Your Decrease in supply graph example images are available. Decrease in supply graph example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Decrease in supply graph example files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for decrease in supply graph example images information connected with to the decrease in supply graph example keyword, you have come to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
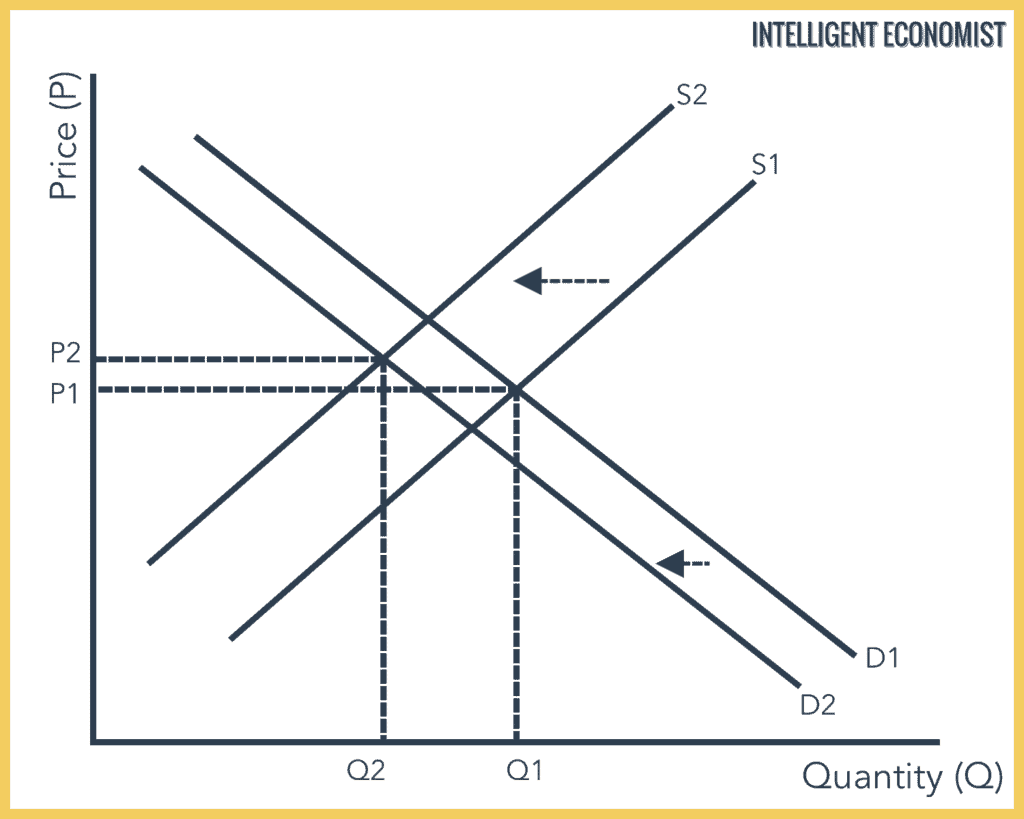
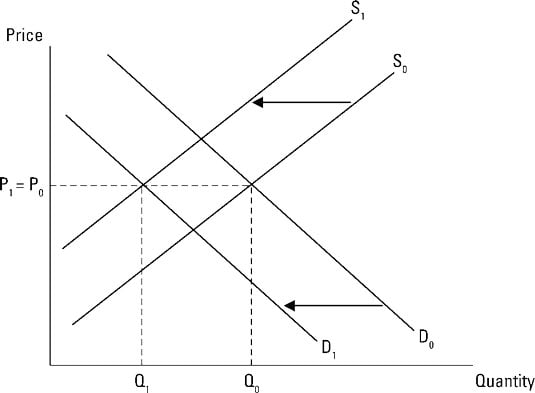
Decrease In Supply Graph Example. When decrease in demand is proportionately more than decrease in supply then leftward shift in demand curve from D to D¹ is proportionately more than leftward shift in supply curve from S to S¹. First the price of inputs will go up so supply will shift left a decrease in supply. A decrease in supply is caused by a change in a supply determinant and results in a decrease in equilibrium quantity and an increase in equilibrium price. In this case the right shift of the demand curve is proportionately more than the leftward shift of the supply curve.
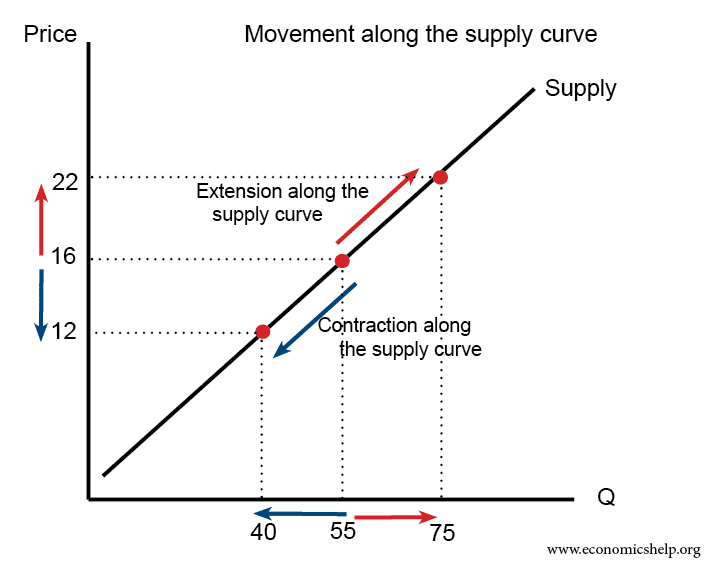 Diagrams For Supply And Demand Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Diagrams For Supply And Demand Economics Help From economicshelp.org
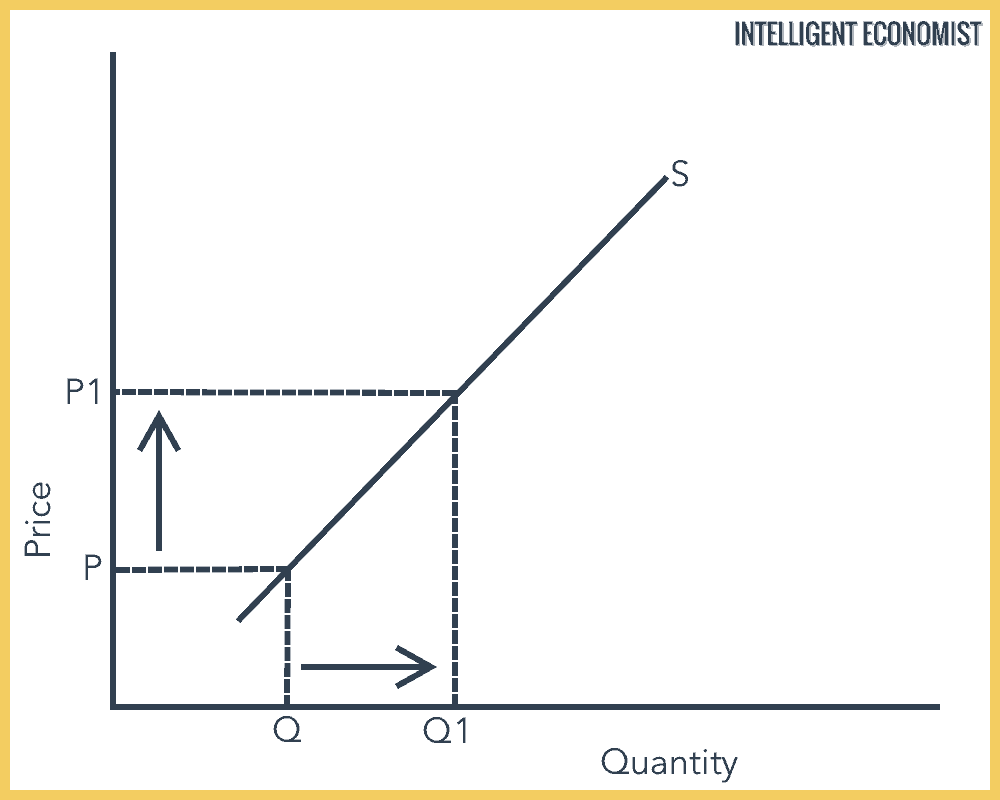
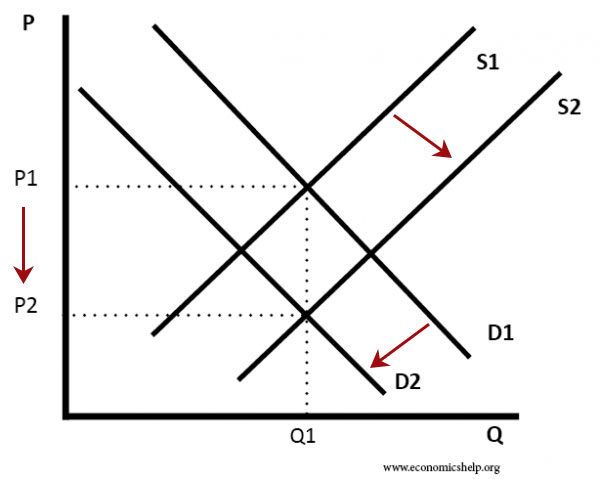
Decrease in supply raises the price. Nothing happens to demand so equilibrium price and quantity both go up. As the price rises to the new equilibrium level the quantity demanded decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month. Since it now costs more to supply tacos you are going to have to charge more for your tacos or shift your supply curve left Sl. Chicken and beef are substitute goods. A decrease in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price illustrated by a leftward shift of the supply curve.
As the price rises to the new equilibrium level the quantity demanded decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month.
Slaughtering the cows will result in an increase in the supply of beef to the market which will in turn lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price of beef and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of beef. Illustrate using a supply and demand diagram. For example all three panels of Figure 311 Simultaneous Decreases in Demand and Supply show a decrease in demand for coffee caused perhaps by a decrease in the price of a substitute good such as tea and a simultaneous decrease in the supply of coffee caused perhaps by bad weather. First the price of inputs will go up so supply will shift left a decrease in supply. When the decrease in demand is greater than the decrease in supply the demand curve shifts more towards left relative to the supply curve. The price of inputs has a negative effect on the supply curve if the price of inputs goes up supply will decrease shift left.
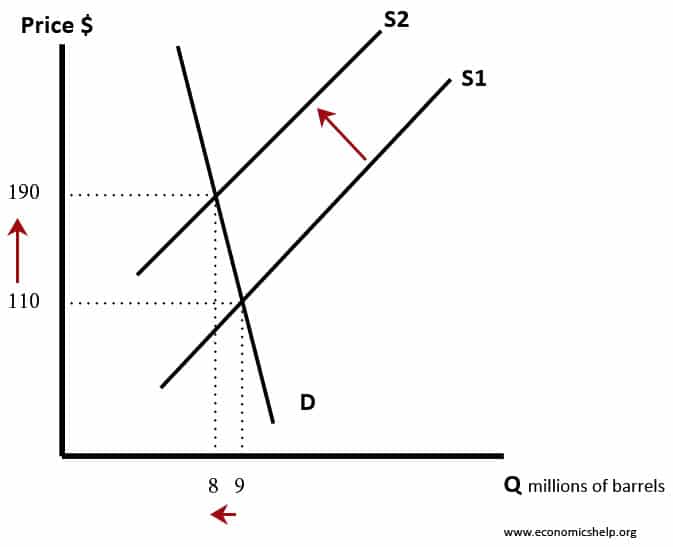 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. The price of inputs has a negative effect on the supply curve if the price of inputs goes up supply will decrease shift left. Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the. If coffee workers organize themselves into a union and gain higher wages two possible things can happen.
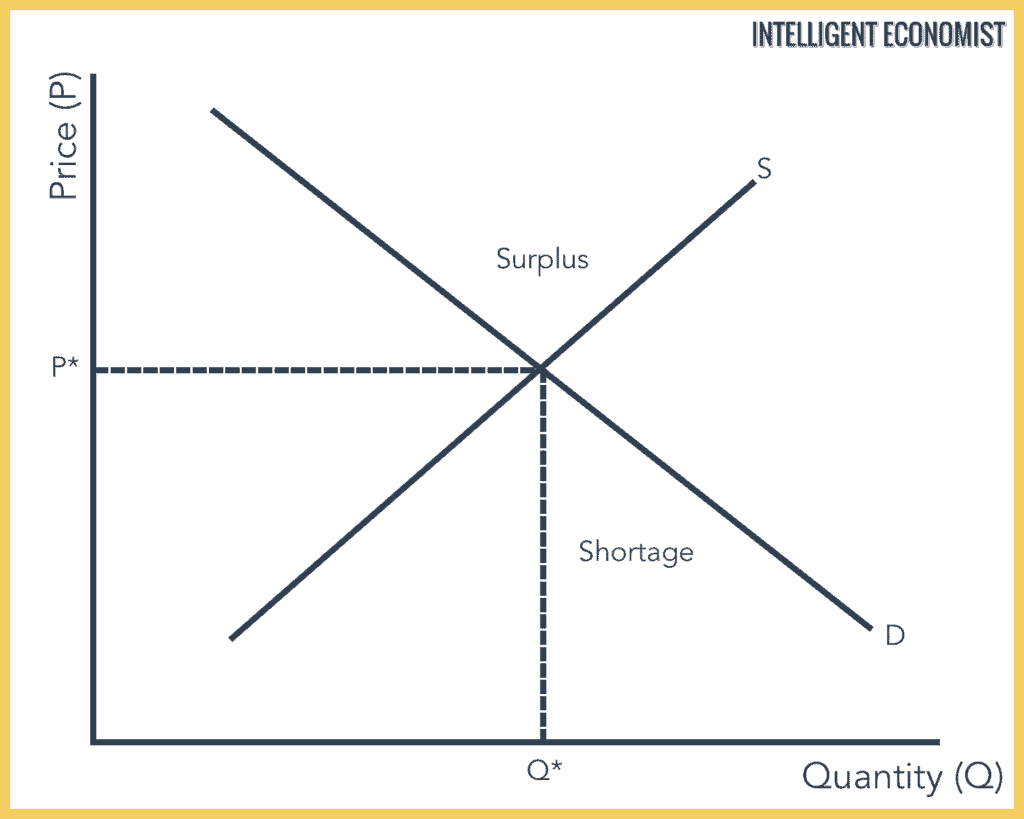 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
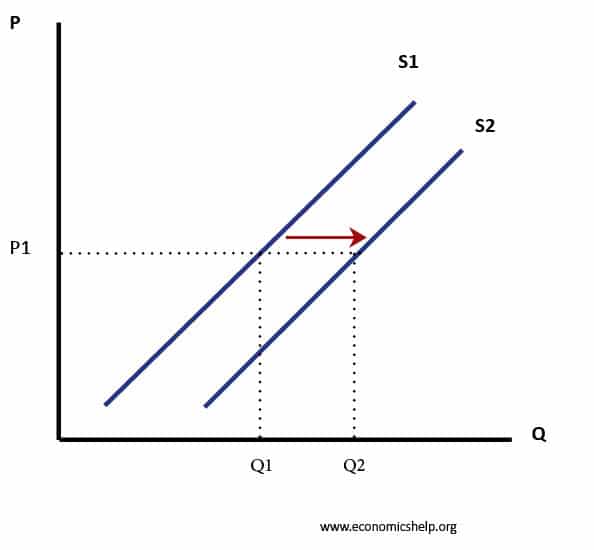
Since it now costs more to supply tacos you are going to have to charge more for your tacos or shift your supply curve left Sl. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. Aggregate supply would decrease if there was an increase in the price of raw materials and energy or it would increase if better training for employees was implemented. Second it is possible that higher wages will result in an increase in income which will increase demand shift it right. Imagine you are running a taco shop and the price of corn goes up.
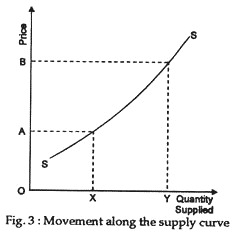 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3. When decrease in demand is proportionately more than decrease in supply then leftward shift in demand curve from D to D¹ is proportionately more than leftward shift in supply curve from S to S¹. From 1985 to 1986 for example the average price of crude oil fell by almost half from 24 a barrel to 12 a barrel. The example supply and demand equilibrium graph below identifies the price point where product supply at a price consumers are willing to pay are equal keeping supply and demand steady. Quantity might increase decrease or not change.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
Chicken and beef are substitute goods. An increase in demand shifts the demand curve rightward and a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve leftward. 43 MARKET EQUILIBRIUM Figure 414a shows the effects of an increase in demand and a decrease in supply. Change in supply refers to a shift either to the left or right in the entire price-quantity relationship that defines a supply curve. A decrease in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price illustrated by a leftward shift of the supply curve.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. 43 MARKET EQUILIBRIUM Figure 414a shows the effects of an increase in demand and a decrease in supply. When the decrease in demand is greater than the decrease in supply the demand curve shifts more towards left relative to the supply curve. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Long-run aggregate supply curve. As the price rises to the new equilibrium level the quantity demanded decreases to 20 million pounds of coffee per month. Essentially a change in supply is. The change may be either an Increase in Supply or Decrease in Supply. Since it now costs more to supply tacos you are going to have to charge more for your tacos or shift your supply curve left Sl.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Change in supply refers to a shift either to the left or right in the entire price-quantity relationship that defines a supply curve. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. The decrease in demand decrease in supply. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3. First the price of inputs will go up so supply will shift left a decrease in supply.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The decrease in aggregate supply caused by the increase in input prices is represented by a shift to the left of the SAS curve because the SAS curve is drawn under the assumption that input prices remain constant. Illustrate using a supply and demand diagram. Nothing happens to demand so equilibrium price and quantity both go up. The change may be either an Increase in Supply or Decrease in Supply. A decrease in supply is caused by a change in a supply determinant and results in a decrease in equilibrium quantity and an increase in equilibrium price.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Decrease in supply raises the price. Hence both equilibrium quantity and price rise. A curve that shows the relationship in. Quantity might increase decrease or not change. Aggregate supply would decrease if there was an increase in the price of raw materials and energy or it would increase if better training for employees was implemented.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
The decrease in demand decrease in supply. In this example the lines from the supply curve and the demand curve indicate that the equilibrium price for 50-inch HDTVs is 500. Nothing happens to demand so equilibrium price and quantity both go up. Increase in demand decrease in supply. Conversely if the price of steel decreases producing a car becomes less expensive.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the. For example all three panels of Figure 311 Simultaneous Decreases in Demand and Supply show a decrease in demand for coffee caused perhaps by a decrease in the price of a substitute good such as tea and a simultaneous decrease in the supply of coffee caused perhaps by bad weather. When decrease in demand is proportionately more than decrease in supply then leftward shift in demand curve from D to D¹ is proportionately more than leftward shift in supply curve from S to S¹. Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Illustrate using a supply and demand diagram. Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the. The example supply and demand equilibrium graph below identifies the price point where product supply at a price consumers are willing to pay are equal keeping supply and demand steady. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. 43 MARKET EQUILIBRIUM Figure 414a shows the effects of an increase in demand and a decrease in supply.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. The change may be either an Increase in Supply or Decrease in Supply. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. Second it is possible that higher wages will result in an increase in income which will increase demand shift it right. Since it now costs more to supply tacos you are going to have to charge more for your tacos or shift your supply curve left Sl.

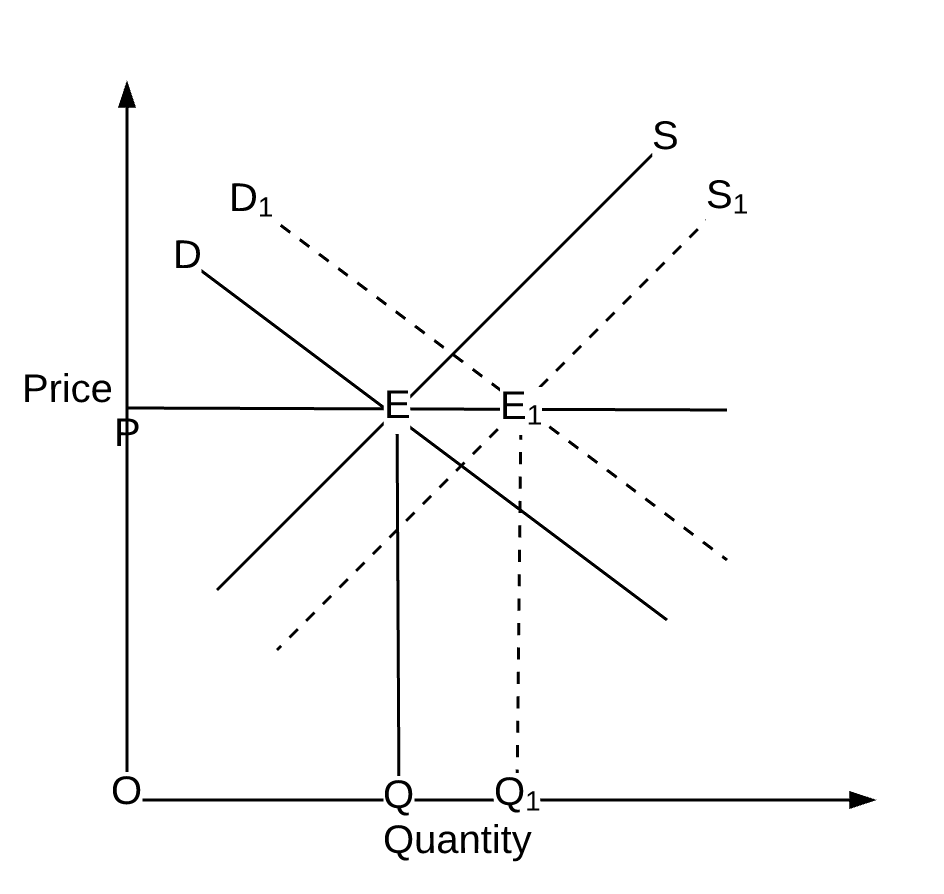
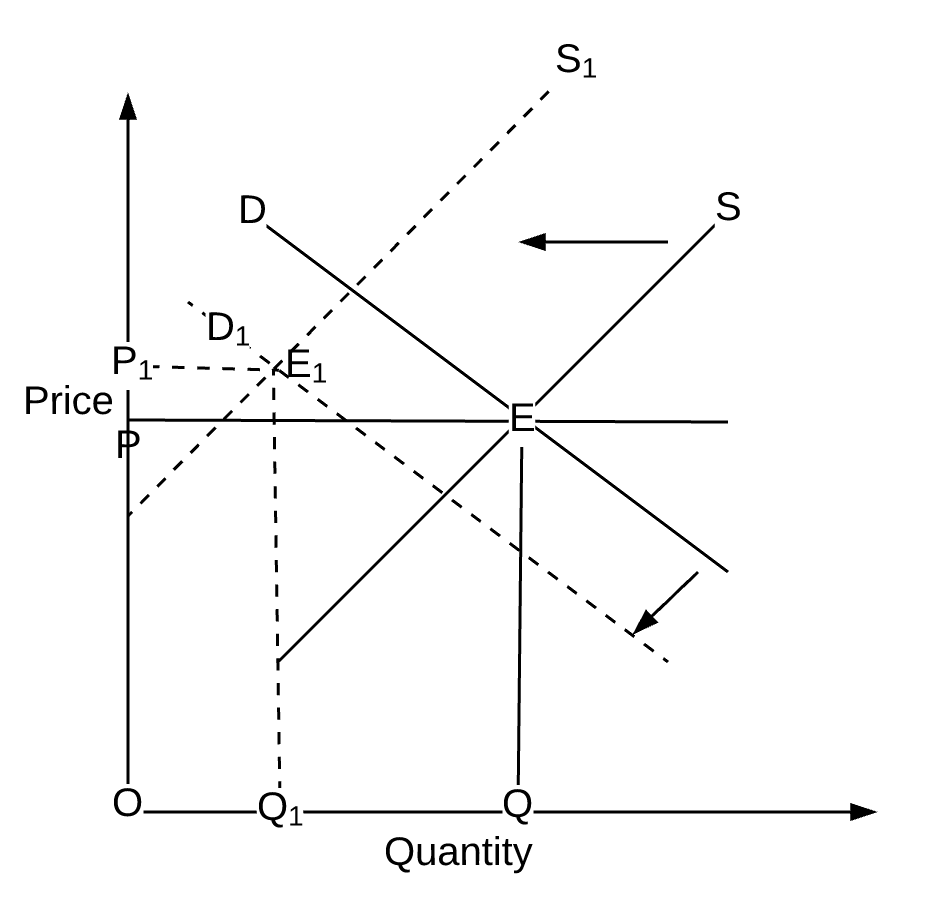
Original Equilibrium is determined at point E when demand curve DD and the original supply curve SS intersect each other. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. A curve that shows the relationship in. Some examples include. A decrease in supply is caused by a change in a supply determinant and results in a decrease in equilibrium quantity and an increase in equilibrium price.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
This decrease in demand is shown by a leftward shift in the demand curve and a movement along the supply curve which creates a surplus in first-class mail at the original price shown as P2. The example supply and demand equilibrium graph below identifies the price point where product supply at a price consumers are willing to pay are equal keeping supply and demand steady. For example all three panels of Figure 311 Simultaneous Decreases in Demand and Supply show a decrease in demand for coffee caused perhaps by a decrease in the price of a substitute good such as tea and a simultaneous decrease in the supply of coffee caused perhaps by bad weather. Hence both equilibrium quantity and price rise. The shortage causes a decrease in the equilibrium price to P3 and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity to Q3.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
Second it is possible that higher wages will result in an increase in income which will increase demand shift it right. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. Effectively there is a fall in both equilibrium quantity and price. Illustrate using a supply and demand diagram.
 Source: boycewire.com
Source: boycewire.com
Some examples include. If coffee workers organize themselves into a union and gain higher wages two possible things can happen. Since it now costs more to supply tacos you are going to have to charge more for your tacos or shift your supply curve left Sl. Since reductions in demand and supply considered separately each cause the. This decrease in demand is shown by a leftward shift in the demand curve and a movement along the supply curve which creates a surplus in first-class mail at the original price shown as P2.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
The decrease in demand decrease in supply. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. A decrease in the willingness and ability of sellers to sell a good at the existing price illustrated by a leftward shift of the supply curve. If the increase in demand is less than the decrease in supply the shift of the demand curve tends to be less than that of the supply curve. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title decrease in supply graph example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






