Your Elasticity formula microeconomics images are ready. Elasticity formula microeconomics are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Elasticity formula microeconomics files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for elasticity formula microeconomics images information related to the elasticity formula microeconomics keyword, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
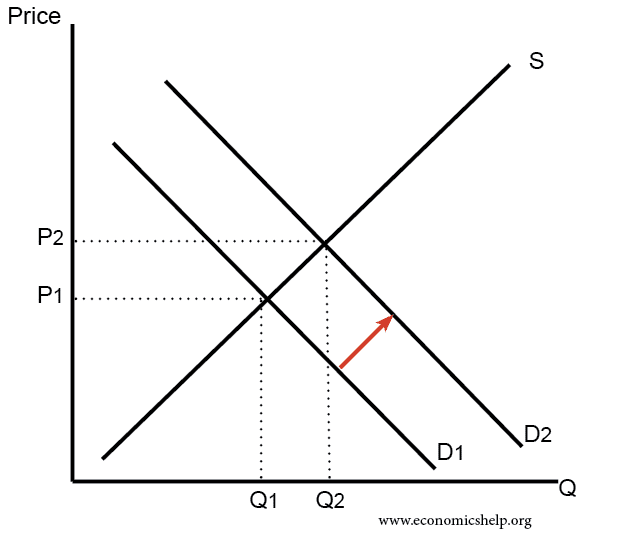
Elasticity Formula Microeconomics. ¾If demand for a good is unit-elastic an increase in price does not change total revenue. The calculation of elasticity using the formula of change in relative quantity over change in relative price results in different values depending on whether the starting point of the calculation is the highest or lowest price. P e r c e n t c h a n g e i n q u a n t i t y Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 1 0 0. Arc E Qd Qd midpoint Qd P P midpoint P is the method for calculating the elasticity of demand.
 Pin By Amara On Economics Microeconomics Study Economics Notes Economics Lessons From pinterest.com
Pin By Amara On Economics Microeconomics Study Economics Notes Economics Lessons From pinterest.com
Let us take for instance a linear demand curve Fig. The measure or coefficient E I of income-elasticity of demand can be obtained by means of the following formula. LatexdisplaystyletextPrice Elasticity of Demandfractextpercent change in quantitytextpercent change in pricelatex. The coefficient of price-elasticity of demand that is obtained at a point on the demand curve is called the point price- elasticity of demand and it is given by the formula 21 or 22. Point A ΔQ ΔP P Q 9 675 45 3 2 Δ Q Δ P P Q 9 675 45 3 2 Elastic. In order to calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price.
The formula for calculating elasticity is.
ΔQuantity ΔP rice 33 50 Δ Q u a n t i t y Δ P r i c e 33 50 067. ¾If demand for a good is unit-elastic an increase in price does not change total revenue. This is called the midpoint method for elasticity and is represented by the following equations. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic. Percent Change Elasticity DemandSupply Cross-Price Elasticity Income Elasticity Consumer Surplus Marginal Product Marginal Cost Total Cost Average Total Cost Average Variable Cost Average Fixed Cost Total Revenue Price x quantity. Let us take for instance a linear demand curve Fig.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
The price elasticity of demand is generally different at different points of the demand curve. Total revenue Price x Quantity. Second owing to the law of demand ie owing to the inverse relation between price and demand. In other words quantity changes faster than price. Opens a modal More on total revenue and elasticity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The measure or coefficient E I of income-elasticity of demand can be obtained by means of the following formula. Elasticity of demand is equal to the percentage change of quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price. Formula How to calculate elasticity. Quantity demanded price Coefficient 1 elastic demand. Second owing to the law of demand ie owing to the inverse relation between price and demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The formula for calculating elasticity is. The price elasticity of demand is generally different at different points of the demand curve. Price Elasticity of Demand can also be calculated using the Total Revenue Test. ΔQuantity ΔP rice 33 50 Δ Q u a n t i t y Δ P r i c e 33 50 067. Dq 0 for dp 0 is obtained and as a consequence of this E p would be negative E p 0 since p q.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Opens a modal Elasticity and strange percent changes. The formula for calculating elasticity is. Second owing to the law of demand ie owing to the inverse relation between price and demand. The measure or coefficient E I of income-elasticity of demand can be obtained by means of the following formula. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Elasticity of Demand on a Linear Demand Curve. Opens a modal Elasticity in the long run and short run. Opens a modal More on total revenue and elasticity. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic. These two calculations give us different numbers.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Price elasticity of demand is a measure that shows how much quantity demanded changes in response to a change in price. Elasticity of demand is equal to the percentage change of quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price. ¾If demand for a good is unit-elastic an increase in price does not change total revenue. Elasticity of Demand on a Linear Demand Curve. Microeconomics — Review of concepts —.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Quantity demanded price Coefficient 1 elastic demand. Microeconomics — Review of concepts —. Elasticity of demand is equal to the percentage change of quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price. Formula How to calculate elasticity. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Formula How to calculate elasticity. Percent Change Elasticity DemandSupply Cross-Price Elasticity Income Elasticity Consumer Surplus Marginal Product Marginal Cost Total Cost Average Total Cost Average Variable Cost Average Fixed Cost Total Revenue Price x quantity. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic. Microeconomics Ultimate Cheat Sheet Formulas Utility Maximizing Rule. ¾If demand for a good is inelastic a higher price increases total revenue.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The formula used here for computing elasticity. P e r c e n t c h a n g e i n q u a n t i t y Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 1 0 0. Elasticity Change in Quantity Change in Price. Dq 0 for dp 0 is obtained and as a consequence of this E p would be negative E p 0 since p q. In order to measure elasticity on the demand curve the midpoint between two points is used as an Arc elasticity measure.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Elasticity Change in Quantity Change in Price. Total revenue and elasticity. Lets look at the practical example mentioned earlier about cigarettes. Opens a modal Elasticity in the long run and short run. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Elasticity of demand is equal to the percentage change of quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic. Change in Price Price End Price Start Price Start. The price elasticity of demand is generally different at different points of the demand curve. Total revenue Price x Quantity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This is called the midpoint method for elasticity and is represented by the following equations. Point A ΔQ ΔP P Q 9 675 45 3 2 Δ Q Δ P P Q 9 675 45 3 2 Elastic. Second owing to the law of demand ie owing to the inverse relation between price and demand. To demonstrate we have calculated the elasticities at a point in each of the zones. This is called the midpoint method for elasticity and is represented by the following equations.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Opens a modal Elasticity in the long run and short run. Total revenue Price x Quantity. Formula Chart AP Microeconomics Unit 2 Supply and Demand Total Revenue price x quantity Total revenue test P Coefficient of price elasticity of demand. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic. To calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Price Elasticity of Demand can also be calculated using the Total Revenue Test. The measure or coefficient E I of income-elasticity of demand can be obtained by means of the following formula. In order to calculate elasticity we will use the average percentage change in both quantity and price. Change in Quantity Quantity End Quantity Start Quantity Start. Microeconomics — Review of concepts —.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
ΔQuantity ΔP rice 33 50 Δ Q u a n t i t y Δ P r i c e 33 50 067. Point A ΔQ ΔP P Q 9 675 45 3 2 Δ Q Δ P P Q 9 675 45 3 2 Elastic. P e r c e n t c h a n g e i n q u a n t i t y Q 2 Q 1 Q 2 Q 1 2 1 0 0. Price effect Sales effect. Let us take for instance a linear demand curve Fig.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The formula for calculating elasticity is. Own-price elasticity of supply can be calculated using mid-point and point-slope formula in the same way as for e P D. Percent Change Elasticity DemandSupply Cross-Price Elasticity Income Elasticity Consumer Surplus Marginal Product Marginal Cost Total Cost Average Total Cost Average Variable Cost Average Fixed Cost Total Revenue Price x quantity. Formula Chart AP Microeconomics Unit 2 Supply and Demand Total Revenue price x quantity Total revenue test P Coefficient of price elasticity of demand. Elasticity and Total Revenue ¾If demand for a good is elastic an increase in price reduces total revenue.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Total revenue and elasticity. 211 For example suppose that the index of the buyers income for good increases from 150 to 165 and consequently the quantity demanded of the good per period increases from 300 units to 360 units. Own-price elasticity of supply can be calculated using mid-point and point-slope formula in the same way as for e P D. Here we compare inelastic and elastic deman. In order to measure elasticity on the demand curve the midpoint between two points is used as an Arc elasticity measure.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Cross-price elasticity of demand e XP D Whereas the own-price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity to a goods own price cross-price elasticity of demand shows us how quantity demand responds to. ΔQuantity ΔP rice 33 50 Δ Q u a n t i t y Δ P r i c e 33 50 067. Elasticity and Total Revenue ¾If demand for a good is elastic an increase in price reduces total revenue. Therefore the price elasticity of demand formula looks like this. Q1 Q2 Q1 Q2 P1 P2 P1 P2 If the formula creates an.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title elasticity formula microeconomics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.