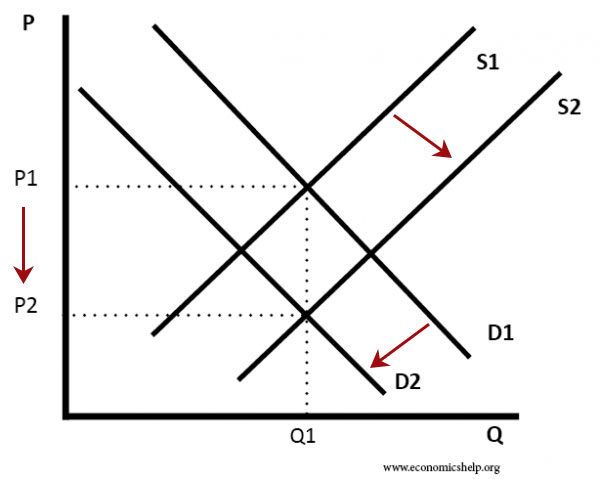 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The tax paid by the. Some of these factors for loanable funds include the same factors that affect demand or supply generally including technology improvements shift in consumer tastes substitution possibilities changes in income of consumers taxes etc. Now we should express the price P without taxation through the new price level P_1 when the. If you want help developing the intuition–or see some examples– of how taxes affect the supply and demand of goods and services potentially the labor. Does taxes increase aggregate demand.
 Source: acqnotes.com
Source: acqnotes.com
Does taxes increase aggregate demand. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in. If price rises by more than the amount of the tax there will be excess supply. If you want help developing the intuition–or see some examples– of how taxes affect the supply and demand of goods and services potentially the labor. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. In some cases a government may impose a tax on a certain goodsuch as tobacco or alcoholwith the specific intention of reducing the quantity that is consumed. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. The relative effect on buyers and sellers is known as the incidence of the tax.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
In order to get them to produce it all youre going to have to pay at least 2 but then if the suppliers or producers are getting 2 the consumers are going to have to pay a dollar more for the tax. If the supply curve is relatively flat the supply is price elastic. The effect of the tax cut on the short-run aggregate supply SRAS curve depends on which model you use. Tax increases do not affect the demand curve nor do they increase supply or demand more or less. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic.

In some cases a tax may cause a decrease in demand of products consumed primarily by individual consumers and an increase in demand of products consumed primarily by firms or government. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic. 2136 if price rises from P 0 to P 2 each of the firms would be eager to produce q 2 units instead of q 0. Some of these factors for loanable funds include the same factors that affect demand or supply generally including technology improvements shift in consumer tastes substitution possibilities changes in income of consumers taxes etc. Does taxes increase aggregate demand.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in. Some of these factors for loanable funds include the same factors that affect demand or supply generally including technology improvements shift in consumer tastes substitution possibilities changes in income of consumers taxes etc.
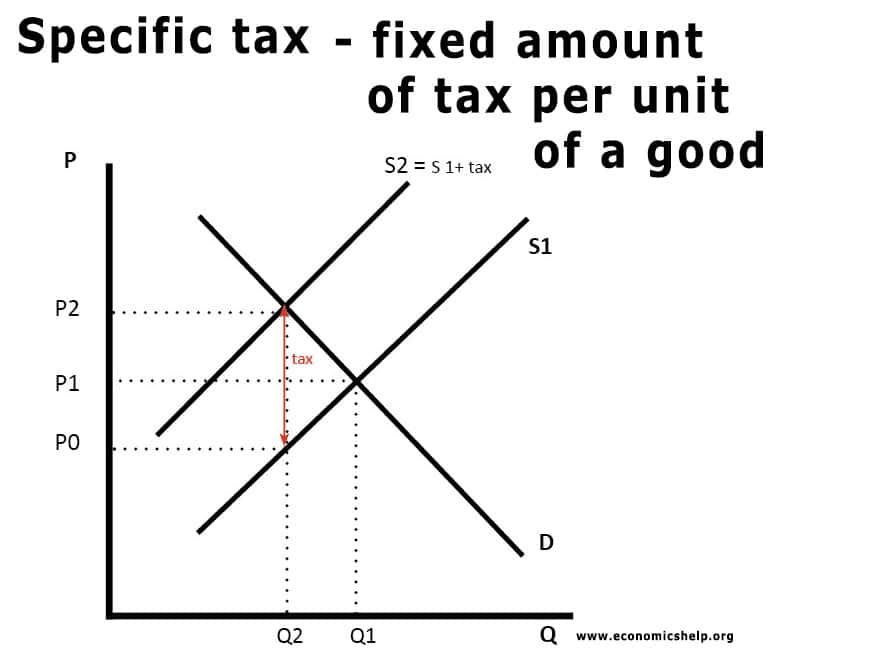 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. 2136 if price rises from P 0 to P 2 each of the firms would be eager to produce q 2 units instead of q 0. In new plant factories and technologies. This would have the same result as a tax on suppliers resulting in hire wages paid but lower wages received. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.
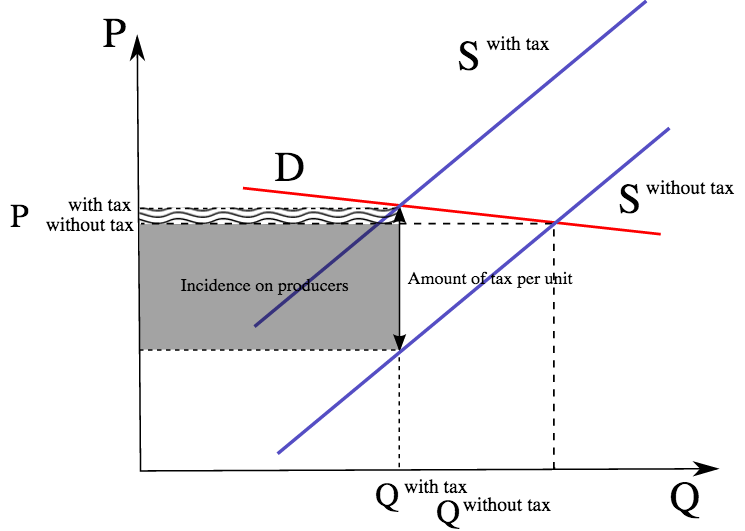
In the graph above the total tax paid by the producer and the consumer is equal to P 0 P 2. If a demand curve is relatively steep the demand is price inelastic. In order to get them to produce it all youre going to have to pay at least 2 but then if the suppliers or producers are getting 2 the consumers are going to have to pay a dollar more for the tax. In new plant factories and technologies. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. How do taxes affect a supply curve. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Taxation shifts a supply curve to the left.
 Source: id.pinterest.com
Source: id.pinterest.com
If price rises by more than the amount of the tax there will be excess supply. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. When demand happens to be price inelastic and supply is price elastic the majority of the tax burden falls upon the consumer. In order to get them to produce it all youre going to have to pay at least 2 but then if the suppliers or producers are getting 2 the consumers are going to have to pay a dollar more for the tax. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how does tax affect supply and demand by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






