Your Aggregate supply and demand graph examples images are ready. Aggregate supply and demand graph examples are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Aggregate supply and demand graph examples files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for aggregate supply and demand graph examples pictures information linked to the aggregate supply and demand graph examples keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our website frequently provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Aggregate Supply And Demand Graph Examples. What causes the AD curve and aggregate supply AS curve to shift respectively. Movements along It The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between the price level and real GDP demanded holding everything else constant. The AD-AS aggregate demand-aggregate supply model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level. In the long-run increases in aggregate demand cause the price of a good or service to increase.

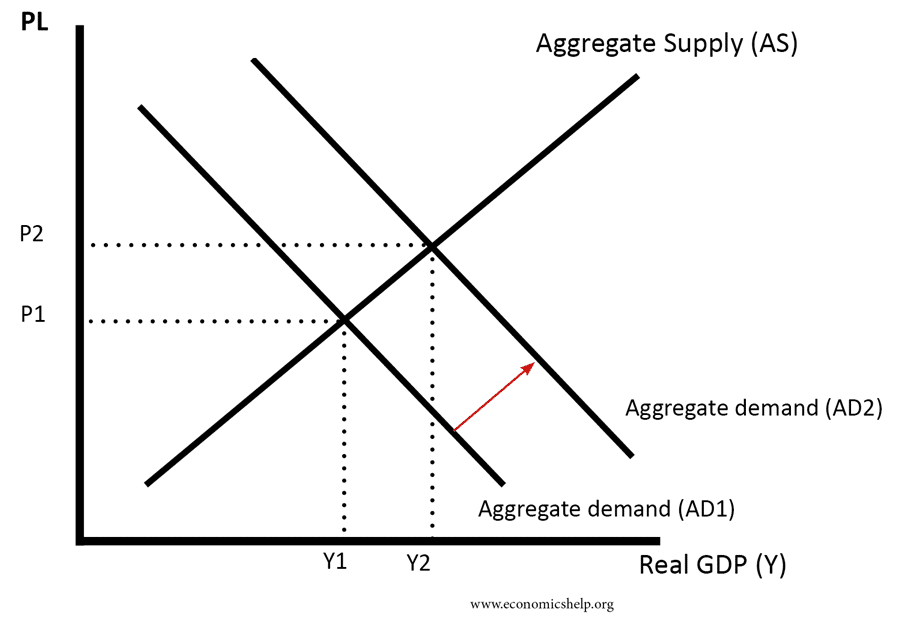
In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. Strictly speaking AD is what economists call total planned expenditure. The aggregate supply curve may reflect either labour market disequilibrium or equilibrium. In the long-run increases in aggregate demand cause the price of a good or service to increase. As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AD will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AD will shift the curve. Shifts of the Aggregate Demand Curve vs.
Example of plotting demand and supply curve graph The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each market price.
How would a change in AD and AS affect the economy. Aggregate Demand-Aggregate Supply Model showing equilibrium at Pe Qe. 3 P a g e The aggregate demand curve is derived from the combinations of price level and level of output at which the goods and money markets are simultaneously in equilibrium. In the long-run increases in aggregate demand cause the price of a good or service to increase. The point where the short-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve meet is always the short-run equilibrium. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply.

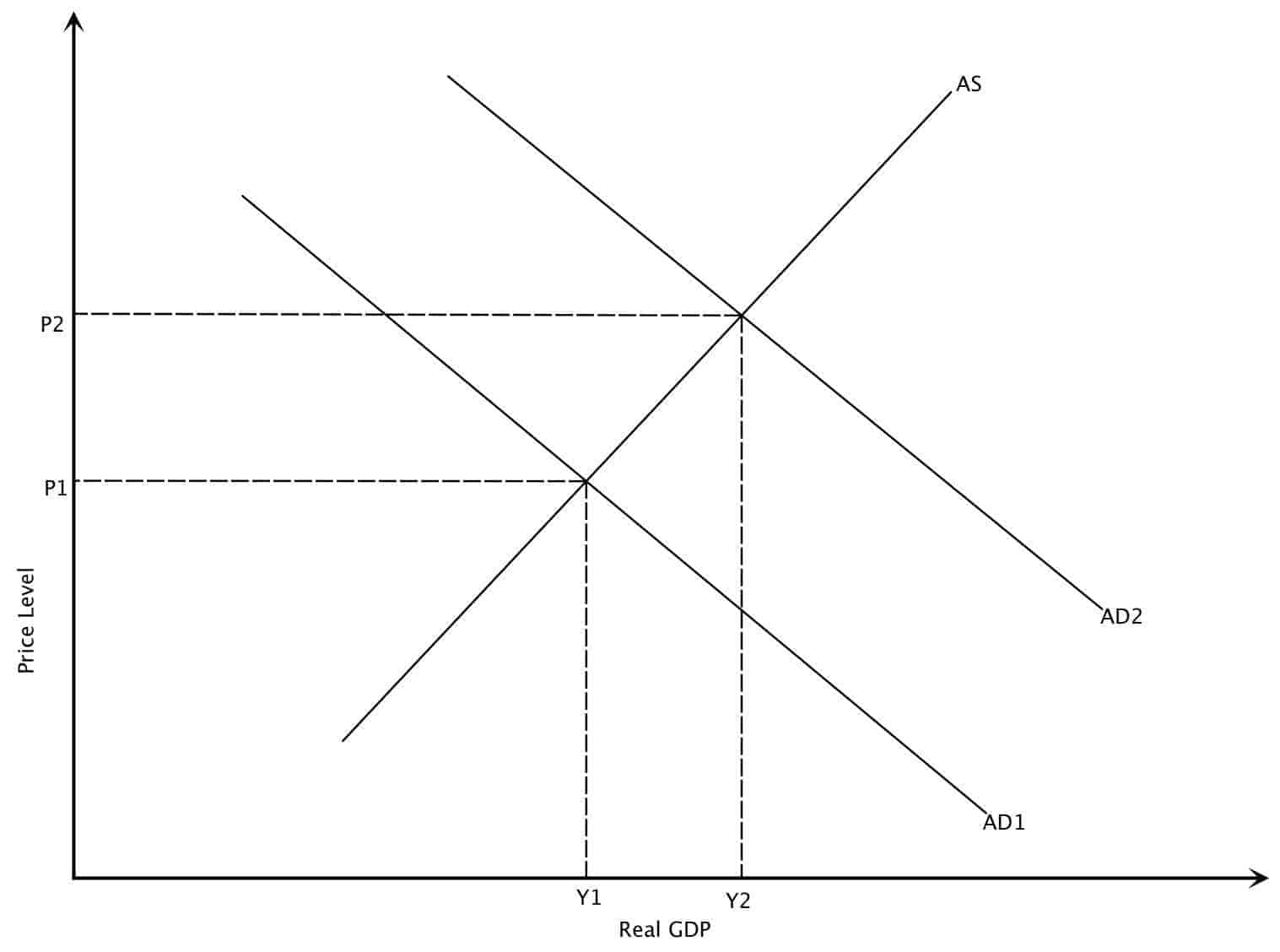
Since the aggregate demandaggregate supply ADAS model represents price as price level and quantity as output a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve results in an increase in the price level and an increase in output. Discuss the reasons why the aggregate demand AD curve slopes downward. When the demand increases the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. Also Know how does aggregate demand affect aggregate supply. In the long-run only capital labor and technology affect the aggregate supply curve because at this point everything in the economy is assumed to be used optimally.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
3 P a g e The aggregate demand curve is derived from the combinations of price level and level of output at which the goods and money markets are simultaneously in equilibrium. Typically there is a positive relationship between aggregate supply and the price level. Examples of events that would increase aggregate supply include an increase in population increased physical capital stock and technological progress. A rightward shift of the demand curve ie. 3 P a g e The aggregate demand curve is derived from the combinations of price level and level of output at which the goods and money markets are simultaneously in equilibrium.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
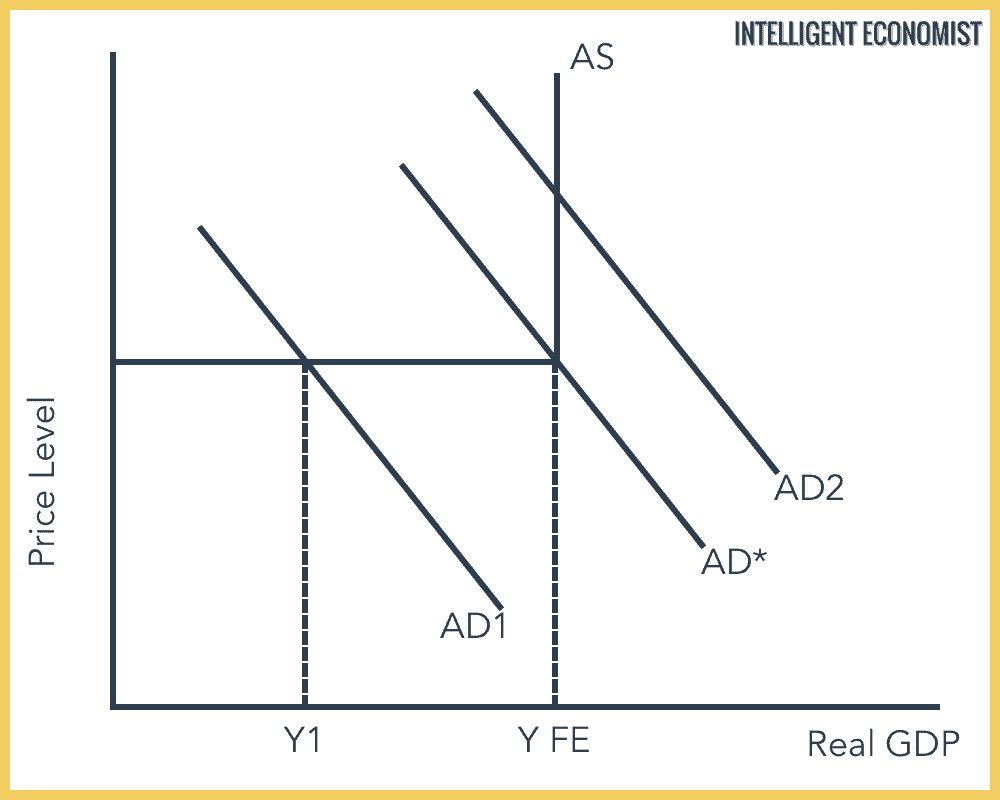
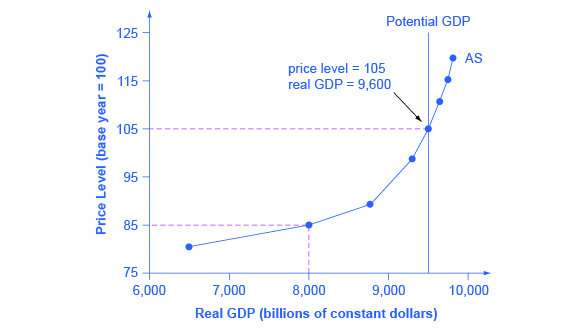
Assume the short-run aggregate supply curve can be expressed algebraically as Y 5000 3000pi and the dynamic aggregate demand curve can be written as Y 5500 - 1000pi. A curve that shows the relationship in. Real GDP and inflation. The aggregate demand curve for the data given in the table is plotted on the graph in Figure 71 Aggregate Demand. In either case it shows how much output is supplied by firms at various potential price levels.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Graph classic Use Createlys easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. When the demand increases the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Graph classic Use Createlys easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. Also Know how does aggregate demand affect aggregate supply. Typically there is a positive relationship between aggregate supply and the price level.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
In the long-run increases in aggregate demand cause the price of a good or service to increase. An individual demand curve shows the quantity of the good a consumer would buy at different prices. Movements along It The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between the price level and real GDP demanded holding everything else constant. Examples of events that would increase aggregate supply include an increase in population increased physical capital stock and technological progress. You can edit this template and create your own diagram.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
A rightward shift of the demand curve ie. Examples of events that would increase aggregate supply include an increase in population increased physical capital stock and technological progress. In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. The AD-AS aggregate demand-aggregate supply model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level. Strictly speaking AD is what economists call total planned expenditure.

In this example the multiplier is 2. In this example the multiplier is 2. In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. An increase of the demand curve causes price and quantity to increase. Assume the short-run aggregate supply curve can be expressed algebraically as Y 5000 3000pi and the dynamic aggregate demand curve can be written as Y 5500 - 1000pi.
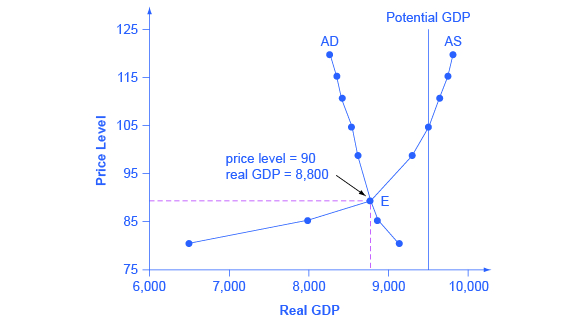 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
When the demand increases the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. How would a change in AD and AS affect the economy. An increase of the demand curve causes price and quantity to increase. Aggregate demand or AD refers to the amount of total spending on domestic goods and services in an economy. Aggregate Supply Over the Short and Long Run.
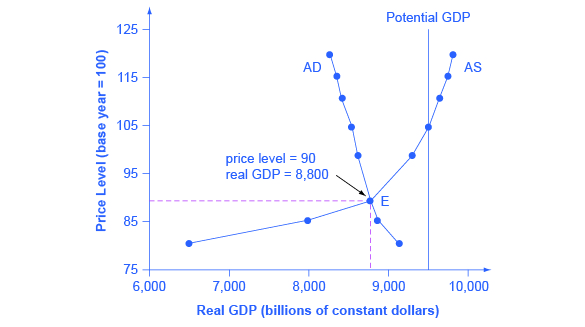 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
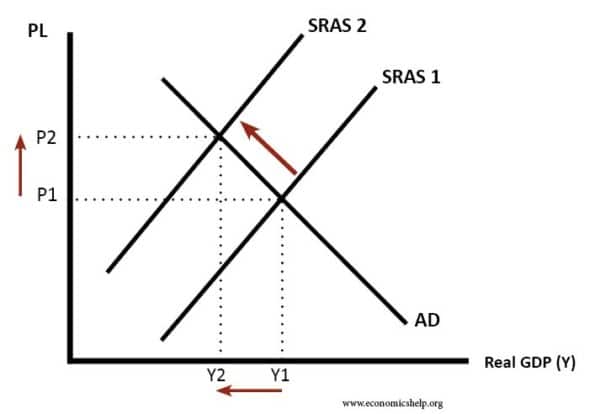
In the short run aggregate supply responds to higher demand and prices by increasing the use of current inputs in the production process. Various points on the aggregate demand curve are found by adding the values of these components at different price levels. The point where the short-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve meet is always the short-run equilibrium. A rightward shift of the demand curve ie. Typically there is a positive relationship between aggregate supply and the price level.
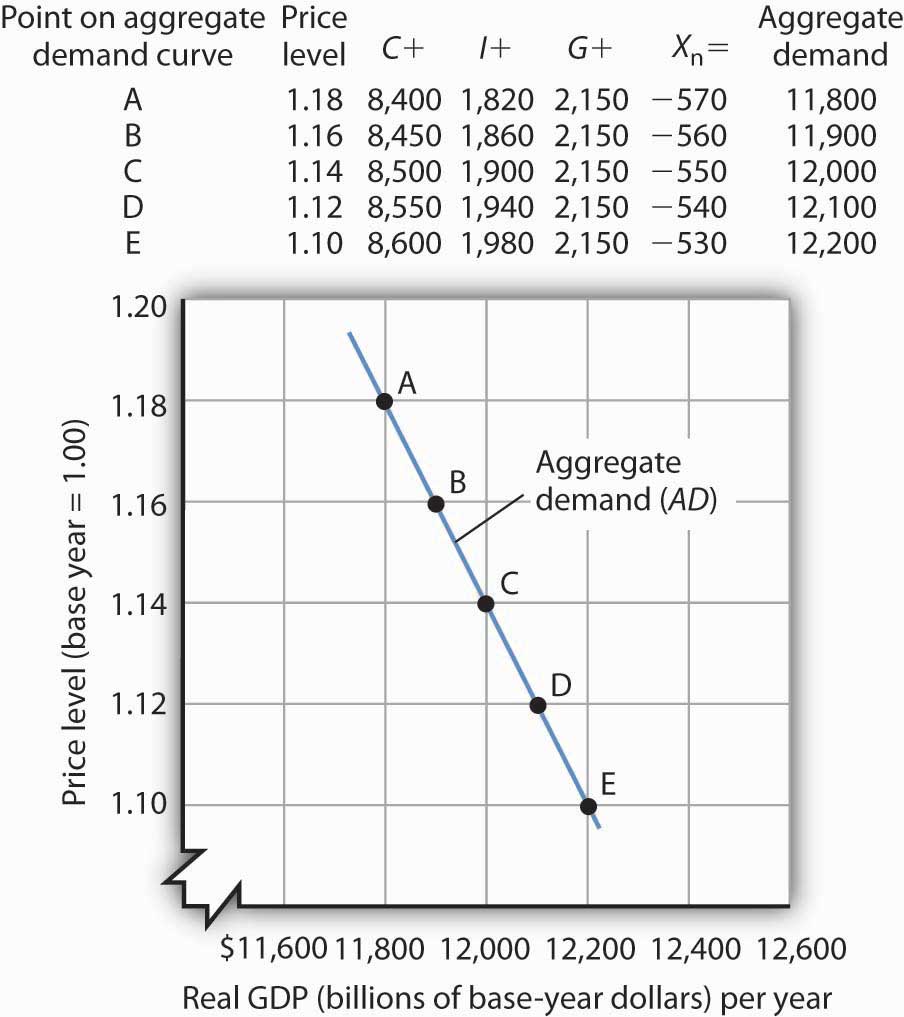 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. Movements along It The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between the price level and real GDP demanded holding everything else constant. Typically there is a positive relationship between aggregate supply and the price level. Notice that we begin at point A where short-run aggregate supply curve 1 meets the long-run aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand curve 1. In the short run aggregate supply responds to higher demand and prices by increasing the use of current inputs in the production process.

You can edit this template and create your own diagram. A shift of the AD curve. Aggregate Demand-Aggregate Supply Model showing equilibrium at Pe Qe. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. The point where the short-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve meet is always the short-run equilibrium.
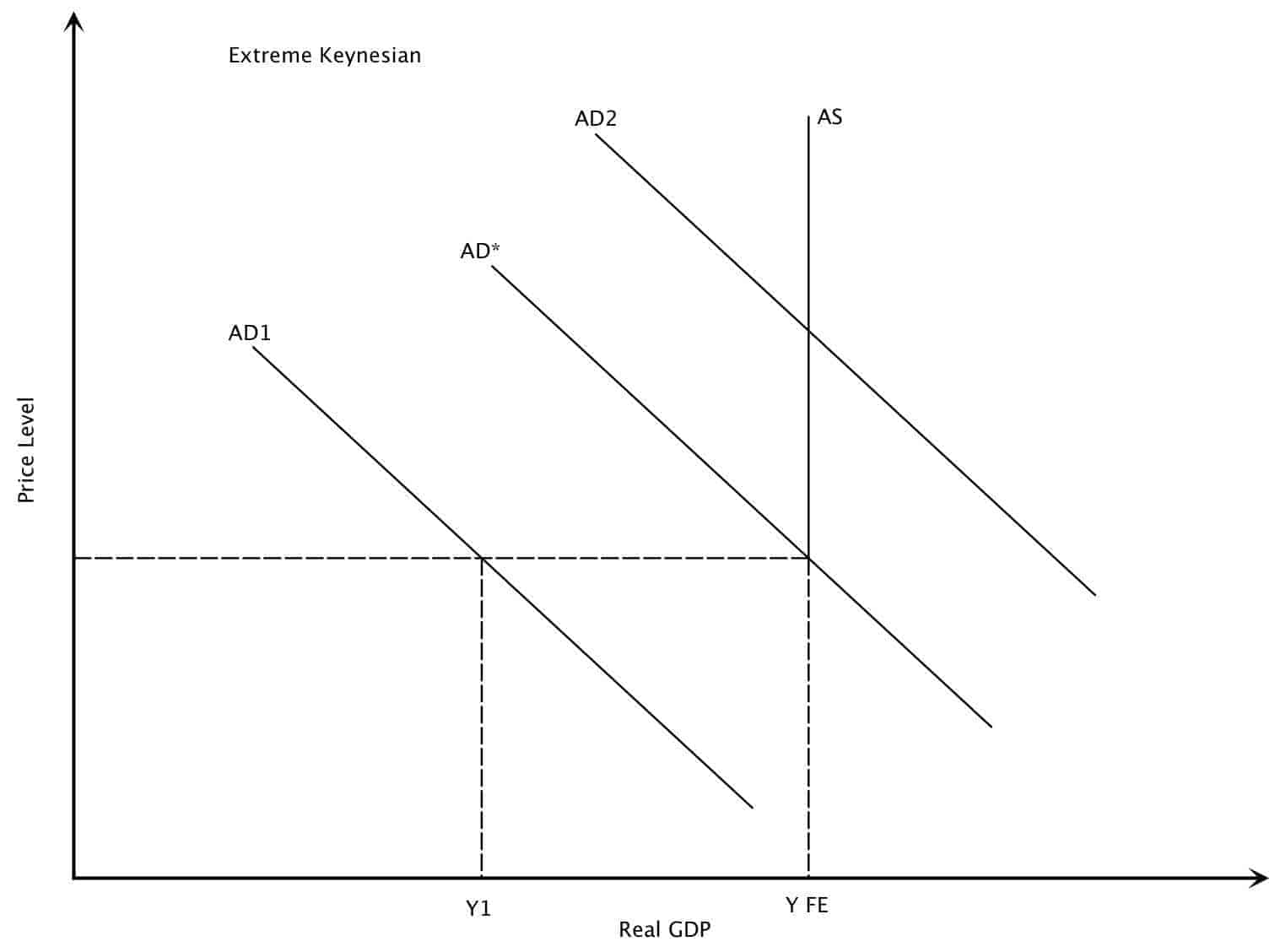 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. The aggregate supply curve may reflect either labour market disequilibrium or equilibrium. You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Also Know how does aggregate demand affect aggregate supply. Since the aggregate demandaggregate supply ADAS model represents price as price level and quantity as output a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve results in an increase in the price level and an increase in output.
 Source: bohatala.com
Source: bohatala.com
Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. The horizontal x-axis shows the real output or GDP of the macroeconomy. When the demand increases the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. Discuss the reasons why the aggregate demand AD curve slopes downward.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The aggregate supply curve may reflect either labour market disequilibrium or equilibrium. Various points on the aggregate demand curve are found by adding the values of these components at different price levels. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators. 3 P a g e The aggregate demand curve is derived from the combinations of price level and level of output at which the goods and money markets are simultaneously in equilibrium. A movement along the AD curve will occur when the price level changes and the change in prices is not caused by a component of real GDP changing.
 Source: ctaar.rutgers.edu
Source: ctaar.rutgers.edu
Find the numerical va. Aggregate Supply Over the Short and Long Run. As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AD will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AD will shift the curve. Real GDP and inflation. Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The horizontal x-axis shows the real output or GDP of the macroeconomy. An individual demand curve shows the quantity of the good a consumer would buy at different prices. In the short run aggregate supply responds to higher demand and prices by increasing the use of current inputs in the production process. In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. Examples of events that cause the curve to shift to the right in the short-run include a decrease in the wage rate an increase in physical capital stock and technological progress.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. In the long-run increases in aggregate demand cause the price of a good or service to increase. Lets work through an example. Various points on the aggregate demand curve are found by adding the values of these components at different price levels. In the long-run only capital labor and technology affect the aggregate supply curve because at this point everything in the economy is assumed to be used optimally.

Aggregate Supply Over the Short and Long Run. A rightward shift of the demand curve ie. Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. For this example refer to. Discuss the reasons why the aggregate demand AD curve slopes downward.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title aggregate supply and demand graph examples by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.