Your Aggregate supply curve shift to right images are ready. Aggregate supply curve shift to right are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Aggregate supply curve shift to right files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for aggregate supply curve shift to right pictures information linked to the aggregate supply curve shift to right interest, you have come to the right site. Our site always gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
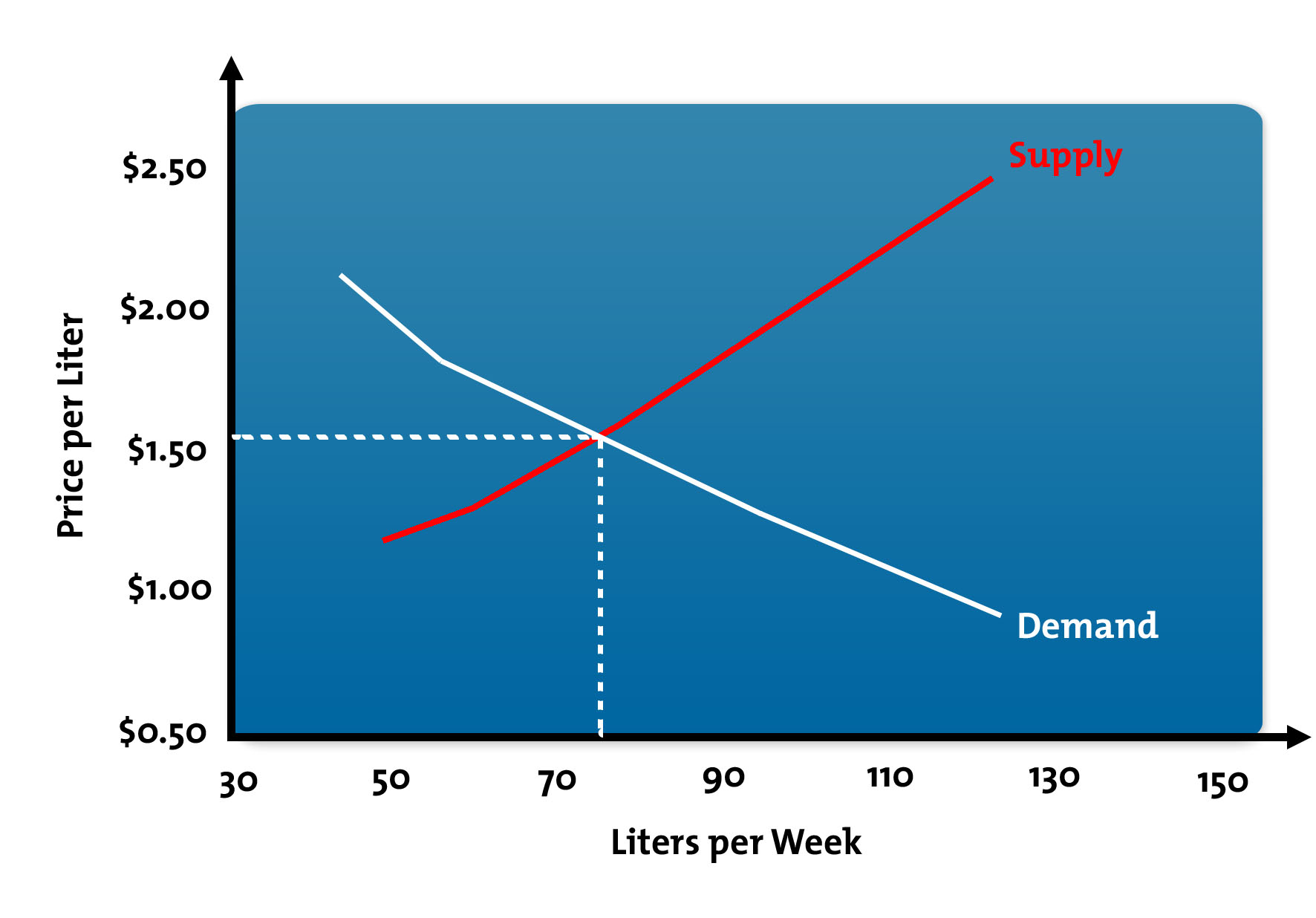
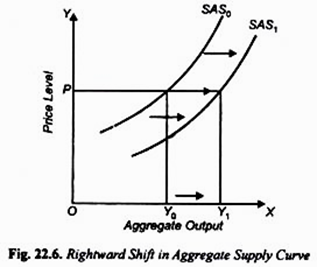
Aggregate Supply Curve Shift To Right. If labor or another input suddenly becomes cheaper there would be a supply shock such that supply curve may shift outward causing the equilibrium price in to drop and the equilibrium quantity to increase. The aggregate supply curve may shift to the right or to the left as shown in Fig. New raw materials mean that new sources of reserves for primary commodities such as oil and gold are found. The effects of reduction in taxes or regulationslaws can also shift the AS curve right Amacher 2019.
 Shape Of Aggregate Supply Curves As Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Shape Of Aggregate Supply Curves As Economics Help From economicshelp.org
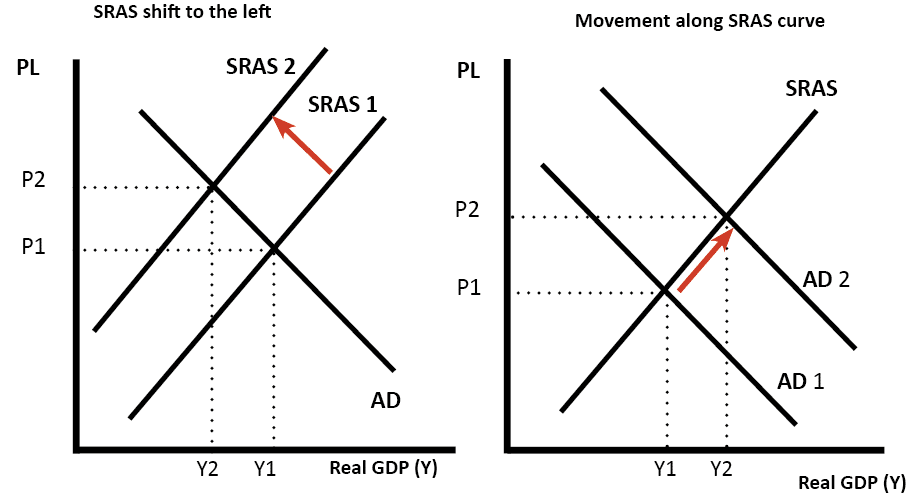
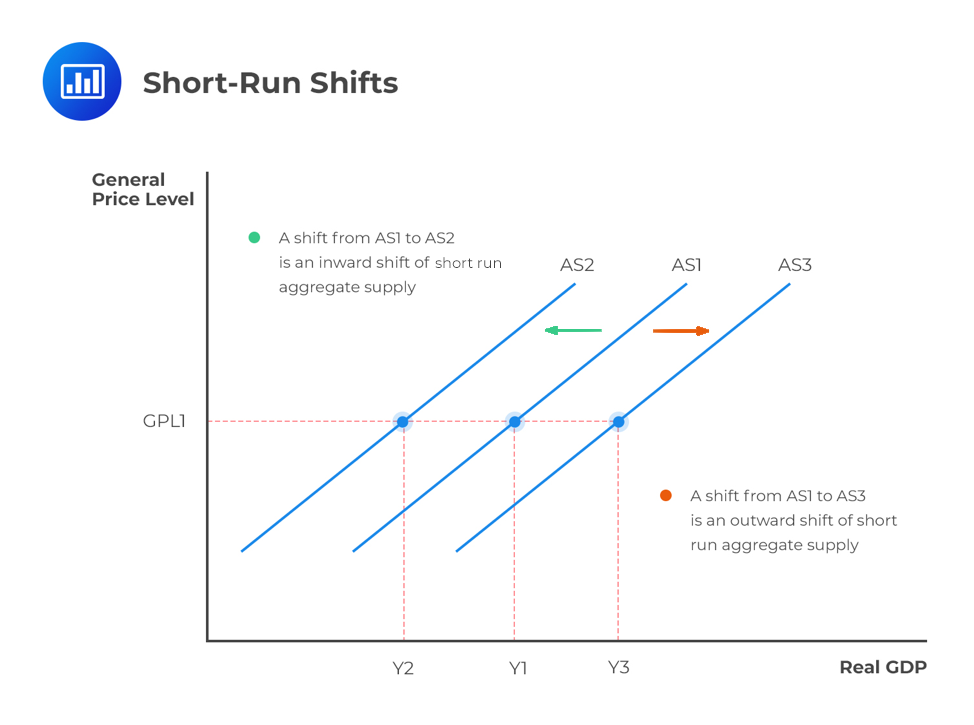
Shifts in the Short-run Aggregate Supply In the short-run examples of events that shift the aggregate supply curve to the right include a decrease in wages an increase in physical capital stock or advancement of technology. The two ADAS diagrams below show shifts in productivity over two time periods. This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS1. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level producers supply a lower quantity of real GDP. An increase in these reserves shifts the AS curves right. This is called a positive supply shock.
Shifts in the aggregate supply curve represent changes in aggregate supply.
The reason is that the same productive resources are still available to the economy but at least some are used to produce greater output as the result of increased productivity. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level producers supply a greater quantity of real GDP. If there must be a choice between the two I would go with demand-based growth efforts as they are much more predictable Strickland 2012. Answer 1 of 2. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. With more resources it is possible to produce more final goods and.
 Source: revisionguru.co.uk
Source: revisionguru.co.uk
Chapter 28 Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand and Inflation. An increase in these reserves shifts the AS curves right. Here the key lesson is that a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right leads to a greater real GDP and to upward pressure on the price level. Conversely a shift of aggregate demand to the left leads to a lower real GDP and a lower price level. That change will shift the AS curve to.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. Shifts in the Short-run Aggregate Supply In the short-run examples of events that shift the aggregate supply curve to the right include a decrease in wages an increase in physical capital stock or advancement of technology. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level producers supply a greater quantity of real GDP. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level producers supply a lower quantity of real GDP. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level producers supply a lower quantity of real GDP.
 Source: college.cengage.com
Source: college.cengage.com
When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level producers supply a lower quantity of real GDP. Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. The aggregate supply curve shows the amount of goods that can be produced at different price levels. Pe and QYrepresent the equilibrium price level and full employment GDP. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible.
 Source: textbook.stpauls.br
Source: textbook.stpauls.br
The effects of reduction in taxes or regulationslaws can also shift the AS curve right Amacher 2019. Aggregate supply is the total value of goods and services produced in an economy. The original equilibrium E0 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS0. The Fed shifts to a more expansionary monetary policy. Shifts in Aggregate Supply a The rise in productivity causes the SRAS curve to shift to the right.
 Source: college.cengage.com
Source: college.cengage.com
Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. The aggregate supply curve may shift labor market disequilibrium or labor market equilibrium. That change will shift the AS curve to.
 Source: bohatala.com
Source: bohatala.com
When the economy reaches its level of full capacity full employment when the economy is on the production possibility frontier the. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. Answer 1 of 2. That change will shift the AS curve to.
 Source: textbook.stpauls.br
Source: textbook.stpauls.br
A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. The original equilibrium E0 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS0. We defined the AS curve as showing the quantity of real GDP producers will supply at any aggregate price level. Shifts in the aggregate supply curve represent changes in aggregate supply.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases. Supply shocks are events that shift the aggregate supply curve. If there must be a choice between the two I would go with demand-based growth efforts as they are much more predictable Strickland 2012. The government raises income taxes. This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS1.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
When SRAS shifts right then the new equilibrium E1 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS1 and then yet another equilibrium E2 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS2. The aggregate supply curve shows the amount of goods that can be produced at different price levels. Lets go through each of these examples of possible aggregate supply curve shifts causes. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level producers supply a lower quantity of real GDP. The two ADAS diagrams below show shifts in productivity over two time periods.
 Source: enotes.com
Source: enotes.com
The effects of reduction in taxes or regulationslaws can also shift the AS curve right Amacher 2019. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases. The aggregate supply curve may shift labor market disequilibrium or labor market equilibrium. The aggregate supply curve may shift to the right or to the left as shown in Fig.
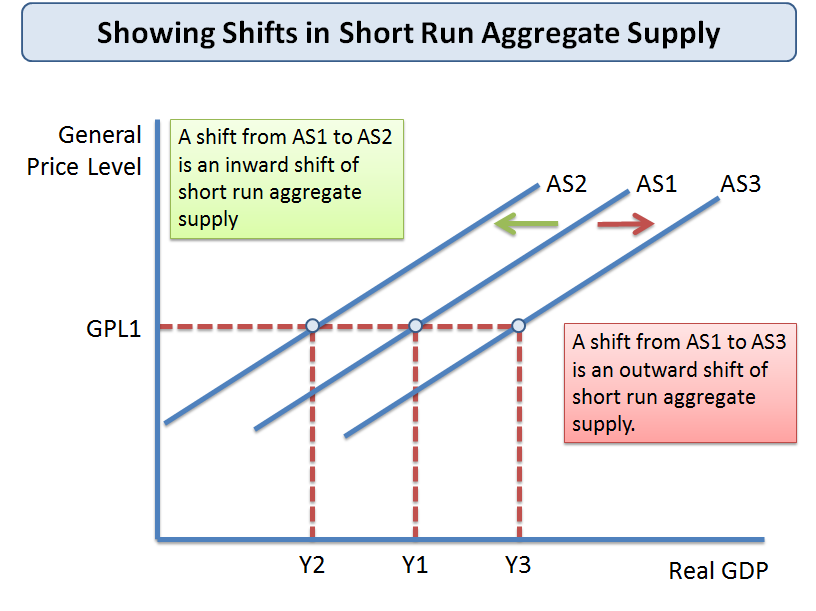 Source: gpeco.weebly.com
Source: gpeco.weebly.com
Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation. Here the key lesson is that a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right leads to a greater real GDP and to upward pressure on the price level. If labor or another input suddenly becomes cheaper there would be a supply shock such that supply curve may shift outward causing the equilibrium price in to drop and the equilibrium quantity to increase.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves. An increase in these reserves shifts the AS curves right. Short run aggregate supply aggregate demand and the long run aggregate supply curves. Here the key lesson is that a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right leads to a greater real GDP and to upward pressure on the price level. This is called a positive supply shock.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Short run aggregate supply aggregate demand and the long run aggregate supply curves. Here the key lesson is that a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right leads to a greater real GDP and to upward pressure on the price level. The reason is that the same productive resources are still available to the economy but at least some are used to produce greater output as the result of increased productivity. Shifts in the Short-run Aggregate Supply In the short-run examples of events that shift the aggregate supply curve to the right include a decrease in wages an increase in physical capital stock or advancement of technology. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level producers supply a lower quantity of real GDP.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. Here the key lesson is that a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right leads to a greater real GDP and to upward pressure on the price level. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. Such shifts occur due to changes in non-price determinants of aggregate supply viz factor prices such as wage rates costs of raw materials etc technology and expectations of producers.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
We defined the AS curve as showing the quantity of real GDP producers will supply at any aggregate price level. Lets go through each of these examples of possible aggregate supply curve shifts causes. The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level producers supply a greater quantity of real GDP. Yes to the right.
 Source: analystprep.com
Source: analystprep.com
The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases. This is called a positive supply shock. Yes to the right. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve.
 Source: ifioque.com
Source: ifioque.com
Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right as productivity increases or the price of key inputs falls making a combination of lower inflation higher output and lower unemployment possible. When SRAS shifts right then the new equilibrium E1 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS1 and then yet another equilibrium E2 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS2. The figuregiven below depictsthe various ways in which the SRAS and LRAS curves can shift. With more resources it is possible to produce more final goods and.
 Source: econindepth.weebly.com
Source: econindepth.weebly.com
When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level producers supply a greater quantity of real GDP. Pe and QYrepresent the equilibrium price level and full employment GDP. The figuregiven below depictsthe various ways in which the SRAS and LRAS curves can shift. Aggregate supply is the total value of goods and services produced in an economy. Which of the following would cause the AD curve to shift to the right.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title aggregate supply curve shift to right by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.