Your Elastic and inelastic regions of demand curve images are available in this site. Elastic and inelastic regions of demand curve are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Elastic and inelastic regions of demand curve files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for elastic and inelastic regions of demand curve pictures information connected with to the elastic and inelastic regions of demand curve keyword, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site always provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Elastic And Inelastic Regions Of Demand Curve. There are five types of elasticity of demand. The cross-price elasticity of demand between your good and a related good is 20. Assume production technology improved. Demand was inelastic between points A and B and elastic between points G and H.

When MR is positive the demand is elastic. Im a little confused however on how to combine these two aspects. Finally the bit you said about elastic and inelastic regions is a bit of a confusion as its not about an elasticity curve itself in separation but rather. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to change in price. In the lower price range In the higher price range In the higher quantity range Depends on the product 2This question has multiple answers. With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative.
Later they also demarcate different regions of the curve where the region to the northwest of the curves midpoint shows elastic demand and the region southeast of the midpoint inelastic demand.
Elasticity of demand refers to the degree in the change in demand when there is a change in another economic factor such as price or income. Select all that apply. Assume production technology improved. When the demand curve is elastic MR falls but is positive. On a graph with both a demand curve and a marginal revenue curve demand will be elastic at all quantities where marginal revenue is positive. So the marginal revenue will be negative and no firm will produce an extra unit if it means.

Monopoly equilibrium is possible only when the elasticity of his average revenue curve is greater than one and such a situation can be shown in Fig. Elasticity of demand refers to the degree in the change in demand when there is a change in another economic factor such as price or income. 1Which region of the demand curve is more elastic. When demand is inelastic then so. If demand for a good or service remains unchanged even.
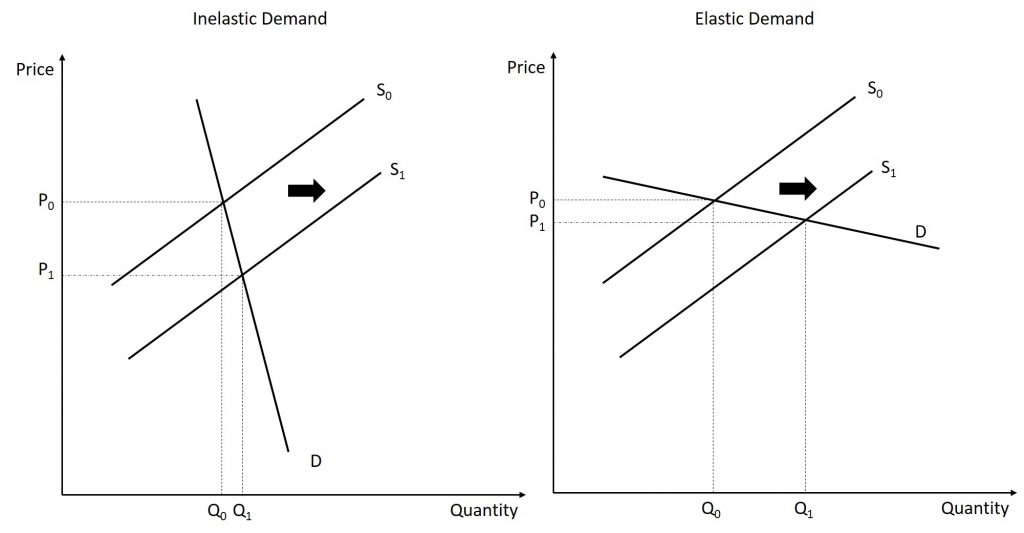 Source: psu.pb.unizin.org
Source: psu.pb.unizin.org
The cross-price elasticity of demand between your good and a related good is 20. Types of Elasticity of Demand. So now we can think of why a monopolist wont produce in the inelastic part of its demand curve. Which is where Marginal Cost is equal to Marginal Revenue. W 140 PRICE Dolars per unit De and QUANTITY PRI Z Demand 0 50 25 QUANTITY Units For each of the regions listed in the following table use the midpoint method to identify if the demand for this good is elastic approximately un.
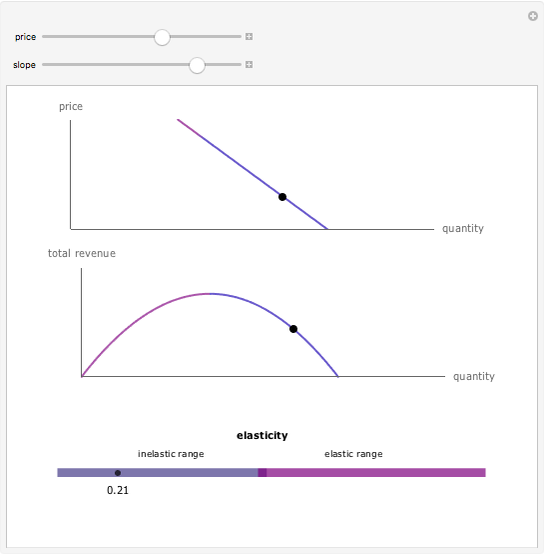 Source: demonstrations.wolfram.com
Source: demonstrations.wolfram.com
Elastic inelastic and unit-elastic demand The following graph shows the demand for a good. Because the price elasticity of demand shows the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a price change assuming that other factors that influence demand are unchanged it reflects movements along a demand curve. Identify the elastic and inelastic regions of the demand curve. W 140 PRICE Dolars per unit De and QUANTITY PRI Z Demand 0 50 25 QUANTITY Units For each of the regions listed in the following table use the midpoint method to identify if the demand for this good is elastic approximately un. The increase in the price decreases the revenue as the demand curve is highly inelastic.

First demand curve is elastic and e -1 A monopolist aims to produce at the point of optimum output. When the demand curve is elastic MR falls but is positive. Conversely if the demand is inelastic the slope will be steep. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to change in price. Identify the elastic and inelastic regions of the demand curve.
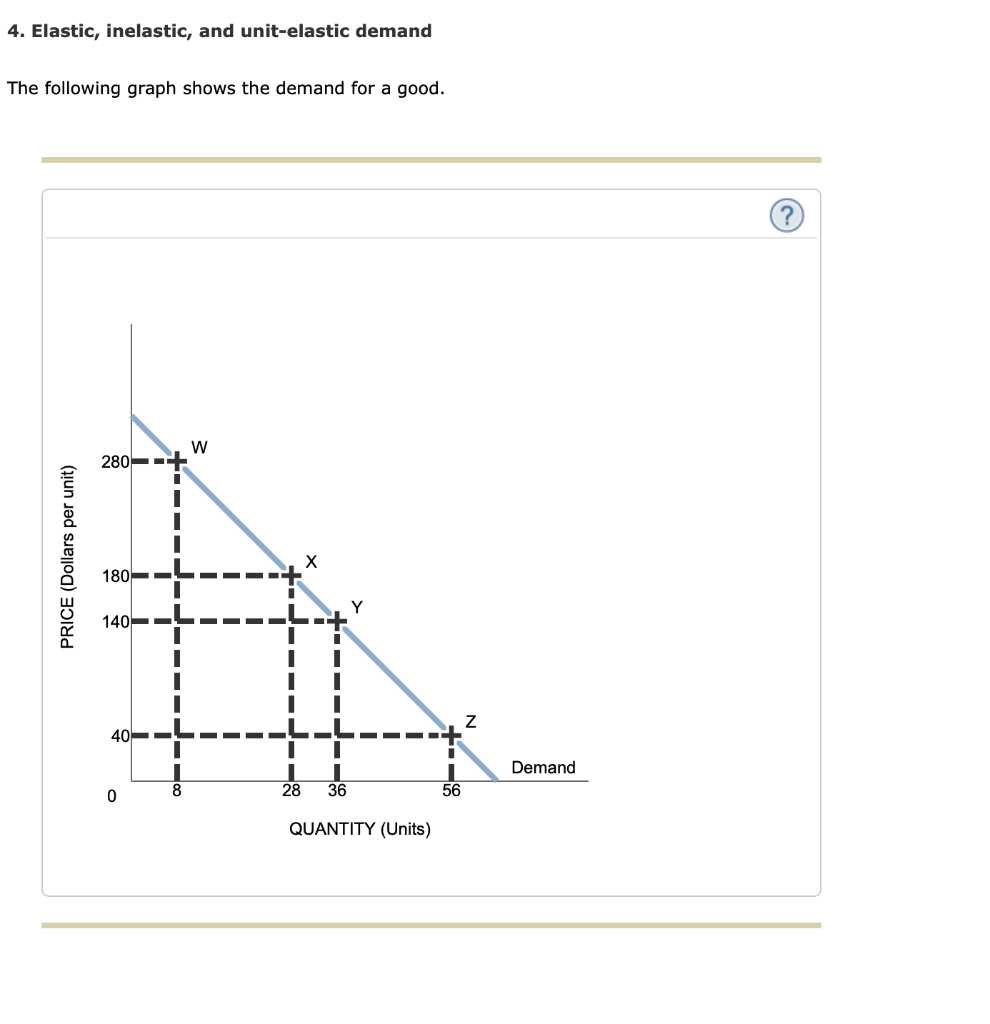 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
If the demand is inelastic then the elasticity of demand has a value less than 1. So now we can think of why a monopolist wont produce in the inelastic part of its demand curve. Price elasticity our tool here is defined as. At the same time consumers income has increased and the good is a normal good. If demand for a good or service remains unchanged even.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Assume production technology improved. When the demand curve is elastic MR falls but is positive. A demand curve is perfectly inelastic if The elasticity of demand is unity The elasticity of demand is zero A change in the price of the good has no effect on the quantity demanded Both a and c Both b and c In the elastic region of the demand curve if the price of the good rises by 10 Quantity demanded will fall by less than 10. You have the following information for your product. At the same time consumers income has increased and the good is a normal good.
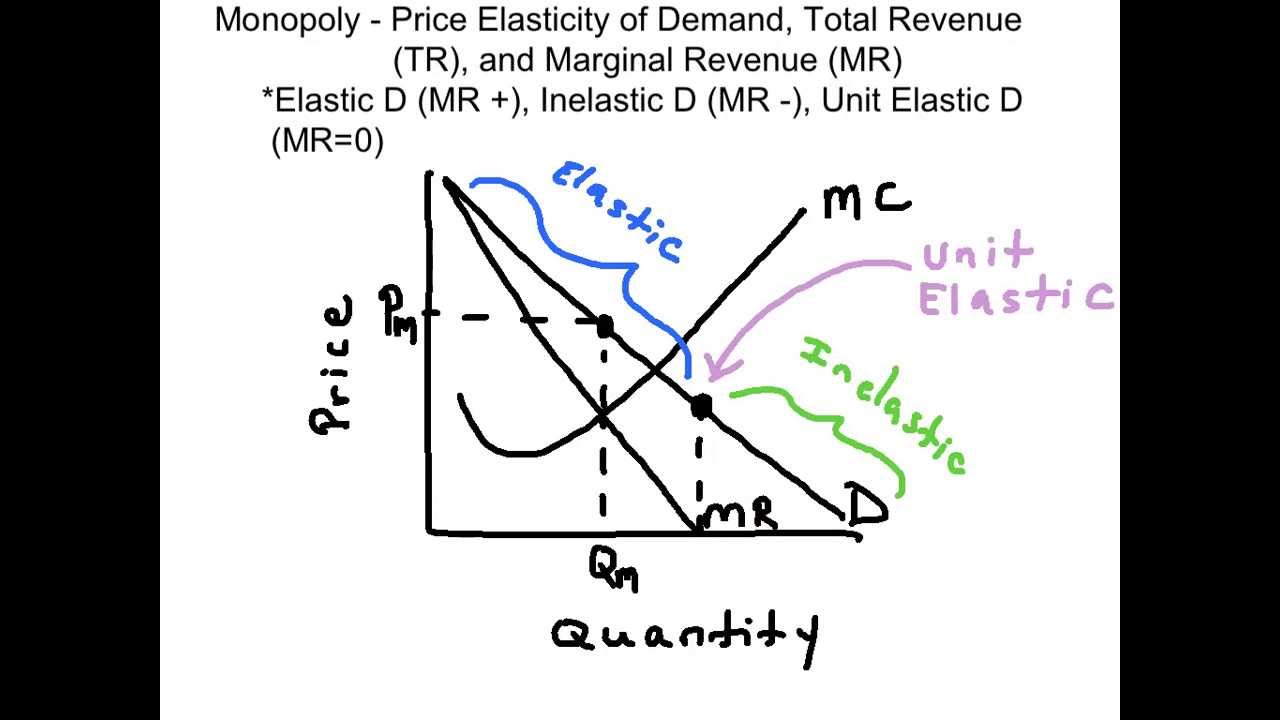 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
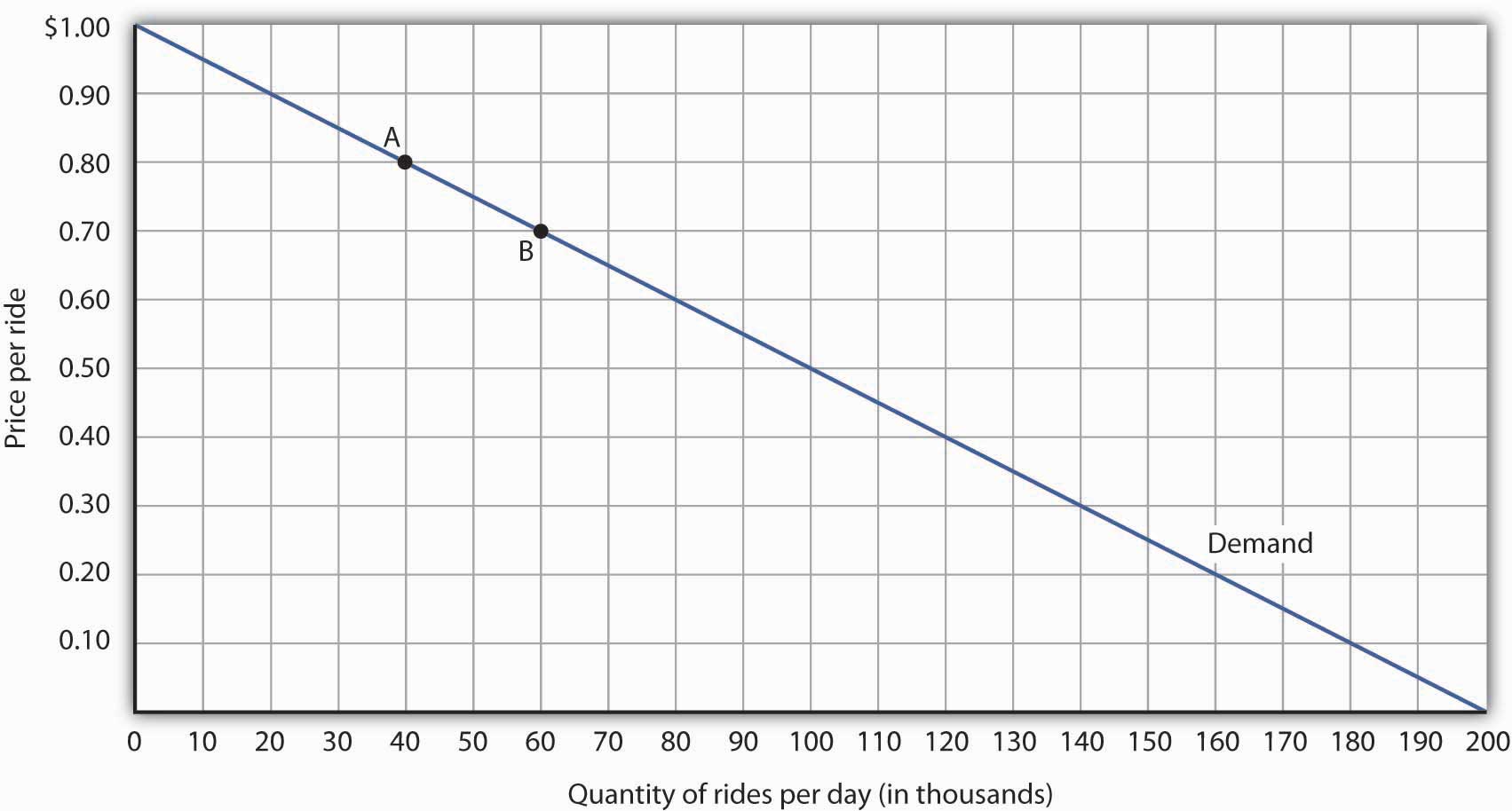
Identify the elastic and inelastic regions of the demand curve. Module Three Quiz 19. Recall that the elasticity between these two points was 045. Demand was inelastic between points A and B and elastic between points G and H. Select all that apply.
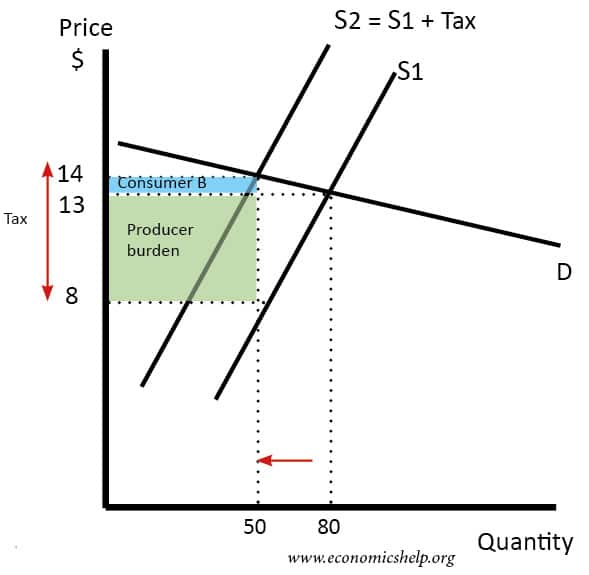 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The variety of demand curvesUsing the graph complete the table that follows by indicating whether each statement is true or false. When the demand is elastic the curve is shallow. Im a little confused however on how to combine these two aspects. A demand curve is perfectly inelastic if The elasticity of demand is unity The elasticity of demand is zero A change in the price of the good has no effect on the quantity demanded Both a and c Both b and c In the elastic region of the demand curve if the price of the good rises by 10 Quantity demanded will fall by less than 10. With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative.
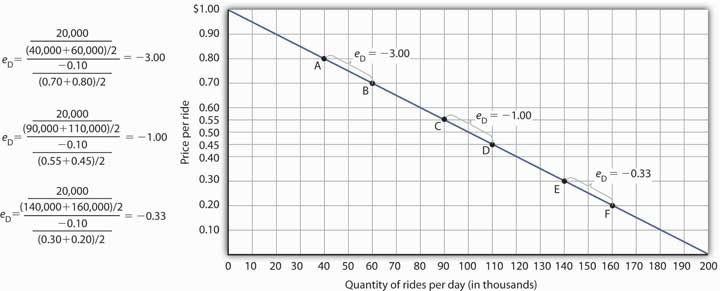 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
On a graph with both a demand curve and a marginal revenue curve demand will be elastic at all quantities where marginal revenue is positive. Finally the bit you said about elastic and inelastic regions is a bit of a confusion as its not about an elasticity curve itself in separation but rather. Identify the elastic and inelastic regions of the demand curve. Assume production technology improved. A demand curve is perfectly inelastic if The elasticity of demand is unity The elasticity of demand is zero A change in the price of the good has no effect on the quantity demanded Both a and c Both b and c In the elastic region of the demand curve if the price of the good rises by 10 Quantity demanded will fall by less than 10.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Elastic inelastic and unit-elastic demand The following graph shows the demand for a good. Demand is unitary elastic ie e p 1 at B in. A product or service has elastic demand when its price elasticity of demand is greater than 1 unit-elastic when price elasticity is 1 and inelastic when the price elasticity is less than 1. The price elasticity of demand is -09. The increase in the price decreases the revenue as the demand curve is highly inelastic.
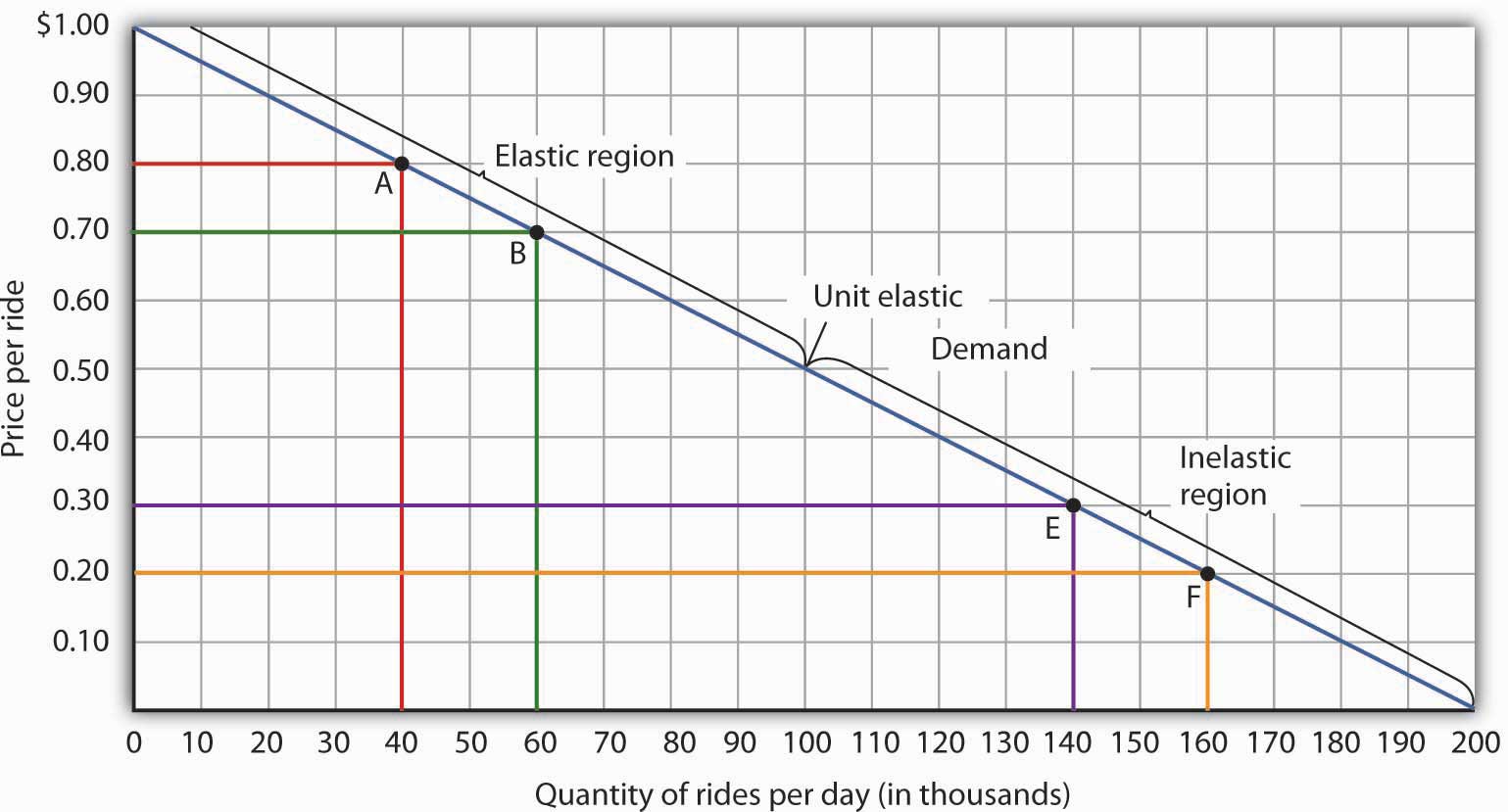 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
When the demand is elastic the curve is shallow. This brings to light the strategy of pricing in the inelastic region of the demand curve. When demand is inelastic then so. The magnitude of the elasticity has increased in absolute value as we moved up along the demand curve from points A to B. Because the price elasticity of demand shows the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a price change assuming that other factors that influence demand are unchanged it reflects movements along a demand curve.
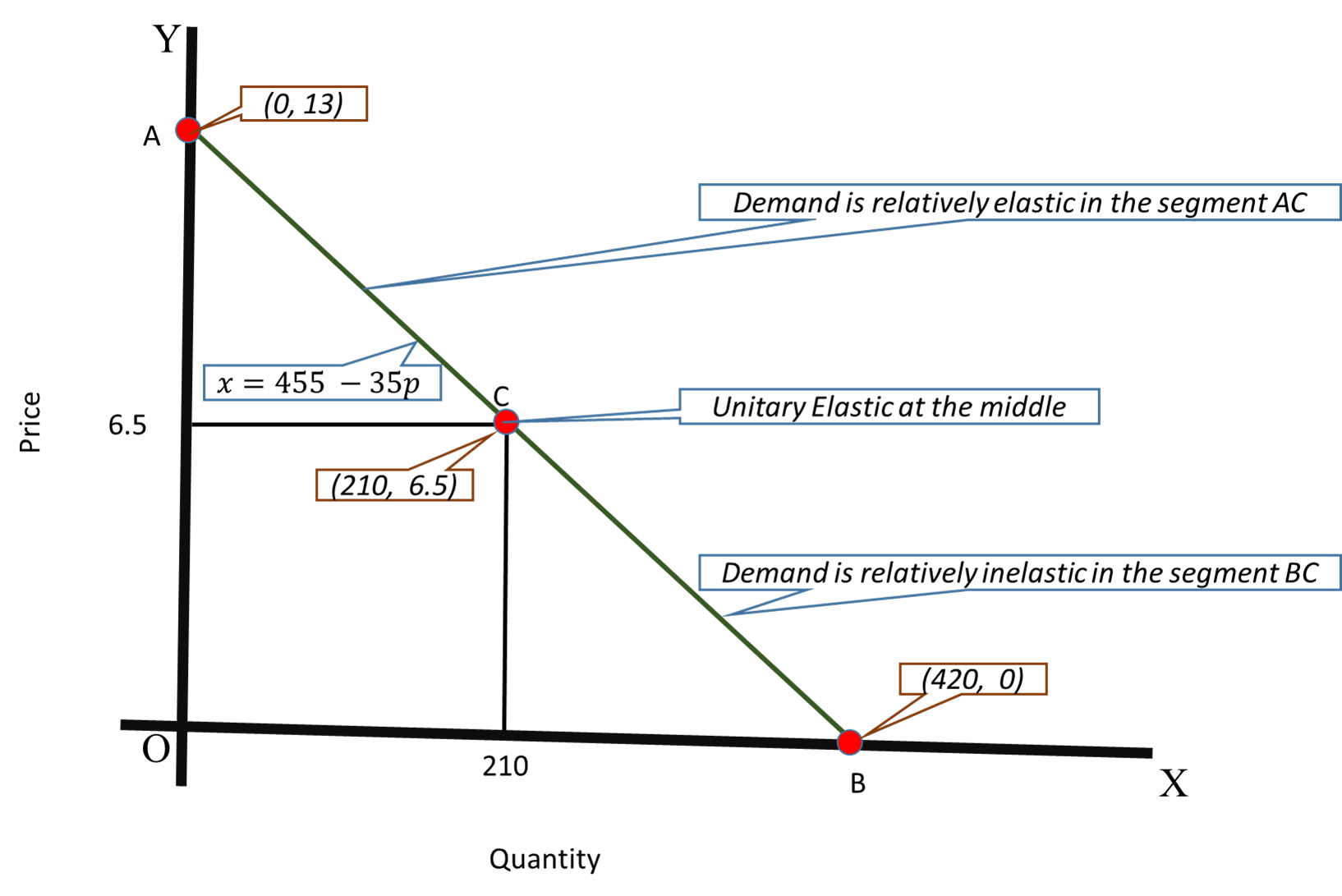 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Assume production technology improved. Elastic vs Inelastic Demand. Monopoly equilibrium is possible only when the elasticity of his average revenue curve is greater than one and such a situation can be shown in Fig. Elastic inelastic and unit-elastic demand The following graph shows the demand for a good. This brings to light the strategy of pricing in the inelastic region of the demand curve.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Conversely if the demand is inelastic the slope will be steep. So now we can think of why a monopolist wont produce in the inelastic part of its demand curve. Supply demand surplus DWL and burdens Elasticity and tax burdens Elastic demand Inelastic demand Elastic supply Inelastic supply If you have a formula for a supply curve and a demand curve you can calculate all sorts of things including the market clearing price or where the two lines intersect and the consumer and producer surplus. Im a little confused however on how to combine these two aspects. This brings to light the strategy of pricing in the inelastic region of the demand curve.

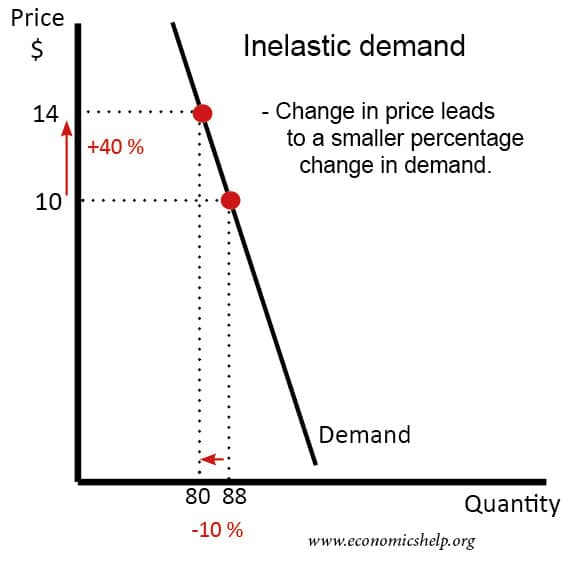
With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative. Elastic inelastic and unit-elastic demandFor each of the regions use the midpoint method to identify whether the demand for this good is elastic approximately unit elastic or inelastic. The line drawn from the example data results in an inelastic demand curve. This brings to light the strategy of pricing in the inelastic region of the demand curve. Using data from the example calculation a demand curve is drawn by placing the price on the Y-axis and demand on the X-axis.

And given that the price P is positive it also follows that. Elasticity of demand refers to the degree in the change in demand when there is a change in another economic factor such as price or income. There are five types of elasticity of demand. Later they also demarcate different regions of the curve where the region to the northwest of the curves midpoint shows elastic demand and the region southeast of the midpoint inelastic demand. Finally the bit you said about elastic and inelastic regions is a bit of a confusion as its not about an elasticity curve itself in separation but rather.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Price elasticity our tool here is defined as. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to change in price. Because the price elasticity of demand shows the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a price change assuming that other factors that influence demand are unchanged it reflects movements along a demand curve. The cross-price elasticity of demand between your good and a related good is 20. Select all that apply.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
At the same time consumers income has increased and the good is a normal good. This brings to light the strategy of pricing in the inelastic region of the demand curve. A demand curve is perfectly inelastic if The elasticity of demand is unity The elasticity of demand is zero A change in the price of the good has no effect on the quantity demanded Both a and c Both b and c In the elastic region of the demand curve if the price of the good rises by 10 Quantity demanded will fall by less than 10. When the demand curve is elastic MR falls but is positive. At the same time consumers income has increased and the good is a normal good.
 Source: revisionguru.co.uk
Source: revisionguru.co.uk
You have the following information for your product. Which is where Marginal Cost is equal to Marginal Revenue. So now we can think of why a monopolist wont produce in the inelastic part of its demand curve. Identify the elastic and inelastic regions of the demand curve. My 60ish second explanation of how to identify the elastic and inelastic range of the demand curve for a monopoly.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title elastic and inelastic regions of demand curve by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






