Your Coefficient of elasticity formula econ images are ready in this website. Coefficient of elasticity formula econ are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Coefficient of elasticity formula econ files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for coefficient of elasticity formula econ images information connected with to the coefficient of elasticity formula econ topic, you have come to the right site. Our website always gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Coefficient Of Elasticity Formula Econ. Change in x change in y. The coefficient of price-elasticity of demand that is obtained at a point on the demand curve is called the point price- elasticity of demand and it is given by the formula 21 or 22. In other words quantity changes faster than price. PED change in the quantity demanded change in price.
 Elasticity Of Demand Ag Decision Maker From extension.iastate.edu
Elasticity Of Demand Ag Decision Maker From extension.iastate.edu
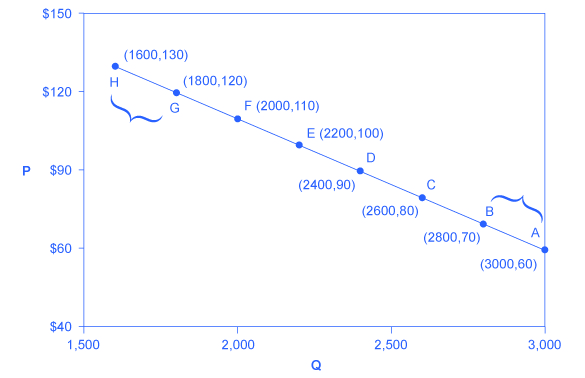
PED Q1 Q0 Q1 Q0 P1 P0 P1 P0 Q0 is the initial quantity. Change in quantity supplied in response to a 1 per cent change in price. Calculating an Elasticity Coefficient Consider the simple demand curve in Graph 1 to the right. Ped change in quantity demanded of good X change in price of good X. For example if the price of a good increases by 5 percent and the quantity demanded decreases by 5 percent then the elasticity at the initial price and quantity is -55 -1. Inverse relationship between quantity demanded and a change in the price.
In example above E S 12 gives that the supply would change by 12 per cent if price changes by 1 per cent.
Therefore by the formula 214 the coefficient of price-elasticity of supply at the point R p 10 q 300 would be. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic. Thats quite simple elasticity coefficient can be seen as a digit signifying the percentage change which can occur in one variable x when another variable y changes by one percent thus the formula for EC is. The coefficient of elasticity is used to quantify the concept of elasticity including price elasticity of demand price elasticity of supply income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand. The basic formula for calculating a coefficient is the QP means change. Q1 Q2 Q1 Q2 P1 P2 P1 P2 If the formula creates an.

Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. The equation can be further expanded to. It is commonly used in Market Research. PED Q1 Q0 Q1 Q0 P1 P0 P1 P0 Q0 is the initial quantity. Quantity has fallen by 33.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
If the factor is equal to 1 the percentage change in price is. Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. PED is the Price Elasticity of Demand QN is the new quantity demanded QI is the initial quantity demanded PN is the new price PI is the initial price. The coefficient can be calculated using the simple endpoint or midpoint formulas or with more. If the factor is equal to 1 the percentage change in price is.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Change in quantity supplied in response to a 1 per cent change in price. Ped change in quantity demanded of good X change in price of good X. The equation can be further expanded to. A numerical measure of the relative response of one variable to changes in another variable. Q1 Q2 Q1 Q2 P1 P2 P1 P2 If the formula creates an.

That is the coefficient may be equal to 1 1. This means that the slope of the demand curve equals minus one making it quite a simple. Economists usually refer to the coefficient of elasticity as the price elasticity of demand a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good computed as the percentage change in the quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. This formula is the formula for arc elasticity or the elasticity between two points on the demand curve. Then the coefficient for price elasticity of the demand of Product A is.
 Source: extension.iastate.edu
Source: extension.iastate.edu
Ped change in quantity demanded of good X change in price of good X. However economists often disregard the negative sign and report the elasticity as an absolute value. Inverse relationship between quantity demanded and a change in the price. It is commonly used in Market Research. This formula is the formula for arc elasticity or the elasticity between two points on the demand curve.

However economists often disregard the negative sign and report the elasticity as an absolute value. VVmaxSKsn1SKsndisplaystyle vfrac V_max SK_sn1SK_sn where n is the Hill coefficient and Ksdisplaystyle K_sis the half-saturation coefficient cf. Ed percentage change in Qd percentage change in Price 20 10 2. Inverse relationship between quantity demanded and a change in the price. This means that the slope of the demand curve equals minus one making it quite a simple.
 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
PED Q1 Q0 Q1 Q0 P1 P0 P1 P0 Q0 is the initial quantity. E -100062800 -214 Sometimes you may be required to solve for quantity or price and are given a point price elasticity of demand measureIn this case you need to backwards solve by rearranging the point price elasticity of demand formula to get the quantity or. The basic formula for calculating a coefficient is the QP means change. Q1 is the final quantity. Ed percentage change in Qd percentage change in Price 20 10 2.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
E -100062800 -214 Sometimes you may be required to solve for quantity or price and are given a point price elasticity of demand measureIn this case you need to backwards solve by rearranging the point price elasticity of demand formula to get the quantity or. Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. Result the equation for price elasticity of demand η equals. Price Elasticity Where Ep represents elasticity coefficient Q shows change in quantity demanded. If the price of Product A increased by 10 the quantity demanded decreased by 20.
 Source: amosweb.com
Source: amosweb.com
ΔQuantity ΔP rice 33 50 Δ Q u a n t i t y Δ P r i c e 33 50 067. Ped change in quantity demanded of good X change in price of good X. Formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand. E -100062800 -214 Sometimes you may be required to solve for quantity or price and are given a point price elasticity of demand measureIn this case you need to backwards solve by rearranging the point price elasticity of demand formula to get the quantity or. The formula for calculating this economic indicator is.

Q1 is the final quantity. The coefficient of price-elasticity of demand that is obtained at a point on the demand curve is called the point price- elasticity of demand and it is given by the formula 21 or 22. New specs require students to include the minus or plus signs along with the coefficient. The coefficient of elasticity is used to quantify the concept of elasticity including price elasticity of demand price elasticity of supply income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand. Quantity has fallen by 33.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
PED Q N - Q I Q N Q I 2 P N - P I P N P I 2 Where. The formula for calculating this economic indicator is. MichaelisMenten rate law then the elasticity coefficient is given by. For example if the price of a good increases by 5 percent and the quantity demanded decreases by 5 percent then the elasticity at the initial price and quantity is -55 -1. New specs require students to include the minus or plus signs along with the coefficient.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The coefficient of elasticity is used to quantify the concept of elasticity including price elasticity of demand price elasticity of supply income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand. Change in quantity supplied in response to a 1 per cent change in price. Price elasticity of demand. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic. If the price of Product A increased by 10 the quantity demanded decreased by 20.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
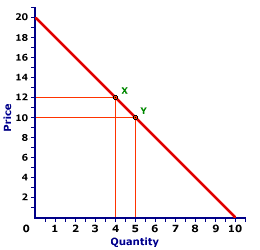
Calculating an Elasticity Coefficient Consider the simple demand curve in Graph 1 to the right. 1 P Q D h B. That is the coefficient may be equal to 1 1. ΔQuantity ΔP rice 33 50 Δ Q u a n t i t y Δ P r i c e 33 50 067. Quantity has fallen by 33.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
PED change in the quantity demanded change in price. If the price of Product A increased by 10 the quantity demanded decreased by 20. New specs require students to include the minus or plus signs along with the coefficient. That is the coefficient may be equal to 1 1. The coefficient can be calculated using the simple endpoint or midpoint formulas or with more.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Q1 Q2 Q1 Q2 P1 P2 P1 P2 If the formula creates an. In example above E S 12 gives that the supply would change by 12 per cent if price changes by 1 per cent. The basic formula for calculating a coefficient is the QP means change. If the price of Product A increased by 10 the quantity demanded decreased by 20. This type of analysis would make elasticity subject to direction which adds unnecessary complication.
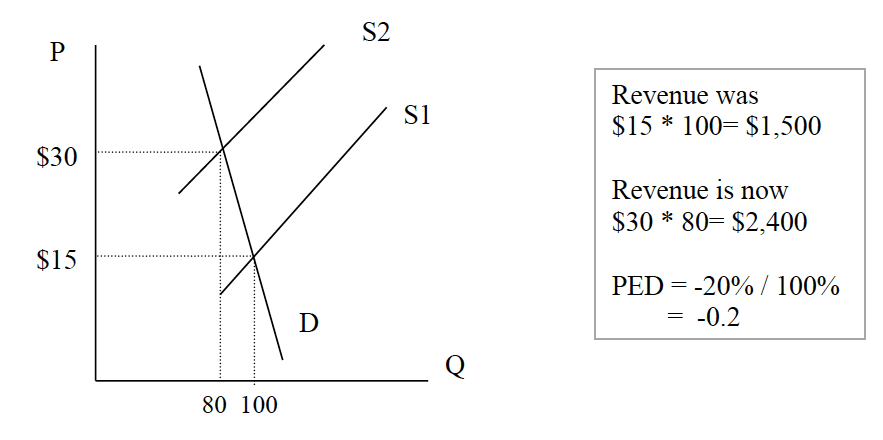 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The coefficient of price-elasticity of demand that is obtained at a point on the demand curve is called the point price- elasticity of demand and it is given by the formula 21 or 22. VVmaxSKsn1SKsndisplaystyle vfrac V_max SK_sn1SK_sn where n is the Hill coefficient and Ksdisplaystyle K_sis the half-saturation coefficient cf. If PED 0 demand is perfectly price inelastic. Quantity has fallen by 33. The coefficient can be calculated using the simple endpoint or midpoint formulas or with more.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The coefficient of elasticity is used to quantify the concept of elasticity including price elasticity of demand price elasticity of supply income elasticity of demand and cross elasticity of demand. Therefore by the formula 214 the coefficient of price-elasticity of supply at the point R p 10 q 300 would be. 1 P Q D h B. In other words quantity changes faster than price. PED will normally be negative ie.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Cross price elasticity of demand midpoint formula often produces three outcomes based on the variation of either the demand and price. In other words quantity changes faster than price. In example above E S 12 gives that the supply would change by 12 per cent if price changes by 1 per cent. Q1 is the final quantity. In other words quantity changes slower than price.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title coefficient of elasticity formula econ by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.