Your Aggregate supply curve shift right explain images are ready. Aggregate supply curve shift right explain are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Aggregate supply curve shift right explain files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for aggregate supply curve shift right explain pictures information linked to the aggregate supply curve shift right explain topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
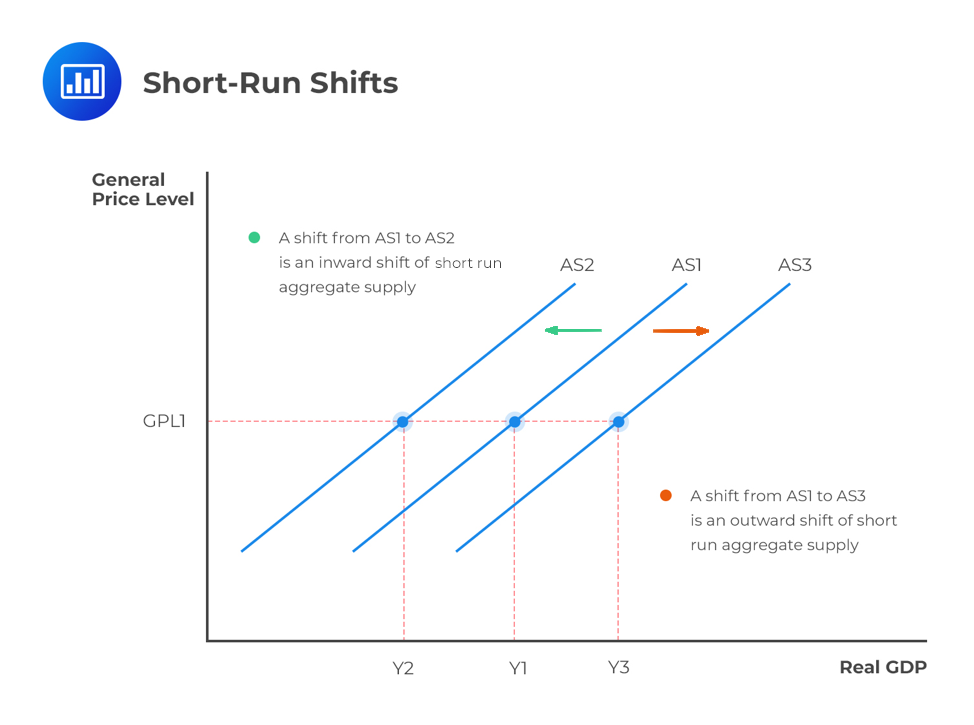
Aggregate Supply Curve Shift Right Explain. Such shifts occur due to changes in non-price determinants of aggregate supply viz factor prices such as wage rates costs of raw materials etc technology and expectations of producers. Cost of labour wages taxes regulation. Thus menu costs are incurred with moving along the SRAS the real GDP amount produced in the economy increases thus. Supply shocks are events that shift the aggregate supply curve.
 Movements Along And Shifts In Aggregate Demand And Supply Curves Analystprep Cfa Exam Study Notes From analystprep.com
Movements Along And Shifts In Aggregate Demand And Supply Curves Analystprep Cfa Exam Study Notes From analystprep.com
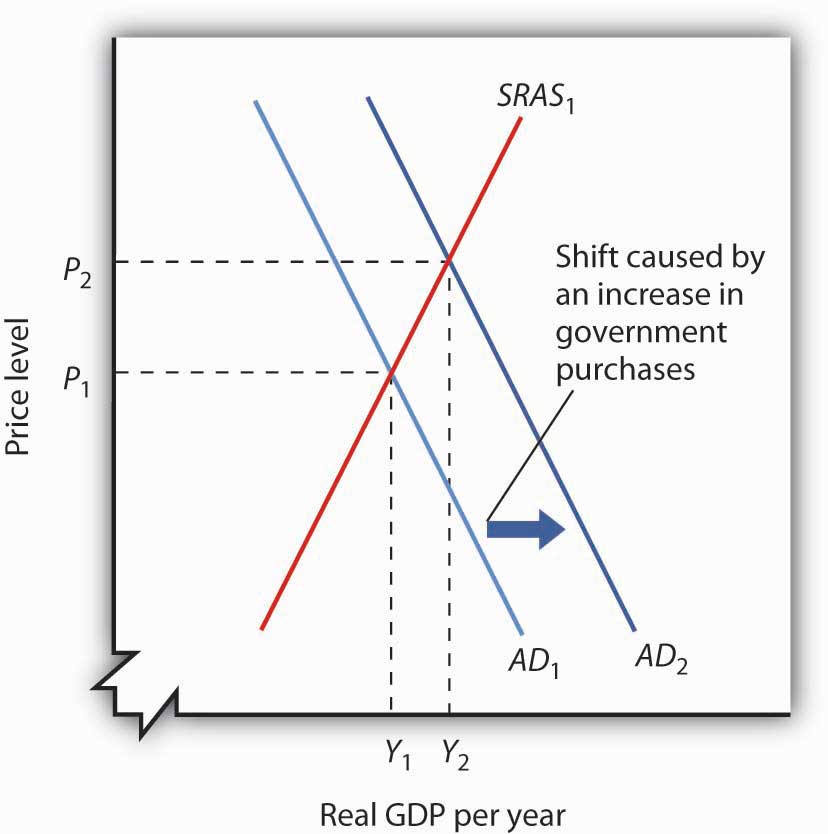
The Fed shifts to a more expansionary monetary policy. The effects of reduction in taxes or regulationslaws can also shift the AS curve right Amacher 2019. Cost of labour wages taxes regulation. The tax cut by increasing consumption shifts the AD curve to the right. Thus menu costs are incurred with moving along the SRAS the real GDP amount produced in the economy increases thus. Such shifts occur due to changes in non-price determinants of aggregate supply viz factor prices such as wage rates costs of raw materials etc technology and expectations of producers.
Levels of tax and subsidies.
Clearly substitution of one good for another cannot explain a shift in overall demand given a shift in overall prices. Generally aggregate supply and the price level have a positive relationship. Chapter 28 Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand and Inflation. For example lower wages lower production costs increase profits and encourage businesses to increase output. Explain the factors of shifting AD curve. When the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts right it represents.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. Pushing the economy beyond normal capacity. A lower input price. The government raises income taxes. An increase in any category of costs will tend to shift the aggregate supply curve upwards.

Two graphs show how aggregate supply can shift and how these shifts affect points of equilibrium. If there must be a choice between the two I would go with demand-based growth efforts as they are much more predictable Strickland 2012. With more resources it is possible to produce more final goods and. The government raises income taxes. Price of raw materials eg.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
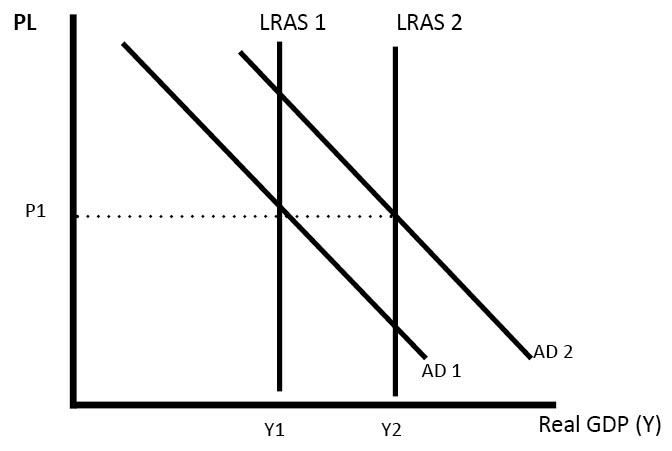
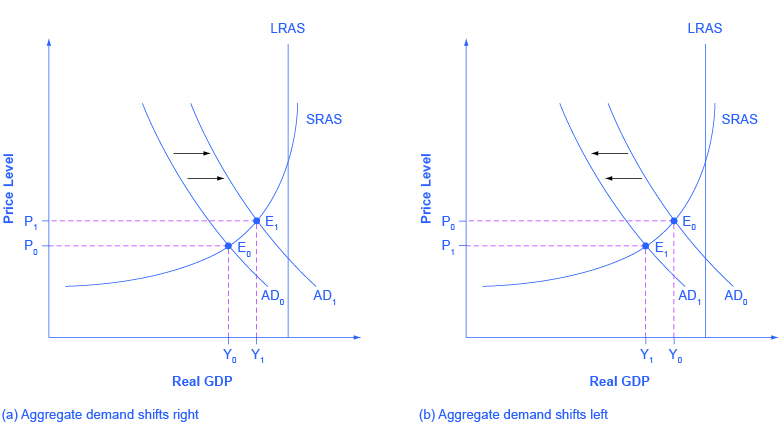
Chapter 28 Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand and Inflation. In the diagram on the right higher AD has led to higher price level and a movement along the SRAS. The government raises income taxes. This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS1. We defined the AS curve as showing the quantity of real GDP producers will supply at any aggregate price level.
 Source: textbook.stpauls.br
Source: textbook.stpauls.br
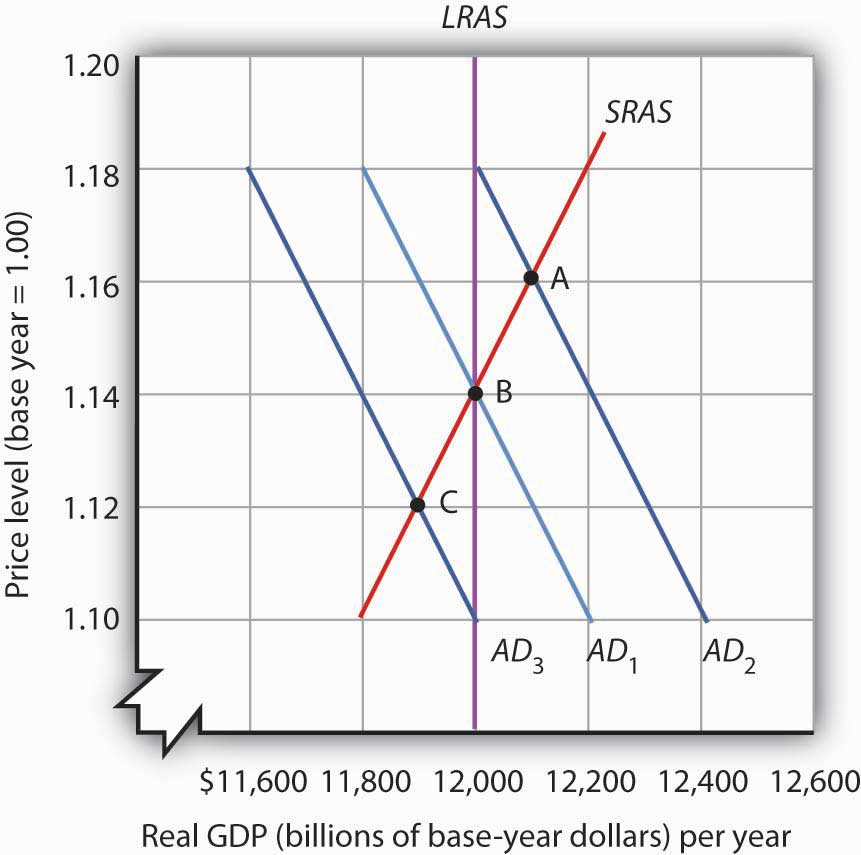
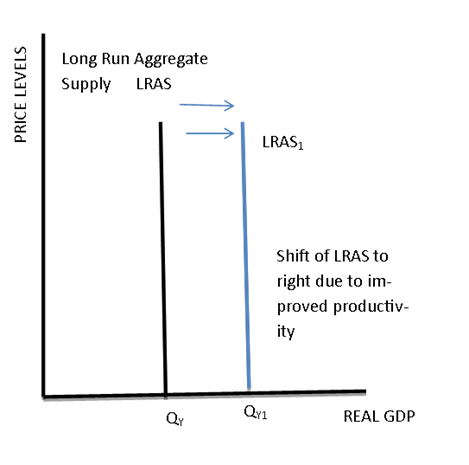
This is called a positive supply shock. Assuming the price level are unchanged the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right when. The aggregate supply curve will shift out to the right as productivity increases. Pushing the economy beyond normal capacity. The original equilibrium E 0 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS 0.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
This might include costs of raw materials transportation or energy costs labor costs or even business taxes. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. If there must be a choice between the two I would go with demand-based growth efforts as they are much more predictable Strickland 2012. The aggregate supply and aggregate demand framework however offers a complementary rationale as illustrated in Figure 2. The graph on the left shows how productivity increases will shift aggregate supply to the right.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Substitution Effects Cannot Explain the Downward slope of the AD Curve The Aggregate Demand Curve depicts the effects on OVERALL DEMAND given a change in the PRICES OF ALL GOODS AND SERVICES. Cost of labour wages taxes regulation. Movements of either AS or AD will result in a different equilibrium output and price level. The effects of reduction in taxes or regulationslaws can also shift the AS curve right Amacher 2019. Levels of tax and subsidies.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The effects of reduction in taxes or regulationslaws can also shift the AS curve right Amacher 2019. Two graphs show how aggregate supply can shift and how these shifts affect points of equilibrium. Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. Levels of tax and subsidies. The government raises income taxes.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
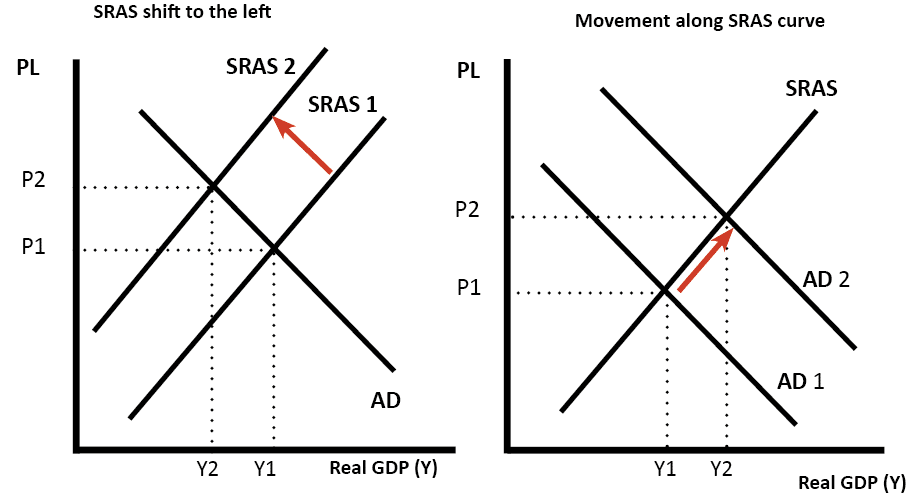
Shifts in Aggregate Supply a The rise in productivity causes the SRAS curve to shift to the right. This is called a positive supply shock. It will shift back to the left as the price of key inputs rises and will shift out to the right if the price of key inputs falls. Aggregate supply also known as total output is the total supply of goods and services produced within an economy in a given period at a given overall priceThe aggregate supply curveAS describes the relationship between price levels and the quantity of output that firms are willing to provide. The graph on the right shows how higher prices for key inputs will shift aggregate supply to the left.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
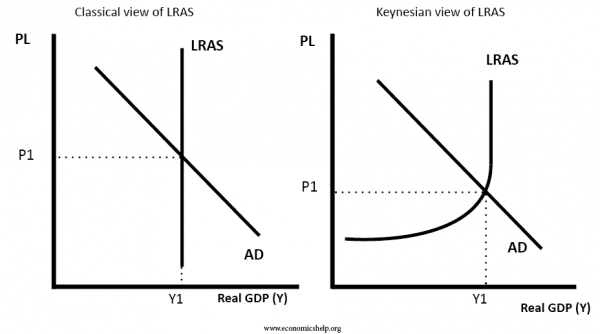
As a result the SRAS shifts the curve to the right which is upward sloping with a positive aggregate output as shown below. The aggregate supply curve will shift out to the right as productivity increases. The graph on the left shows how productivity increases will shift aggregate supply to the right. Which of the following would cause the AD curve to shift to the right. Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves.
 Source: ifioque.com
Source: ifioque.com
Factors affecting the SRAS curve. Long Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium is the meeting point of the three curves. A lower input price. It will shift back to the left as the price of key inputs rises and will shift out to the right if the price of key inputs falls. The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Explain the factors of shifting AD curve. Aggregate supply also known as total output is the total supply of goods and services produced within an economy in a given period at a given overall priceThe aggregate supply curveAS describes the relationship between price levels and the quantity of output that firms are willing to provide. Assuming the price level are unchanged the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right when. Classical view of long run aggregate supply. This shifts the long run aggregate supply curve to the right to LRAS1.
 Source: textbook.stpauls.br
Source: textbook.stpauls.br
Chapter 28 Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand and Inflation. Thus menu costs are incurred with moving along the SRAS the real GDP amount produced in the economy increases thus. The Fed shifts to a more expansionary monetary policy. In the diagram on the right higher AD has led to higher price level and a movement along the SRAS. Such shifts occur due to changes in non-price determinants of aggregate supply viz factor prices such as wage rates costs of raw materials etc technology and expectations of producers.

Explain the factors of shifting AS curve. An increase in any category of costs will tend to shift the aggregate supply curve upwards. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth. If there must be a choice between the two I would go with demand-based growth efforts as they are much more predictable Strickland 2012. We defined the AS curve as showing the quantity of real GDP producers will supply at any aggregate price level.
 Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
As a result the SRAS shifts the curve to the right which is upward sloping with a positive aggregate output as shown below. An increase in any category of costs will tend to shift the aggregate supply curve upwards. The graph on the right shows how higher prices for key inputs will shift aggregate supply to the left. Firms become pessimistic about the future growth of GDP sales and profits. The graph on the left shows how productivity increases will shift aggregate supply to the right.
 Source: web.mnstate.edu
Source: web.mnstate.edu
Assuming the price level are unchanged the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right when. Assuming the price level are unchanged the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right when. A lower input price. Differentiate between the change and shift in AD and AS. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth.
 Source: albert.io
Source: albert.io
Movements of either AS or AD will result in a different equilibrium output and price level. Factors affecting the SRAS curve. The tax cut by increasing consumption shifts the AD curve to the right. The Fed shifts to a more expansionary monetary policy. Differentiate between the change and shift in AD and AS.
 Source: analystprep.com
Source: analystprep.com
The original equilibrium E 0 is at the intersection of AD and SRAS 0. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. The graph on the right shows how higher prices for key inputs will shift aggregate supply to the left. The original equilibrium during a recession is at point E 0 relatively far from the full employment level of output. For example lower wages lower production costs increase profits and encourage businesses to increase output.
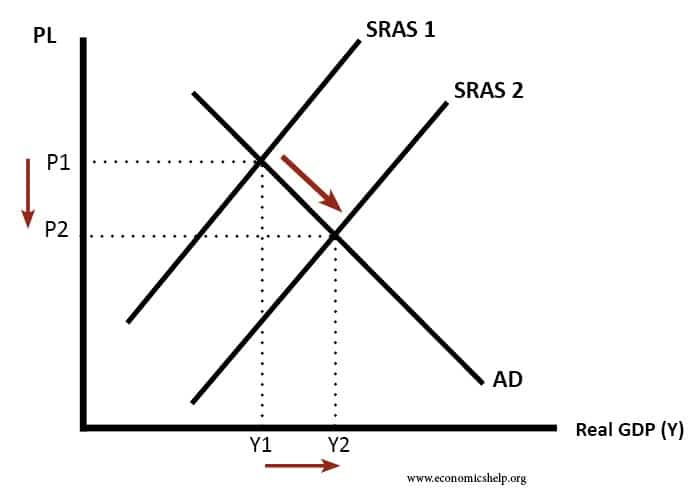 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
If there must be a choice between the two I would go with demand-based growth efforts as they are much more predictable Strickland 2012. The aggregate supply curve will shift out to the right as productivity increases. Short run aggregate supply aggregate demand and the long run aggregate supply curves. Which of the following would cause the AD curve to shift to the right. An increase in any category of costs will tend to shift the aggregate supply curve upwards.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title aggregate supply curve shift right explain by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






