Your Decrease in supply with increse in wage rate graph images are ready. Decrease in supply with increse in wage rate graph are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Decrease in supply with increse in wage rate graph files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for decrease in supply with increse in wage rate graph images information connected with to the decrease in supply with increse in wage rate graph interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Decrease In Supply With Increse In Wage Rate Graph. Between points A and B the positive substitution effect of the wage increase outweighs the negative income effect. In the short run an increase in the money supply leads to a fall in the interest rate and a decrease in the money supply leads to a rise in the interest rate. First the MS decreases 1 which CAUSES. The interest rate to increase 2 which CAUSES.
 Supply Of Labour Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Supply Of Labour Economics Help From economicshelp.org
More infomation on this topic can be f. I Increase in Supply. Long-Run Aggregate Supply Long-run aggregate supply LRAS is the measure of the aggregate real production of goods and services at full-employment levels and when wages are responsive to or move in conjunction with price levels. This will result in a higher equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium quantity in the market for automobiles. The interest rate to increase 2 which CAUSES. Changes in the supply of labor have an effect on the wage rate.
A decrease in the supply of strawberries.
A decrease in the supply of strawberries. What happens to aggregate supply when wages increase. Changes in the supply of labor have an effect on the wage rate. In the short run an increase in the money supply leads to a fall in the interest rate and a decrease in the money supply leads to a rise in the interest rate. When there is an increase in supply demand remaining unchanged the supply curve shifts towards right from SS to S 1 S 1 Fig. 175 150 125 100 75 50 25 400 300 350 250 150 200 100 50 REAL GDP.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
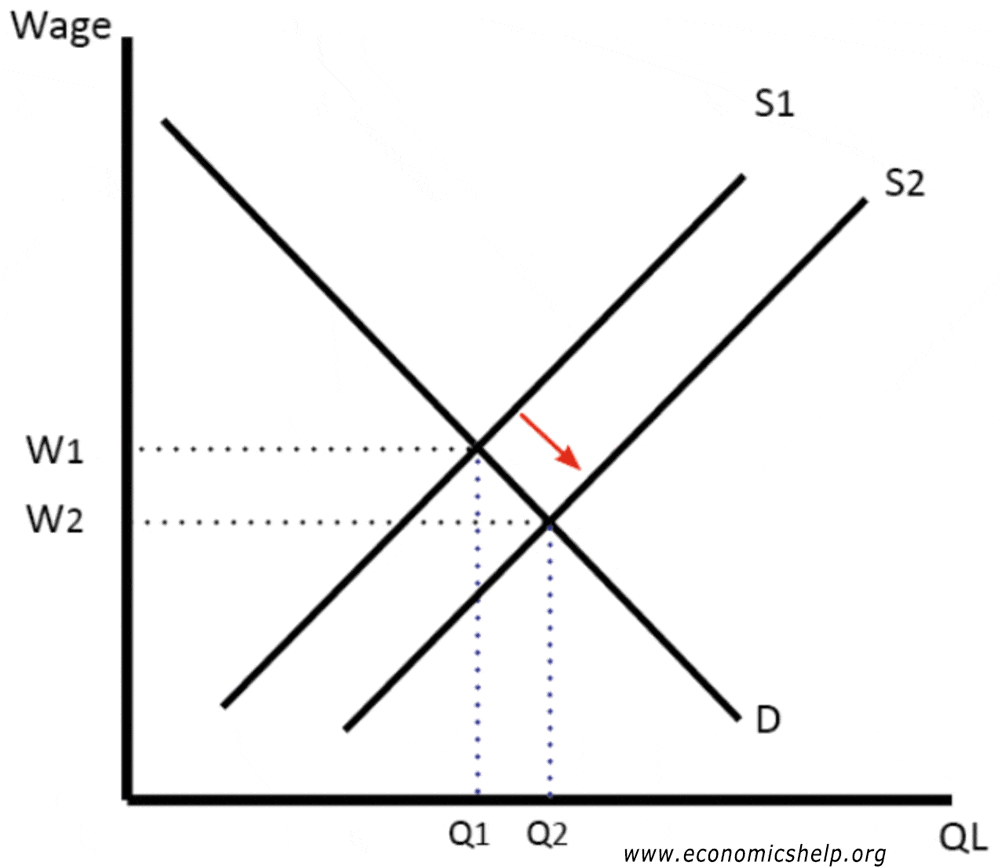
The interest rate must fall to r2 to achieve equilibrium. The supply curve will shift to the left and the wage rate will increase. For L1 to decrease to L2 and W1 to increase to W2 you need to have a decreased supply at S that more than compensates for any decrease or increase in the demand for labor. What happens to aggregate supply when wages increase. The increase in the wage rate will shift the automobile supply curve to the left along a given demand curve.

Decrease in aggregate supply AS in a hypothetical economy. A rise in the money wage rate makes the aggregate supply curve shift inward meaning that the quantity supplied at any price level declines. Figure 2512 An Increase in the Money Supply. When the price gets pushed up to P2 the quantity supply and quantity demand shift along their graphs. So prices go up until supply and demand are in equilibrium again.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
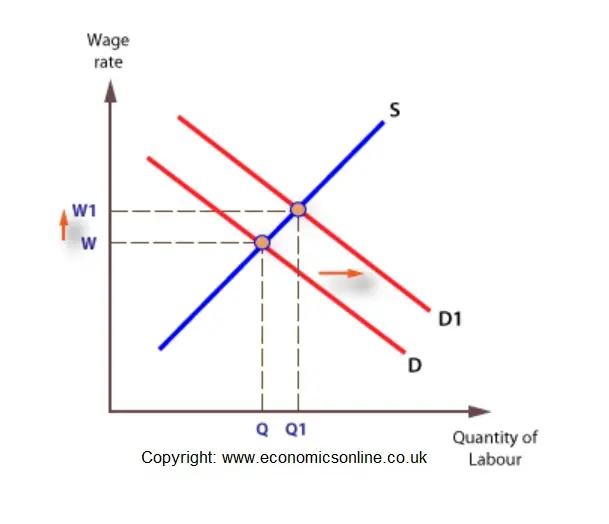
Module 29 explained that in the long run its a different story. Increase in demand decrease in supply. Suppose there is a decrease in aggregate demand which is shown by a leftward shift in AD as shown in Figure 2. If the increase in demand is less than the decrease in supply the shift of the demand curve tends to be less than that of the supply curve. The supply curve will shift to the right and the wage rate will decrease.
 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
What happens to aggregate supply when wages increase. The supply curve will shift to the right and the wage rate will decrease. Figure 2512 An Increase in the Money Supply. As wages increase the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left to restore long-run equilibrium. The decrease in the money supply CAUSES the interest rate to go up.
 Source: faculty.washington.edu
Source: faculty.washington.edu
The demand curve will shift to the right and the wage rate will increase. For L1 to decrease to L2 and W1 to increase to W2 you need to have a decreased supply at S that more than compensates for any decrease or increase in the demand for labor. And because of that individual would would want to work more. If we put it all together we get. Figure 2512 An Increase in the Money Supply.
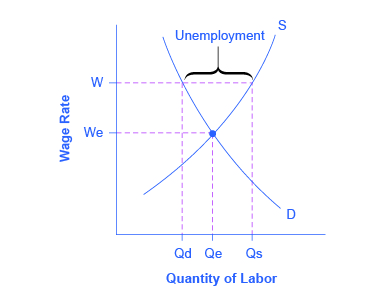 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
The wage rate is a determinant of the supply of automobiles but not a determinant of the demand for automobiles. 3- per dozenand thread have no opening balance and its purchase rate is Rs. Suppose there is a decrease in aggregate demand which is shown by a leftward shift in AD as shown in Figure 2. Changes in the supply of labor have an effect on the wage rate. The supply curve will shift to the left and the wage rate will increase.

An increase in the wage rate paid to workers producing good X would be represented by which of the graphs in Exhibit 44. Module 29 explained that in the long run its a different story. Zenvelo 36791 Great Answer 0 Flag as. More infomation on this topic can be f. The aggregate demand for labour will be negatively related to the real wage rate for the same reason that the demand curve for labour in any industry is negatively sloped—at lower wages firms will substitute the less expensive labour for capital.
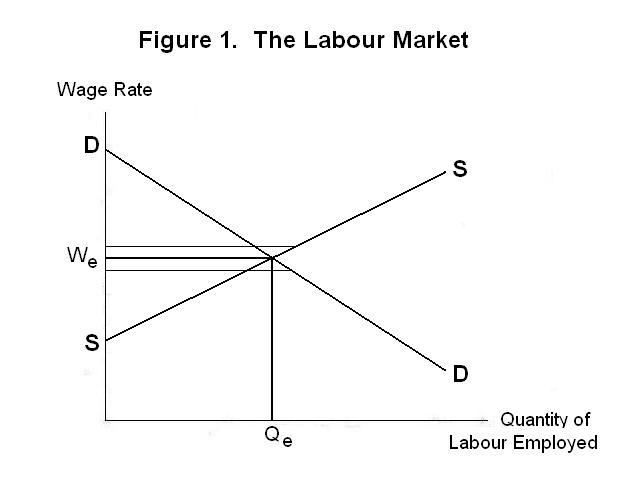 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
The supply curve will shift to the left and the wage rate will increase. More infomation on this topic can be f. Playing with S and D. This video goes over the process of including a minimum wage a price floor on your typical supply and demand graph. When there is an increase in supply demand remaining unchanged the supply curve shifts towards right from SS to S 1 S 1 Fig.
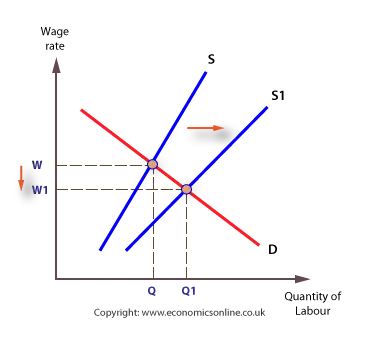 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
When the price gets pushed up to P2 the quantity supply and quantity demand shift along their graphs. Figure 2512 An Increase in the Money Supply. Decrease in price leads. Specifically aggregate supply shifts to the left from AS The following graph shows to AS2 causing the quantity of output supplied at a price level of 125 to fall from 250 billion to 150 billion 200 AS2 AS. The decrease in the money supply CAUSES the interest rate to go up.
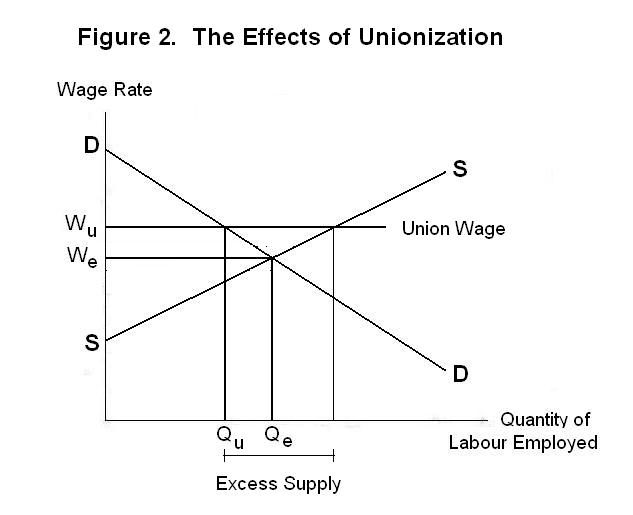 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
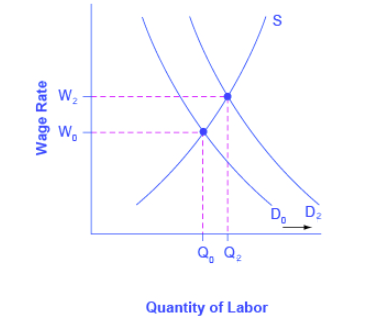
Employment and the wage rate were respectively L1 and W1 before Q2. This is modeled in Figure 3 where we put the real wage rate—that is the nominal wage rate divided by the price level—on the vertical axis. The quantity supply increase so now Q3 people are willing to work but thats not really that important. In the short run an increase in the money supply leads to a fall in the interest rate and a decrease in the money supply leads to a rise in the interest rate. Over time wages decrease and as they do the SRAS shifts to the right due to the decrease in firms cost of production.
 Source: pressbooks.oer.hawaii.edu
Source: pressbooks.oer.hawaii.edu
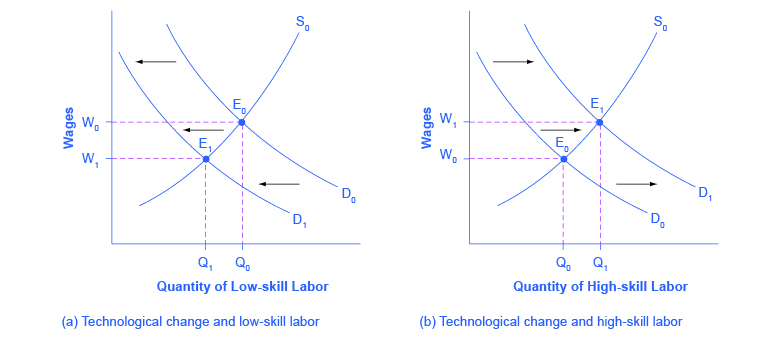
The wage rate is a determinant of the supply of automobiles but not a determinant of the demand for automobiles. This leads to competition among sellers which reduces the price. The quantity supply increase so now Q3 people are willing to work but thats not really that important. And chances are demand for of goods is the same as before the wage increase just at a higher price. The supply of labor shifts when there are changes in the population changes in preferences and social norms and changes in wage rates and opportunities in other markets.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
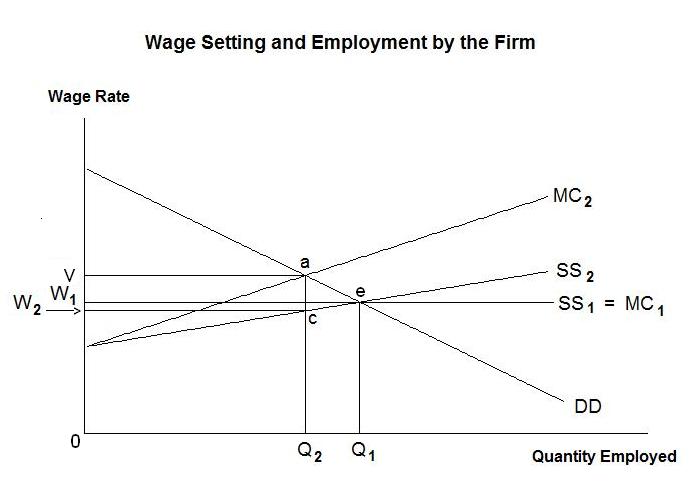
The supply curve will shift to the left and the wage rate will increase. This leads to competition among sellers which reduces the price. The amount of investment to decrease 3 the graph does not shift this CAUSES. Button have an opening balance of 50 dozen and purchase rate is Rs. And because of that individual would would want to work more.
 Source: economicshelp.org
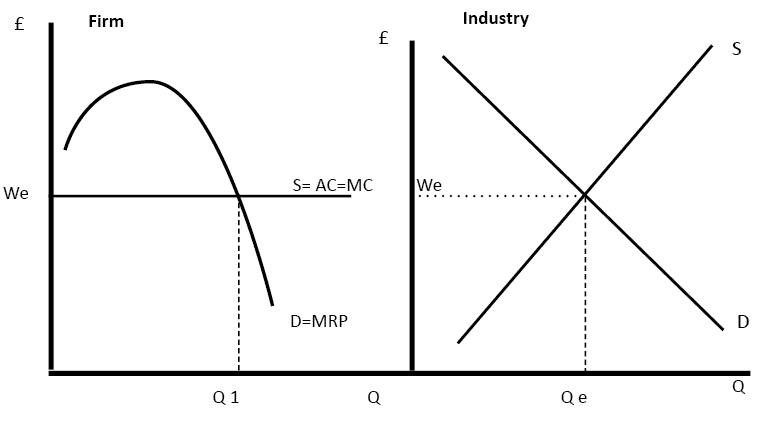
Source: economicshelp.org
The wage rate is a determinant of the supply of automobiles but not a determinant of the demand for automobiles. An increase in the wage rate paid to workers producing good X would be represented by which of the graphs in Exhibit 44. The increase in the wage rate will shift the automobile supply curve to the left along a given demand curve. The wage rate is a determinant of the supply of automobiles but not a determinant of the demand for automobiles. None of the above.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
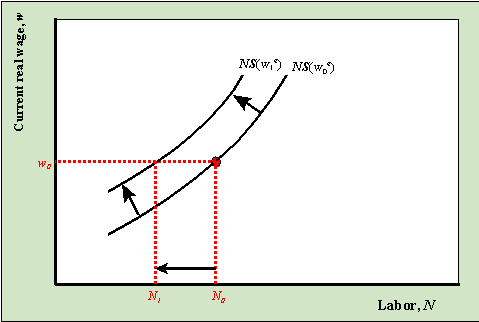
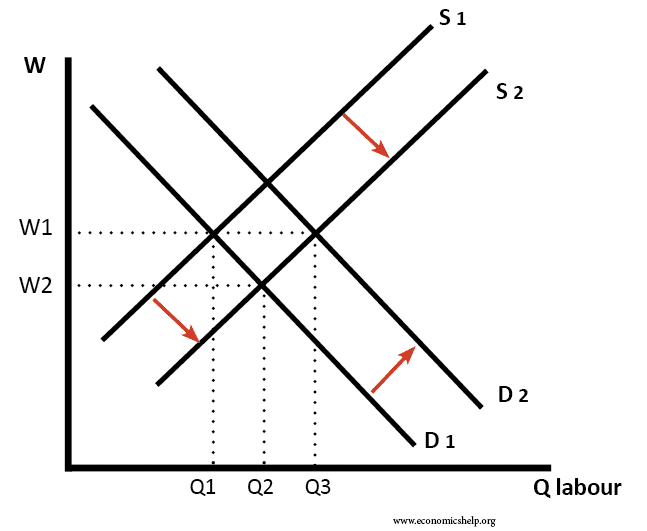
The chart below pictures the labor market with demand curve D and supply curve S. The Fed increases the money supply by buying bonds increasing the demand for bonds in Panel a from D1 to D2 and the price of bonds to Pb2. First the MS decreases 1 which CAUSES. Figure 2512 An Increase in the Money Supply. When wages increase the SRAS decreases and as wages decrease SRAS increases.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
If the cost of other inputs such as the cost of energy rises it will have a similar effect on the supply curve. And chances are demand for of goods is the same as before the wage increase just at a higher price. Decrease in price leads. When the price gets pushed up to P2 the quantity supply and quantity demand shift along their graphs. Changes in the money supply dont affect the interest rate at all.
 Source: pressbooks.oer.hawaii.edu
Source: pressbooks.oer.hawaii.edu
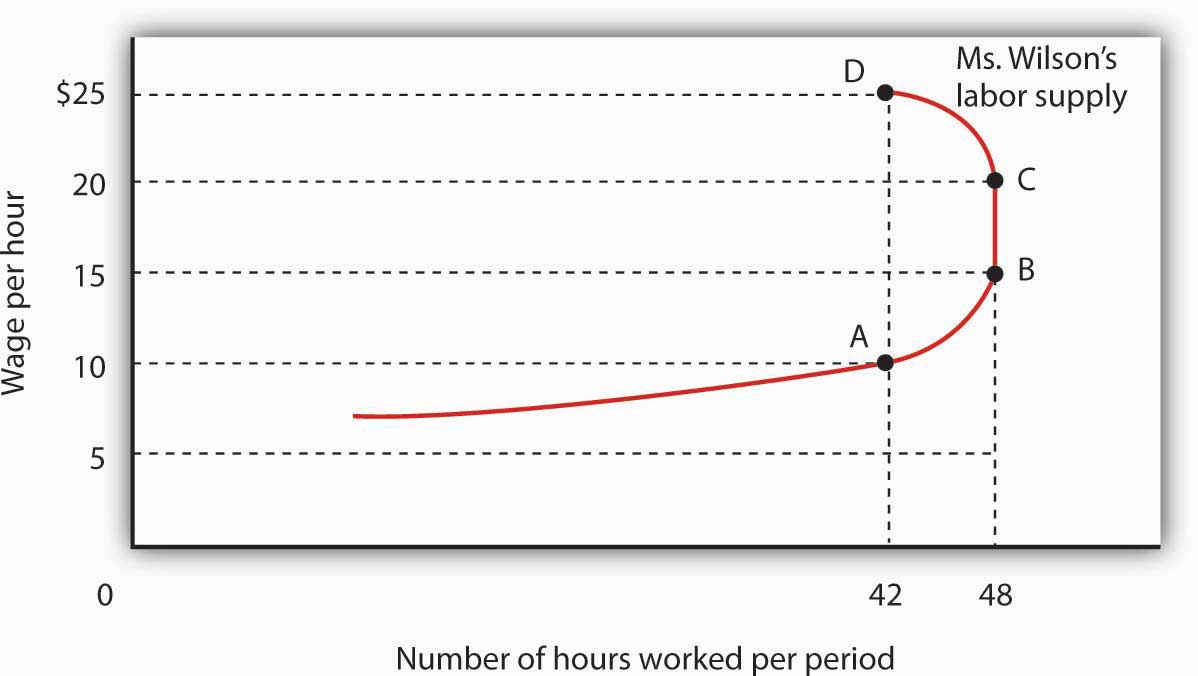
When there is an increase in supply demand remaining unchanged the supply curve shifts towards right from SS to S 1 S 1 Fig. As wages increase the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left to restore long-run equilibrium. Let us study it by analysing how an increase in wage rate will affect labor supply. None of the above. The demand curve will shift to the right and the wage rate will increase.

When the price gets pushed up to P2 the quantity supply and quantity demand shift along their graphs. Over time wages decrease and as they do the SRAS shifts to the right due to the decrease in firms cost of production. As wages increase the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left to restore long-run equilibrium. 175 150 125 100 75 50 25 400 300 350 250 150 200 100 50 REAL GDP. According to the graph above which of the following will necessarily result in a decrease in output.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
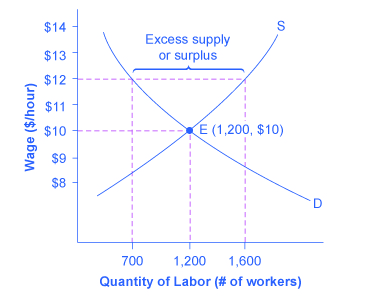
175 150 125 100 75 50 25 400 300 350 250 150 200 100 50 REAL GDP. Decrease in price leads. Playing with S and D. The chart below pictures the labor market with demand curve D and supply curve S. A decrease in the supply of labor will typically cause an increase in the wage rate.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title decrease in supply with increse in wage rate graph by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.