Your Cross price elasticity calculation example images are ready in this website. Cross price elasticity calculation example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Cross price elasticity calculation example files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for cross price elasticity calculation example images information connected with to the cross price elasticity calculation example keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Cross Price Elasticity Calculation Example. How To Calculate Cross Elasticity Of Demand MP3 Download. The cost of Good A rises to 100. It should be noted that cross elasticity of demand for substitutes is always positive. For example McDonalds may increase the price of its products by 20 percent.
 Chapter 5 Elasticity And Its Application Flashcards Quizlet From quizlet.com
Chapter 5 Elasticity And Its Application Flashcards Quizlet From quizlet.com
Implies two goods are complements. That means that when the price of product X increases the demand for product Y also increases. The PED is calculated as below. The average price of coffee is 122 15 and percentage change in the price of coffee is 2-115 6666 percent so the cross elasticity of demand of tea relative to the price of coffee will be 33336666 50. Positive Cross Price Elasticity occurs when the formula produces a result greater than 0. The cost of Good A rises to 100.
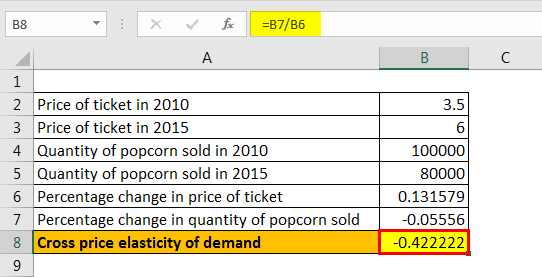
As a result the demand for petrol at a fuel station reduced from 100 liters per day to 80 liters per day.
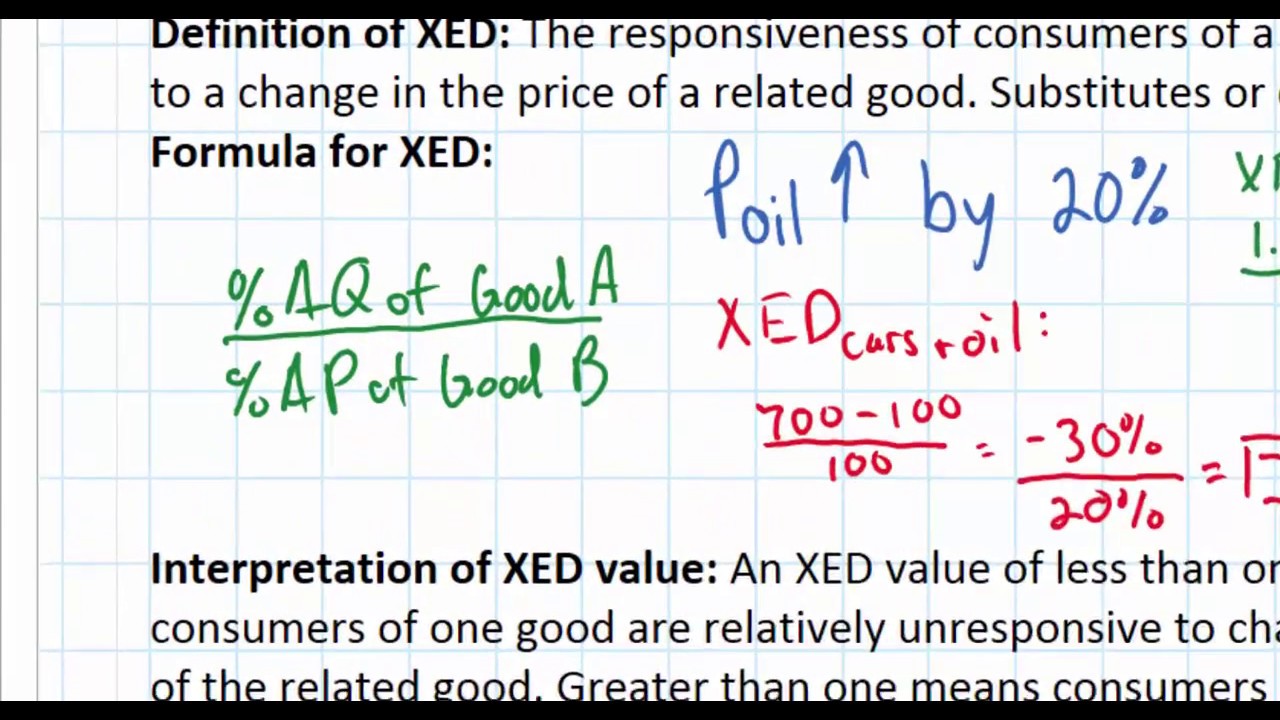
If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other. The percent change in the quantity of sprockets demanded is 105. The cross elasticity of demand of butter with respect to margarine is 081 so 1 increase in the price of margarine will increase the demand for butter by 081. Assume that the petrol price was INR 50 per liter which increased to INR 60 per liter. Using the example values of 89 and 35 solve for the cross-price elasticity. If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
Formula to calculate Cross Elasticity of Demand. Implies two goods are complements. The cross elasticity of demand of butter with respect to margarine is 081 so 1 increase in the price of margarine will increase the demand for butter by 081. That means that when the price of product X increases the demand for product Y also increases. Were going from one good to another.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
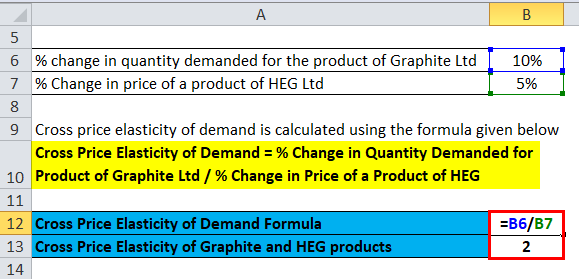
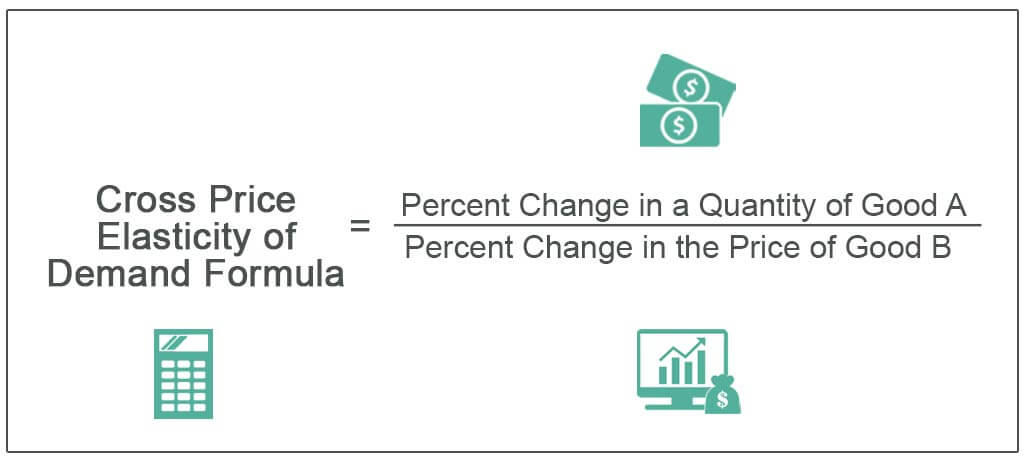
Examples of price elasticity of demand. ΔQ X Change in quantity demanded of product X. Types of cross elasticity of demand. Demand for the second good increases when the price of the first good increases. Original new price of product A original new quantity of product B change in quantitychange in price What does Positive Cross Price Elasticity Mean.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
Original new price of product A original new quantity of product B change in quantitychange in price What does Positive Cross Price Elasticity Mean. We identified it from well-behaved source. Examples of price elasticity of demand. The products are substitutes. You can calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand by dividing the percentage change in the demand quantity for an item by the percentage change in the price of the related item.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
For example McDonalds may increase the price of its products by 20 percent. Thats why we call it cross elasticity. Were going from one good to another. What does Negative Cross Price Elasticity Mean. Example 2 Cross price elasticity of demand 3000 4000 3000 4000 250 350 250 350 -1 7 -1 6 67 or 0857.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
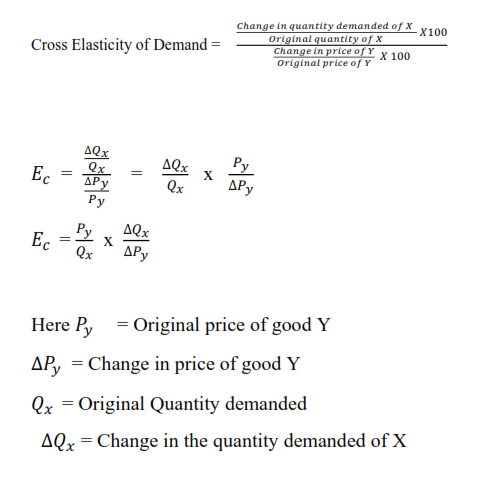
E_P_ydfracDelta Q_xdDelta P_y But. Original new price of product A original new quantity of product B change in quantitychange in price What does Positive Cross Price Elasticity Mean. We identified it from well-behaved source. Thats why we call it cross elasticity. The cross-price elasticity of demand Change in quantity of goods demand X Change in price of goods Y.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Consumers purchase more B when the price of A increases. Assume that the petrol price was INR 50 per liter which increased to INR 60 per liter. Positive Cross Price Elasticity occurs when the formula produces a result greater than 0. The products are substitutes. Cross Price Elasticity Formula.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
PY Price of the product. Here are a number of highest rated How To Calculate Cross Elasticity Of Demand MP3 upon internet. The cross elasticity of demand of butter with respect to margarine is 081 so 1 increase in the price of margarine will increase the demand for butter by 081. For example McDonalds may increase the price of its products by 20 percent. Cross price elasticity XED change in demand of product A change of price of product B 89 35 254.
 Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Source: wallstreetmojo.com
This indicates that the. P y Original price of product Y. That means that when the price of product X increases the demand for product Y also increases. For example McDonalds may increase the price of its products by 20 percent. Types of cross elasticity of demand.
 Source: theintactone.com
Source: theintactone.com
Examples of price elasticity of demand. The PED is calculated as below. Cross elasticity change in quantity demanded of good X change in the price of good Y Δ quantity demanded of goods x percentage change in quantity demanded Δ Price of goods y percentage change in Income of Consumer. Thats why we call it cross elasticity. Market equilibrium and consumer and producer surplus.
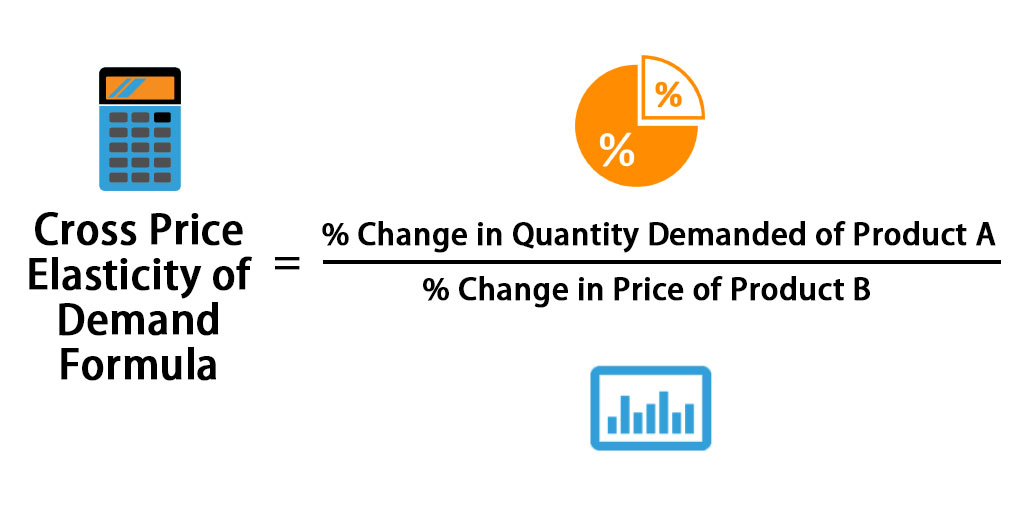 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
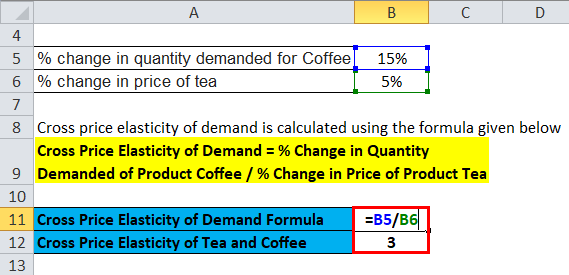
The percent change in the quantity of sprockets demanded is 105. If the cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods is positive it implies that the two goods are substitutes. A cross-price elasticity example could include two goods such as coffee and tea. Assume that the petrol price was INR 50 per liter which increased to INR 60 per liter. Q X Original quantity demanded of product X.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand 105 percent 286 percent 037 Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand 105 percent 286 percent 037. Its submitted by dispensation in the best field. Thats why we call it cross elasticity. Implies two goods are complements. PY Price of the product.
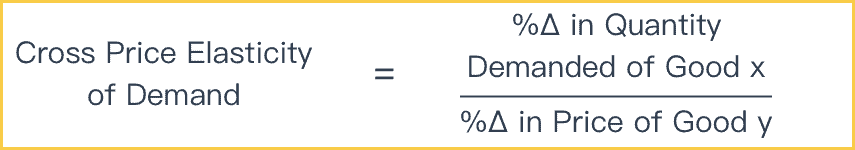 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Cross elasticity of demand XED quantifies the percentage change in quantity demand for an item after a change in the price. The cross-price elasticity of demand measures how the demand for one good is impacted by a change in the price of another good. If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other. A cross-price elasticity example could include two goods such as coffee and tea. So lets just say for simplicity roughly 5.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Implies two goods are complements. So if you have 67 divided by 5 you get to roughly 134. That means that when the price of product X increases the demand for product Y also increases. You can calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand by dividing the percentage change in the demand quantity for an item by the percentage change in the price of the related item. From this formula the following can be deduced.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
Consumers purchase more B when the price of A increases. This is a positive value greater than zero which indicates products A and B are substitutes of one another. How To Calculate Cross Elasticity Of Demand MP3 Download. Change in the quantity demandedprice. So lets just say for simplicity roughly 5.

Q X Original quantity demanded of product X. Implies two goods are complements. Cross price elasticity of demand XED QXQX PYPY Where QX Quantity of product X. Cross price elasticity XED change in demand of product A change of price of product B 89 35 254. Using the example values of 89 and 35 solve for the cross-price elasticity.
 Source: simplynotes.in
Source: simplynotes.in
ΔQ X Change in quantity demanded of product X. And in a mathematical formula it will look like this. If the cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods is positive it implies that the two goods are substitutes. Cross elasticity change in quantity demanded of good X change in the price of good Y Δ quantity demanded of goods x percentage change in quantity demanded Δ Price of goods y percentage change in Income of Consumer. A cross-price elasticity example could include two goods such as coffee and tea.
 Source: enotesworld.com
Source: enotesworld.com
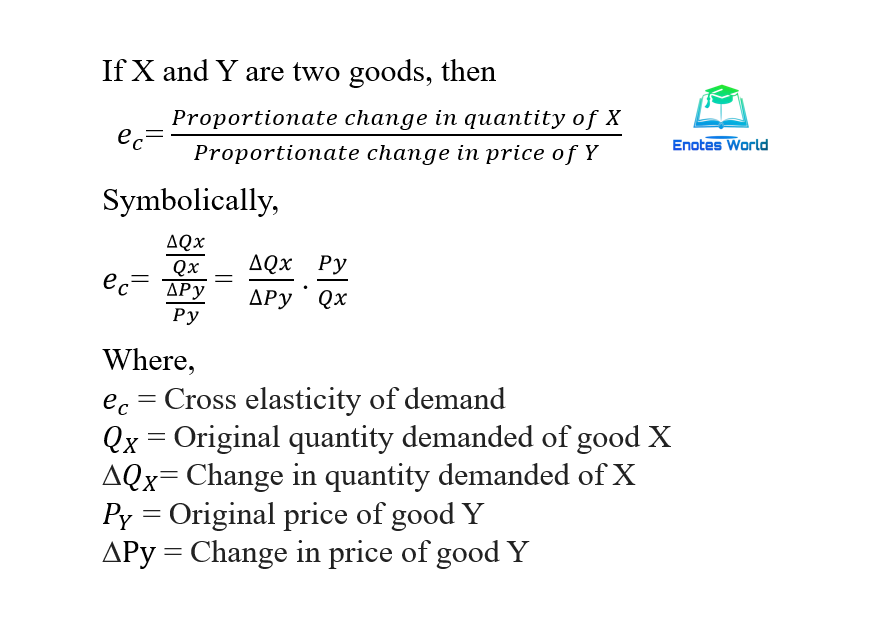
A cross-price elasticity example could include two goods such as coffee and tea. Here ec is the cross elasticity of demand. Were going from one good to another. Calculate the corresponding quantity of Good B demanded. The PED is calculated as below.
 Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Using the example values of 89 and 35 solve for the cross-price elasticity. Formula to calculate Cross Elasticity of Demand. The cross-price elasticity of demand measures how the demand for one good is impacted by a change in the price of another good. Using the example values of 89 and 35 solve for the cross-price elasticity. Here are some price elasticity of demand examples.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title cross price elasticity calculation example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.