Your Exponential function mean value theorem images are available. Exponential function mean value theorem are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Exponential function mean value theorem files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for exponential function mean value theorem images information related to the exponential function mean value theorem keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site always provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Exponential Function Mean Value Theorem. Since f is differentiable on the interior it has to be a point where fc0. Use this information to guess a value for the instantaneous velocity of particle at 1202pm. The function is a sum of a polynomial and an exponential function both of which are continuous and differentiable everywhere. A x 1 x 2 b.
 Mean Value Theorem Example Square Root Function Video Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Mean Value Theorem Example Square Root Function Video Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Next because f x f x is a polynomial it is continuous and differentiable everywhere and so we could use Rolles Theorem to see that there must be a real value c c so that f c 0 f c 0. Sketch pictures to illustrate why the Mean Value Theorem is true. We compute f b f a b a e 3 e 2. It is one of the most important results in real analysis. 0 t 1 h. The x -value of this point is the c in the MVT.
Understand how Rolles theorem relates to the mean value theorem understand the mean value theorem and when its conditions are satisfied find points in an interval that satisfy the mean value theorem for a given function.
We look for c. Next because f x f x is a polynomial it is continuous and differentiable everywhere and so we could use Rolles Theorem to see that there must be a real value c c so that f c 0 f c 0. FxF0F0over 1x cdotsFn-10over n-1xn-1 Fn c_nover n xn. Assuming that the position function. Limits of Piece-wise Functions The Squeeze Theorem Continuity and the Intermediate Value Theorem Definition of continuity Continuity and piece-wise functions Continuity properties Types of discontinuities The Intermediate Value Theorem Summary of using continuity to evaluate limits Limits at Infinity Limits at infinity and horizontal asymptotes. Since f x exists everywhere in a b we know the f is both continuous and differentiable.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
Understand the statement of the Mean Value Theorem. The Exponential Function e x Taking our definition of e as the infinite n limit of 1 1 n n it is clear that e x is the infinite n limit of 1 1 n n x. S t s t is differentiable we can apply the Mean Value Theorem to conclude that at some time. We compute f b f a b a e 3 e 2. Let pt denote the distance in meters to the right of the origin of a particle at time tminutes after noon.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
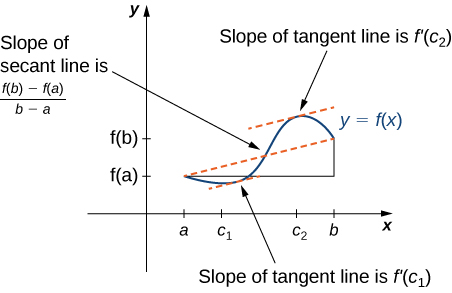
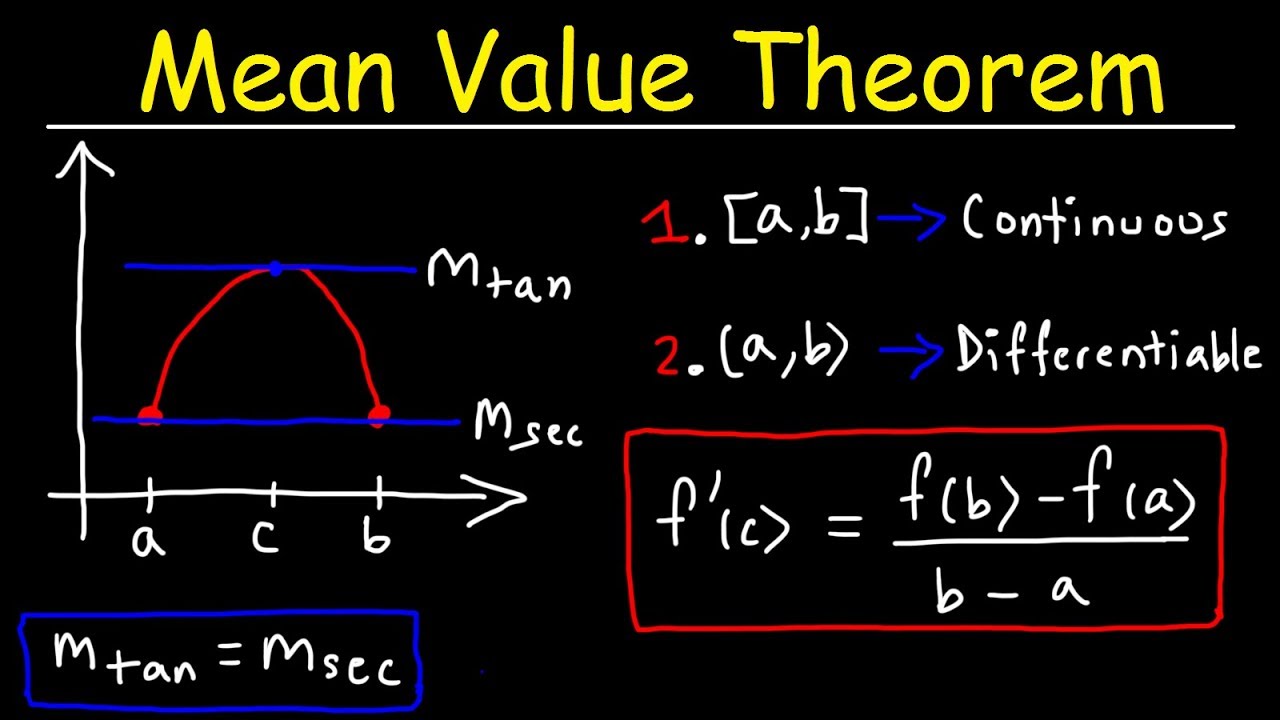
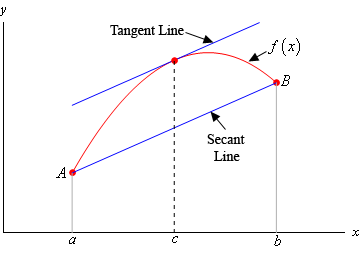
We look for c. Mean Value Theorem Suppose that f f has a derivative on the interval ab a b and is continuous on the interval ab a b. Like we did in the previous proof we can pick any x 1 x 2 a b such that x 1 x 2. Limits of Piece-wise Functions The Squeeze Theorem Continuity and the Intermediate Value Theorem Definition of continuity Continuity and piece-wise functions Continuity properties Types of discontinuities The Intermediate Value Theorem Summary of using continuity to evaluate limits Limits at Infinity Limits at infinity and horizontal asymptotes. The Mean Value Theorem says that for a function that meets its conditions at some point the tangent line has the same slope as the secant line between the ends.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Mean Value Theorem Suppose that f f has a derivative on the interval ab a b and is continuous on the interval ab a b. Next because f x f x is a polynomial it is continuous and differentiable everywhere and so we could use Rolles Theorem to see that there must be a real value c c so that f c 0 f c 0. We solve it in steps. We compute f b f a b a e 3 e 2. Limits of Piece-wise Functions The Squeeze Theorem Continuity and the Intermediate Value Theorem Definition of continuity Continuity and piece-wise functions Continuity properties Types of discontinuities The Intermediate Value Theorem Summary of using continuity to evaluate limits Limits at Infinity Limits at infinity and horizontal asymptotes.
 Source: bishsoft.org
Source: bishsoft.org
For this function there are two values and such that the tangent line to. The function is a sum of a polynomial and an exponential function both of which are continuous and differentiable everywhere. Roughly speaking the Extreme Value Theorem says that there has to be a maximum and a minimum. We can now answer our second question above. If its in the interior Fermats Theorem says that it has to be a critical point.
 Source: cliffsnotes.com
Source: cliffsnotes.com
Students will be able to. Assuming that the position function. Taylors theorem Taylors formula - The extended mean value theorem. The approximation of the exponential function by polynomial using Taylors or Maclaurins formula Properties of the power series expansion of the exponential function. Try to find the value of c before reading further.
 Source: matheno.com
Source: matheno.com
Sketch pictures to illustrate why the Mean Value Theorem is true. Sketch pictures to illustrate why the Mean Value Theorem is true. That means we can use the Mean Value Theorem. The x -value of this point is the c in the MVT. In mathematics the mean value theorem states roughly that for a given planar arc between two endpoints there is at least one point at which the tangent to the arc is parallel to the secant through its endpoints.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
If f is a function that is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there is a point c in a b such that f. The MVT guarantees there is a c x 1 x 2 where. The Mean Value Theorem says that for a function that meets its conditions at some point the tangent line has the same slope as the secant line between the ends. The function is a sum of a polynomial and an exponential function both of which are continuous and differentiable everywhere. Taylors theorem Taylors formula - The extended mean value theorem.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Roughly speaking the Extreme Value Theorem says that there has to be a maximum and a minimum. Assuming that the position function. Determine whether Rolles Theorem or the Mean Value Theorem can be applied. We solve it in steps. Therefore the conditions for the Mean Value Theorem.
 Source: tutorial.math.lamar.edu
Source: tutorial.math.lamar.edu
The x -value of this point is the c in the MVT. C fbfa ba f c f b f a b a. That means we can use the Mean Value Theorem. Understand how Rolles theorem relates to the mean value theorem understand the mean value theorem and when its conditions are satisfied find points in an interval that satisfy the mean value theorem for a given function. We look for c.

Taylors theorem Taylors formula - The extended mean value theorem. Since f is differentiable on the interior it has to be a point where fc0. This is the Mean Value Theorem with f x e x a 1 and b 3. We compute f b f a b a e 3 e 2. The Mean Value Theorem says that for a function that meets its conditions at some point the tangent line has the same slope as the secant line between the ends.
 Source: nagwa.com
Source: nagwa.com
Mean Value Theorem Suppose that f f has a derivative on the interval ab a b and is continuous on the interval ab a b. Let pt denote the distance in meters to the right of the origin of a particle at time tminutes after noon. Use this information to guess a value for the instantaneous velocity of particle at 1202pm. This in turn means that the sum is also continuous and differentiable everywhere and so the function will be continuous on left - 23 right and differentiable on left - 23 right. Roughly speaking the Extreme Value Theorem says that there has to be a maximum and a minimum.

We solve it in steps. Sketch pictures to illustrate why the Mean Value Theorem is true. This theorem is used to prove statements about a function on an interval starting from local hypotheses about. Determine whether Rolles Theorem or the Mean Value Theorem can be applied. Understand the statement of the Mean Value Theorem.

C 0 1 c 0 1 the speed of the car was exactly. Since f is differentiable on the interior it has to be a point where fc0. Understand how Rolles theorem relates to the mean value theorem understand the mean value theorem and when its conditions are satisfied find points in an interval that satisfy the mean value theorem for a given function. We look for c. This is the Mean Value Theorem with f x e x a 1 and b 3.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Understand the statement of the Extreme Value Theorem. For this function there are two values and such that the tangent line to. We derive the derivative of the natural exponential function. If f is a function that is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there is a point c in a b such that f. A x 1 x 2 b.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Use this information to guess a value for the instantaneous velocity of particle at 1202pm. That means we can use the Mean Value Theorem. This in turn means that the sum is also continuous and differentiable everywhere and so the function will be continuous on left - 23 right and differentiable on left - 23 right. Mean Value Theorem Suppose that f f has a derivative on the interval ab a b and is continuous on the interval ab a b. We look for c.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
Assuming that the position function. We solve it in steps. Let pt denote the distance in meters to the right of the origin of a particle at time tminutes after noon. F a f b 0 f a f b 0. It is one of the most important results in real analysis.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
Find the values guaranteed by Rolles Theorem or the Mean Value Theorem. We derive the derivative of the natural exponential function. That means we can use the Mean Value Theorem. Understand the statement of the Mean Value Theorem. If f is a function that is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there is a point c in a b such that f.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
If f is a function that is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there is a point c in a b such that f. Since f x exists everywhere in a b we know the f is both continuous and differentiable. After completing this section students should be able to do the following. By Taylors Theorem we have for n a fixed positive integer. We look for c.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title exponential function mean value theorem by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






