Your Graph showing demand and supply decreasing images are available. Graph showing demand and supply decreasing are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Graph showing demand and supply decreasing files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for graph showing demand and supply decreasing images information linked to the graph showing demand and supply decreasing interest, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
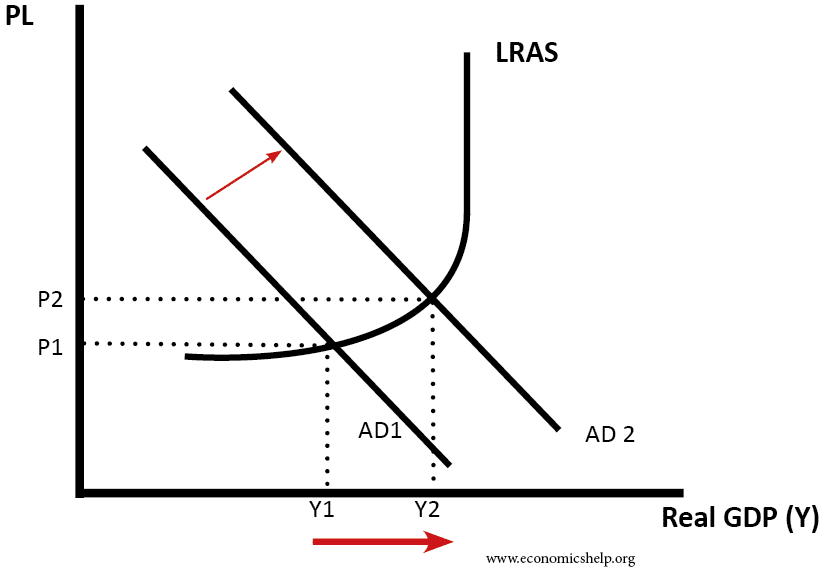
Graph Showing Demand And Supply Decreasing. Demand increases greater than a supply decrease. Let us first consider a rise in demand as in Fig. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. In this diagram the supply curve shifts to the left.
 Equilibrium And Its Adjustment Economics Notes Study Materials Ma Economics From pinterest.com
Equilibrium And Its Adjustment Economics Notes Study Materials Ma Economics From pinterest.com
A Rise in Demand. Demand decreased equal to a supply decrease. The original demand curve is D and the supply is S. In Graph 2 supply decreases thus causing an increase in price and a decrease in quantity. From Graph 1 you can see that an increase in supply will cause the price to decline and the quantity to rise. Let us first consider a rise in demand as in Fig.
Note in the graphs on the next page show that if the supply curve shifts upward a smaller quantity will be supplied at any given price.
Demand is not affected by Change in Price of Unrelated Goods. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3. When the magnitudes of the decrease in both demand and supply are equal it leads to a proportionate shift of both the demand and supply curve. We may now consider a change in the conditions of demand such as a rise in the income of buyers. 49 rows The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each. Shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
37 demand for the commodity is OQ at a price of OP. View the full answer. Decrease in Demand is shown by leftward shift in demand curve from DD to D 2 D 2. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same but there is a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. Demand is not affected by Change in Price of Unrelated Goods.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In Graph 2 supply decreases thus causing an increase in price and a decrease in quantity. An extension on the demand curve is due to lower price leading to higher demand. Show graphically and explain the change in equilibrium price and quantity. 49 rows The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Demand decreased equal to a supply decrease. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3. Demand falls from OQ to OQ 2 due to unfavourable change in other factors at the same price OP. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same but there is a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. Shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A decrease in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price illustrated by a leftward shift of the supply curve. Prices too far below 500 can increase demand and lead to a product shortage. A Demand Curve for Gasoline. D P or we can draw it graphically as in Figure 22. Graph demand and supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This decrease in demand is shown by a leftward shift in the demand curve and a movement along the supply curve which creates a surplus in first-class mail at the original price shown as P2. In Graph 2 supply decreases thus causing an increase in price and a decrease in quantity. An extension on the demand curve is due to lower price leading to higher demand. Long-run aggregate supply curve. A Demand Curve is a diagrammatic illustration reflecting the price of a product or service and its quantity in demand in the market over a given period.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Graph 3 shows an increase in demand resulting in both a higher price and a higher quantity. A curve that shows the relationship in. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3. Here is the supply and demand graph showing a demand decrease. Show graphically and explain the change in equilibrium price and quantity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We may now consider a change in the conditions of demand such as a rise in the income of buyers. The original demand curve is D and the supply is S. This decrease in demand is shown by a leftward shift in the demand curve and a movement along the supply curve which creates a surplus in first-class mail at the original price shown as P2. These points are then graphed and the line connecting them is the demand curve D. Demand increases greater than a supply decrease.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Supply increases more than a demand decrease. A Rise in Demand. We may now consider a change in the conditions of demand such as a rise in the income of buyers. Here is the supply and demand graph showing a demand decrease. The downward slope of the demand curve again illustrates the law of demandthe inverse relationship between prices and quantity demanded.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The downward slope of the demand curve again illustrates the law of demandthe inverse relationship between prices and quantity demanded. 49 rows The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each. 37 demand for the commodity is OQ at a price of OP. For example all three panels of Figure 311 Simultaneous Decreases in Demand and Supply show a decrease in demand for coffee caused perhaps by a decrease in the price of a substitute good such as tea and a simultaneous decrease in the supply of coffee caused perhaps by bad weather. Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
37 demand for the commodity is OQ at a price of OP. Long-run aggregate supply curve. These points are then graphed and the line connecting them is the demand curve D. Decrease in Demand is shown by leftward shift in demand curve from DD to D 2 D 2. The decrease in demand decrease in supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
When the magnitudes of the decrease in both demand and supply are equal it leads to a proportionate shift of both demand and supply curve. Demand is not affected by Change in Price of Unrelated Goods. The demand schedule shows that as price rises quantity demanded decreases and vice versa. A decrease in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price illustrated by a leftward shift of the supply curve. 37 demand for the commodity is OQ at a price of OP.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Demand decreased equal to a supply decrease. A curve that shows the relationship in. Here DD is the original demand curve SS is the original supply curve D1D1 is the new demand curve when demand decreases. A decrease in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price illustrated by a leftward shift of the supply curve. An extension on the demand curve is due to lower price leading to higher demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. A Demand Curve is a diagrammatic illustration reflecting the price of a product or service and its quantity in demand in the market over a given period. Demand decreased equal to a supply decrease. For example all three panels of Figure 319 Simultaneous Decreases in Demand and Supply show a decrease in demand for coffee caused perhaps by a decrease in the price of a substitute good such as tea and a simultaneous decrease in the supply of coffee caused perhaps by bad weather. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A decrease in supply is caused by a change in a supply determinant and results in a decrease in equilibrium quantity and an increase in equilibrium price. When the magnitudes of the decrease in both demand and supply are equal it leads to a proportionate shift of both the demand and supply curve. Graph 3 shows an increase in demand resulting in both a higher price and a higher quantity. The demand schedule shows that as price rises quantity demanded decreases and vice versa. 49 rows The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Demand increases greater than a supply decrease. You must also however realize that when costs of production rise we can also speak of a decrease in supply. This decrease in demand is shown by a leftward shift in the demand curve and a movement along the supply curve which creates a surplus in first-class mail at the original price shown as P2. Graph demand and supply. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
311 are not demand curves as they show the relationship between demand for the given commodity and price of a related good. Show graphically and explain the change in equilibrium price and quantity. You must also however realize that when costs of production rise we can also speak of a decrease in supply. View the full answer. Note that the demand curve in that figure labeled.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We can write this relationship between quantity demanded and price as an equation. This can be confusing at first since the supply curve shifts upward on the graph. Business Economics QA Library Graph demand and supply. Note that the demand curve in that figure labeled. Supply increases more than a demand decrease.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the. The demand schedule shows that as price rises quantity demanded decreases and vice versa. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3. It must be noted that a demand curve shows the relationship between the quantity demanded of a given commodity and its price. Graph demand and supply.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title graph showing demand and supply decreasing by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.