Your Calculate elasticity of price tr and mr images are ready in this website. Calculate elasticity of price tr and mr are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Calculate elasticity of price tr and mr files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for calculate elasticity of price tr and mr images information related to the calculate elasticity of price tr and mr keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our website frequently provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
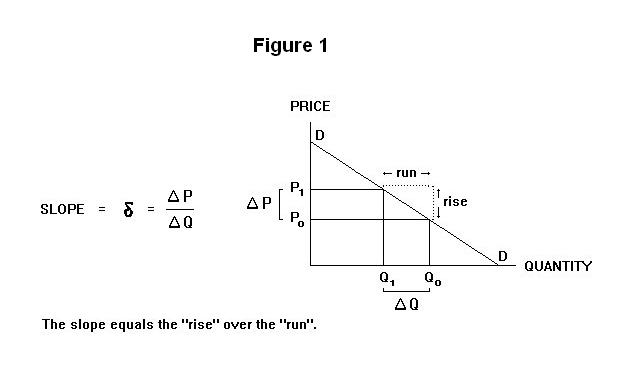
Calculate Elasticity Of Price Tr And Mr. First we calculate the change in revenue by multiplying the baked volume by a new price and then subtracting the original revenue. TR 1 Price x Quantity 20 x 15 Rs. The smaller the price elasticity of demand the greater the price mark-up. From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue.
 Elasticity Total Revenue And Marginal Revenue From economics.utoronto.ca
Elasticity Total Revenue And Marginal Revenue From economics.utoronto.ca
Also explain the relationship between AR and MR. Total revenue is calculated as follows. Therefore the total revenue is. This is very useful relationship and should be noted carefully. The price of the product is 50. From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue.
Change in Total Revenue 149 51 150 50 7599 7500 99.
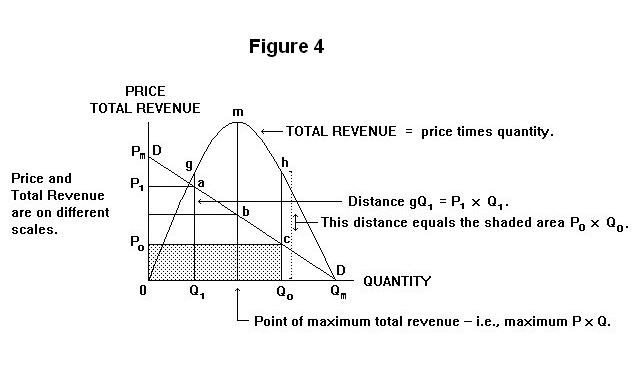
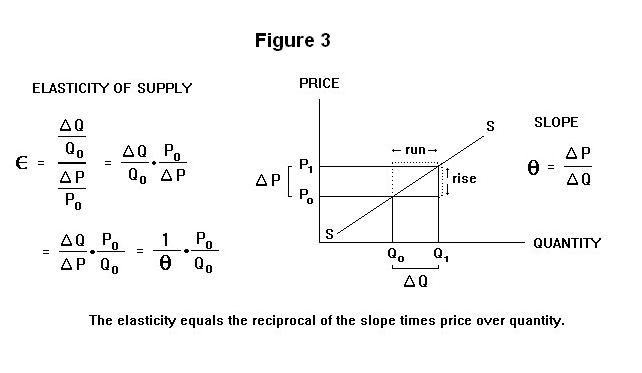
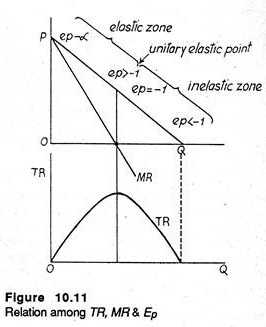
The smaller the price elasticity of demand the greater the price mark-up. The elasticity of price Percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service divided by the percentage change in price. The expression shows that to maximise profit the price mark-up should equal the inverse of the demand elasticity. Total revenue is calculated as follows. P MC 1 1 E p. A We can find the price elasticity of demand as follows.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
The price of the product is 50. From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue. From the definition of marginal revenue we know that. TR AR MR and Elasticity of demand. Three Types of Revenue AR MR TR and Price Elasticity E.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Economics QA Library From the given table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue. Therefore the total revenue is. TR AR MR and Elasticity of demand. Marginal revenue is the derivative of total revenue with respect to demand. 50 - 50 0 553 Page 3 554 If MR 0 TR is at its maximum.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
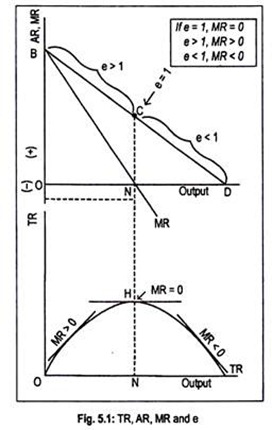
MR AR e 1e The relationship between the AR curve and MR curve depends upon the elasticity of AR curve AR DD Price 1. From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue. The relationship among total average and marginal revenues under imperfect competition is explained with the help of a table 51 and Fig. Marginal Revenue MR Divide the change in TR by the change in quantity sold. Therefore the total revenue is.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
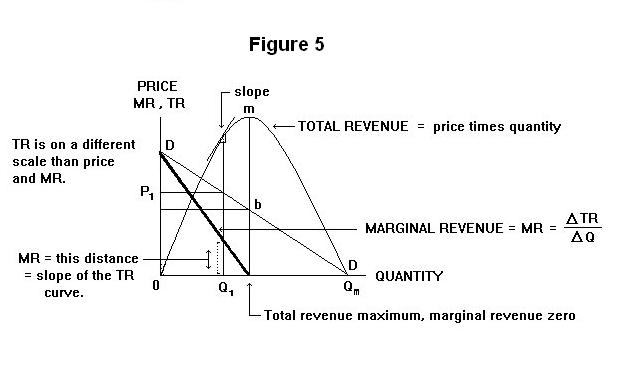
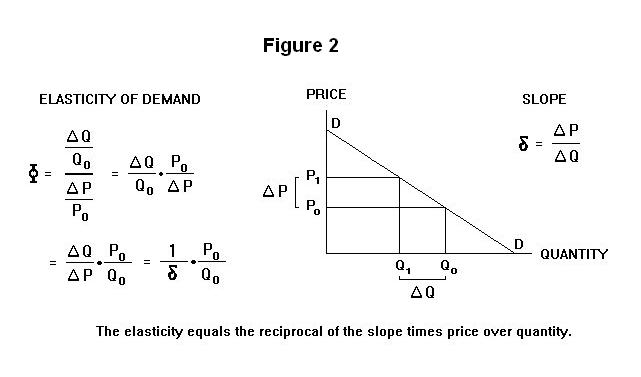
Total Revenue TR Price P Marginal Revenue MR Dollars Quantity Demanded Q Dollars Price Elasticity of Demand Dollars 5000 4500 1. And a change in quantity is one. E_ddfrac Delta Q Delta Pdfrac dfrac Q_2-Q_1 05. 18 and the quantity demanded is 16 units. Change in Total Revenue 149 51 150 50 7599 7500 99.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Instead use what you know about elasticity along different segments of a linear demand curve to determine the elasticity of each price-quantity combination. A We can find the price elasticity of demand as follows. And a change in quantity is one. This is very useful relationship and should be noted carefully. The expression shows that to maximise profit the price mark-up should equal the inverse of the demand elasticity.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
P MC 1 1 E p. The left hand side is the mark-up of price over marginal cost expressed as percentage of price. Three Types of Revenue AR MR TR and Price Elasticity E. The elasticity of price Percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service divided by the percentage change in price. MR dTR dQ.

Eco point price elasticity of demand problems. It is because horizontal TR means when price falls quantity demanded rises in the same proportion. Price Quantity Total Revenue Marginal Revenue 6 0 5 100 4 200 3 300 2 400 1 500 0 600. E_ddfrac Delta Q Delta Pdfrac dfrac Q_2-Q_1 05. MR n TR n TR n-1.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Price Quantity Total Revenue Marginal Revenue 6 0 5 100 4 200 3 300 2 400 1 500 0 600. Also explain the relationship between AR and MR. The price of the product is 50. TR AR MR and Elasticity of demand. The elasticity of price Percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service divided by the percentage change in price.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Price Quantity Total Revenue Marginal Revenue 6 0 5 100 4 200 3 300 2 400 1 500 0 600. From the schedule provided below calculate the total revenue demand curve and the price elasticity of demand. 4000 3500 3 3000 4 2500 2000 1500 10. Define elasticity of supply and find the price from the given statement. From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
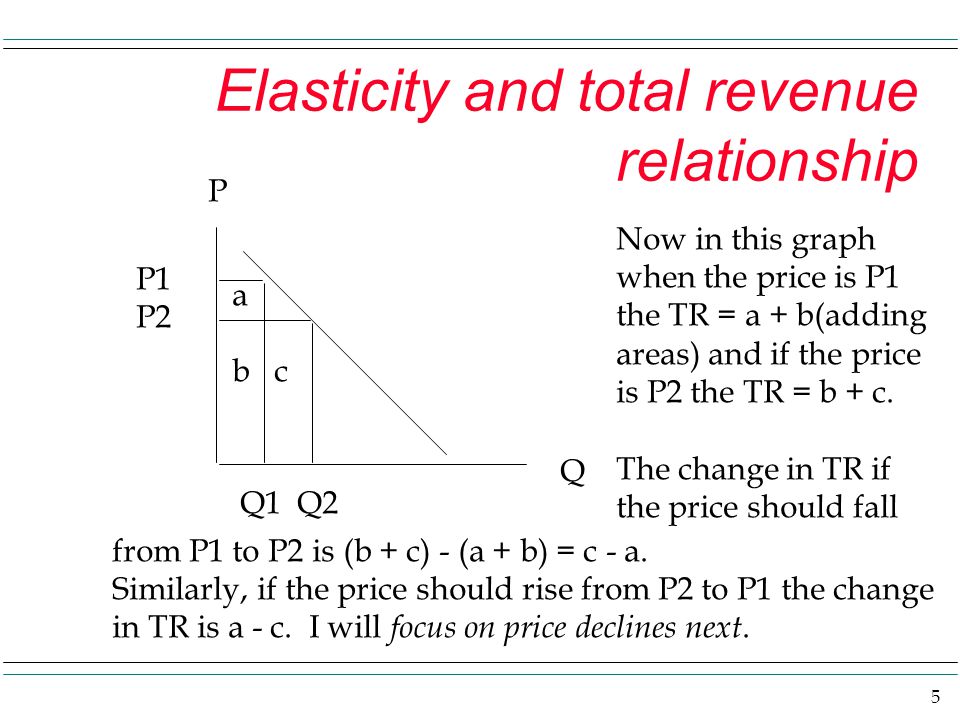
TR 2 Price x Quantity 18 x 16 Rs. Therefore the total revenue is. It is because horizontal TR means when price falls quantity demanded rises in the same proportion. Marginal revenue is the derivative of total revenue with respect to demand. We are now in a position to describe the relationship between three types of revenue namely AR MR and TR on the one side and price elasticity of demand on the other.
 Source: ar.pinterest.com
Source: ar.pinterest.com
Price Quantity Total Revenue Marginal Revenue 6 0 5 100 4 200 3 300 2 400 1 500 0 600. It is because horizontal TR means when price falls quantity demanded rises in the same proportion. Eco point price elasticity of demand problems. This is very useful relationship and should be noted carefully. If Es of a good is 2 and a firm supplies 200 units at price of Rs 8 per unit then at what price will the firm supply 250 units.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The left hand side is the mark-up of price over marginal cost expressed as percentage of price. Ii When TR is a horizontal straight line MR is zero. The elasticity of price PED. The expression shows that to maximise profit the price mark-up should equal the inverse of the demand elasticity. TR 2 Price x Quantity 18 x 16 Rs.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
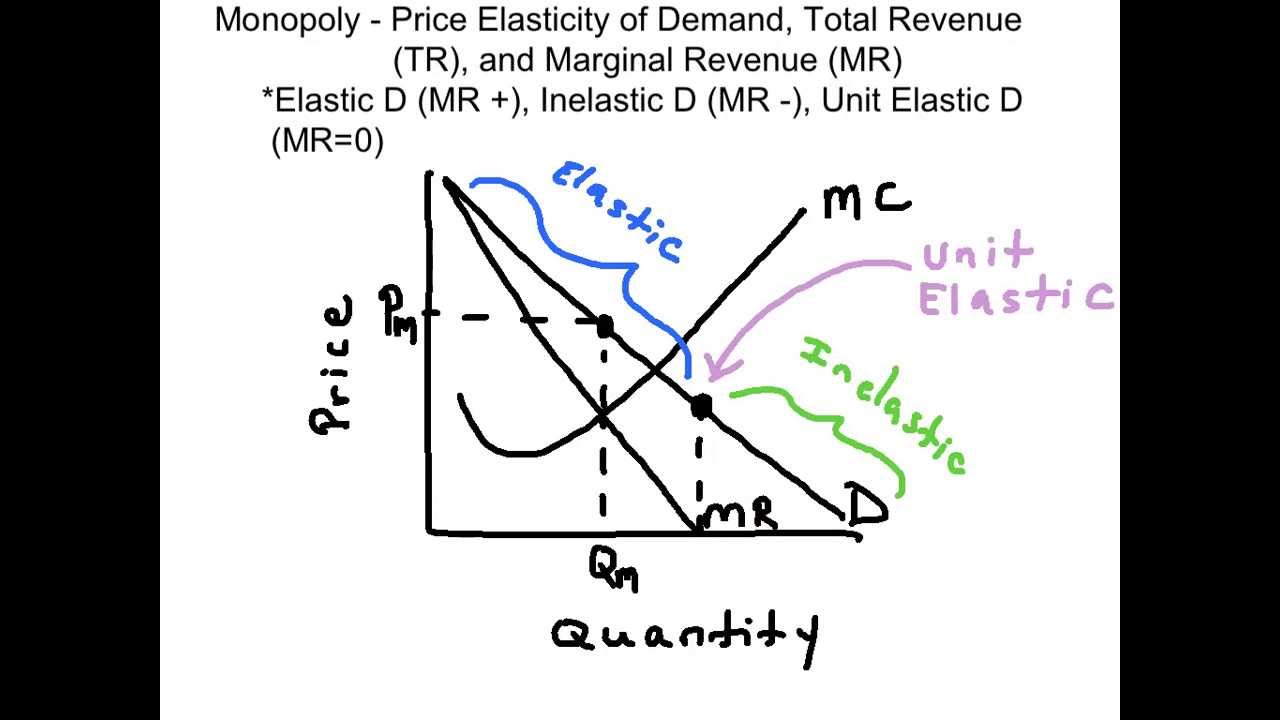
Total revenue is calculated as follows. Three Types of Revenue AR MR TR and Price Elasticity E. Ii When TR is a horizontal straight line MR is zero. From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue. 56 Fixed cost demand and profit TC 20 TR QP 24Q - 3Q2 MR TR 24 - 6Q If MR 0 then Q 4 if Q 4.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
56 Fixed cost demand and profit TC 20 TR QP 24Q - 3Q2 MR TR 24 - 6Q If MR 0 then Q 4 if Q 4. Total revenue is calculated as follows. 5 Q 2 Q 1 P 2 P 1 0. And a change in quantity is one. Demand is elastic inelastic or unit elastic.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
For example for AR 10 and e 2 Thus for e I MR 0. The left hand side is the mark-up of price over marginal cost expressed as percentage of price. And a change in quantity is one. 18 and the quantity demanded is 16 units. The demand curve is given by.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Calculate the elasticity of supply if a 15 increase in the price of soya bean oil increases. The price of the product is 50. With the help of the above formula it is possible to find MR given AR price and elasticity of demand. Instead use what you know about elasticity along different segments of a linear demand curve to determine the elasticity of each price-quantity combination. The relation between AR MR and elasticity of demand e can now be written as.

Total revenue is calculated as follows. For example for AR 10 and e 2 Thus for e I MR 0. Also explain the relationship between AR and MR. Change in Total Revenue 149 51 150 50 7599 7500 99. Scenario 2 Price is Rs.
 Source: wisdomjobs.com
Source: wisdomjobs.com
From the give table calculate Elasticity of Price Total Revenue and Marginal Revenue. Marginal revenue is the derivative of total revenue with respect to demand. Calculate the elasticity of supply if a 15 increase in the price of soya bean oil increases. Price Quantity Total Revenue Marginal Revenue 6 0 5 100 4 200 3 300 2 400 1 500 0 600. First we calculate the change in revenue by multiplying the baked volume by a new price and then subtracting the original revenue.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title calculate elasticity of price tr and mr by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.