Your Aggregate demand curve must shift to the left images are available in this site. Aggregate demand curve must shift to the left are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Aggregate demand curve must shift to the left files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for aggregate demand curve must shift to the left images information linked to the aggregate demand curve must shift to the left interest, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with hints for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Aggregate Demand Curve Must Shift To The Left. 195 In the dynamic aggregated demand and aggregate supply model inflation occurs if A the AD curve shifts more to the right than the RAS curve. The govermment wishes to increase real GDP to 14 trillion. Left if taxes increased. Changes in aggregate demand are not caused by changes in the price level.
 Is Lm In Action From 2012books.lardbucket.org
Is Lm In Action From 2012books.lardbucket.org
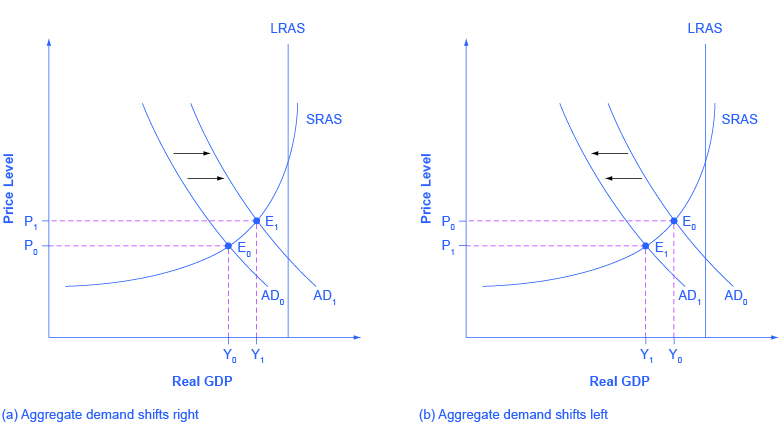
Consumers might spend less because the cost of living is rising or because government taxes have. A shift to the left of the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 3 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has decreased. 195 In the dynamic aggregated demand and aggregate supply model inflation occurs if A the AD curve shifts more to the right than the RAS curve. The aggregate demand curve. Whether these changes in output and price level are relatively large or relatively small and how the change in equilibrium relates to potential GDP depends on whether the shift in the AD curve is happening in the relatively flat or relatively steep portion of the AS curve. Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
The Keynesian Perspective will discuss the components of aggregate demand and the factors that affect them.
In this example the multiplier is 2. The aggregate demand curve tends to shift to the left when total consumer spending declines. An increase in money supply causes a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve. Shift to the left. Whereas the second is due to a shift in aggregate supply to the left. Decreases so aggregate supply shifts left.

An increase in money supply causes a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve. For incorrect answers click the option twice to empty the box. A reduction in money supply on the other hand shifts the aggregate demand curve leftwards. Here the discussion will sketch two broad categories that could cause AD curves. The govermment wishes to increase real GDP to 14 trillion.
 Source: s-cool.co.uk
Source: s-cool.co.uk
Shift to the left. D The aggregate supply curve would shift to the right 2 Suppose that initially equilibrium real GDP is 13 trillion. 195 In the dynamic aggregated demand and aggregate supply model inflation occurs if A the AD curve shifts more to the right than the RAS curve. Central banks through various monetary policies control money supply. If the stock of physical capital is high the aggregate demand curve will.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
The aggregate supply curve will shift out to the right as productivity increases. A decrease in the interest rate C. The first is a result of a shift in the aggregate demand curve to the right. Whether these changes in output and price level are relatively large or relatively small and how the change in equilibrium relates to potential GDP depends on whether the shift in the AD curve is happening in the relatively flat or relatively steep portion of the AS curve. When the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left the total quantity of goods and services demanded at any given price level falls.

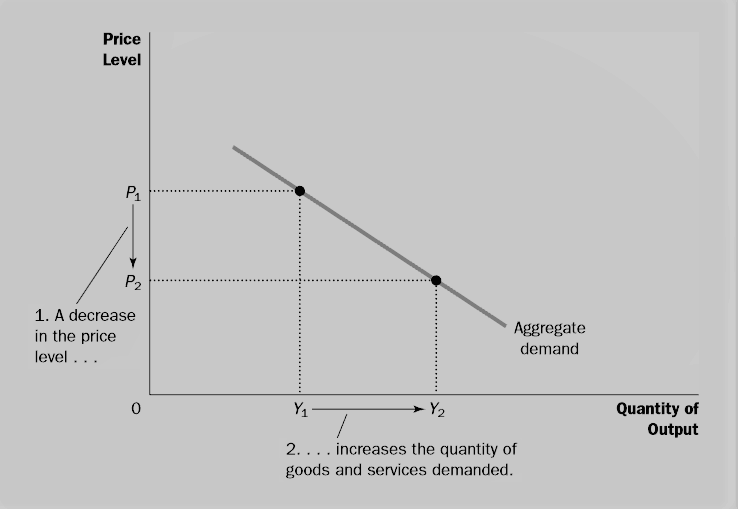
Recall that the price level is not directly in the equation for aggregate demand. Unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as aggregate demand shifts the economy along the short-run aggregate supply curve. In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. 1 A The aggregate demand curve would shift to the right. Conversely a shift of aggregate demand to the left leads to a lower real GDP and a lower price level.
 Source: ilearnthis.com
Source: ilearnthis.com
Decreases so aggregate demand shifts left. Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left. Increases in taxes will decrease consumption and shift the AD curve to the left while decreases in taxes will increase consumption and shift the AD curve to the right. Whereas the second is due to a shift in aggregate supply to the left. C The aggregate supply curve would shift to the left.
 Source: tutor2u.net
Source: tutor2u.net
The aggregate demand curve tends to shift to the left when total consumer spending declines. The govermment wishes to increase real GDP to 14 trillion. Which of the following will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left A. Unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as short-run aggregate supply shifts the economy along the aggregate demand curve. Left if taxes increased.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
An improvement in technology. In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. Slopes downward in part because as the price level falls the ability of households and firms to borrow cheaply increases. The govermment wishes to increase real GDP to 14 trillion. An improvement in technology.
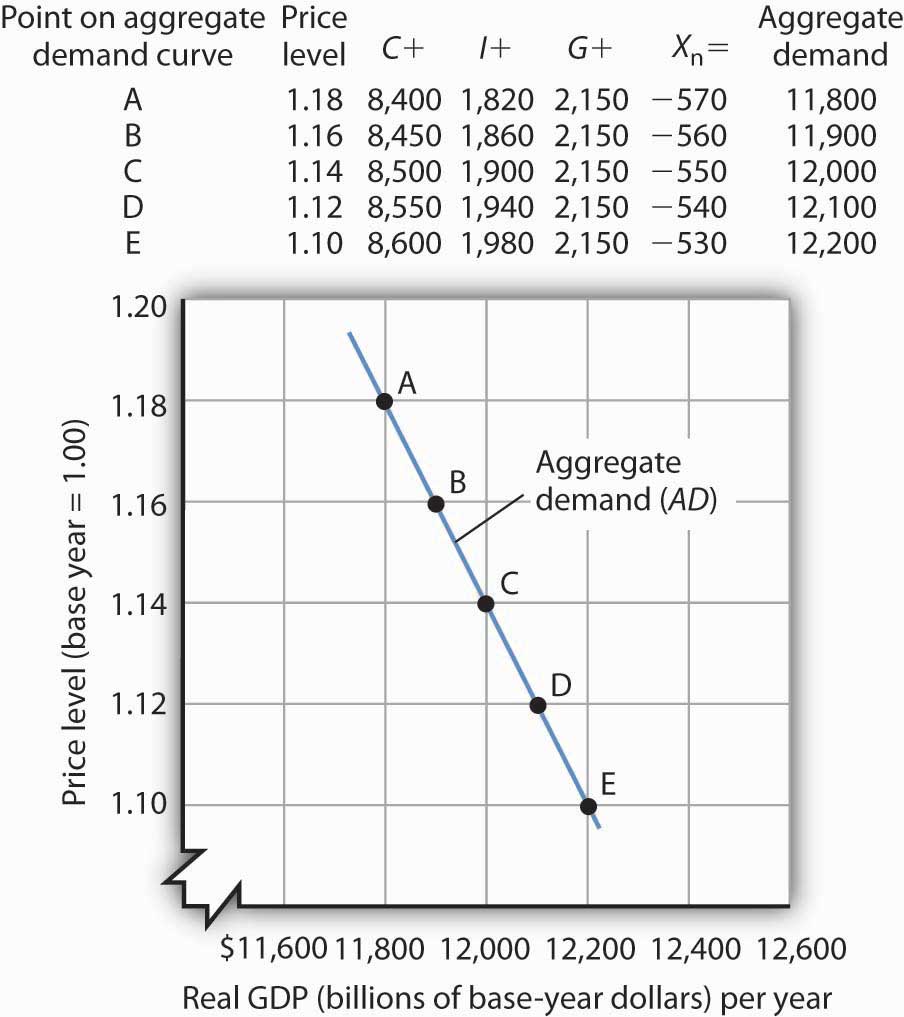 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The aggregate supply curve will shift out to the right as productivity increases. It will shift back to the left as the price of key inputs rises and will shift out to the right if the price of key inputs falls. Decreases so aggregate demand shifts left. A housing bubble collapse that caused a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve. Each of the following is a factor that can shift the aggregate demand curve except.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
In this example the multiplier is 2. Increases so aggregate demand shifts right. D the economy is in short-run macroeconomic equilibrium. Right if taxes decreased. Movements of either AS or AD will result in a different equilibrium output and price level.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Whereas the second is due to a shift in aggregate supply to the left. The belief that a higher rate of growth in real GDP will lead to. Changes in the price level. Each of the following is a factor that can shift the aggregate demand curve except. Whether these changes in output and price level are relatively large or relatively small and how the change in equilibrium relates to potential GDP depends on whether the shift in the AD curve is happening in the relatively flat or relatively steep portion of the AS curve.
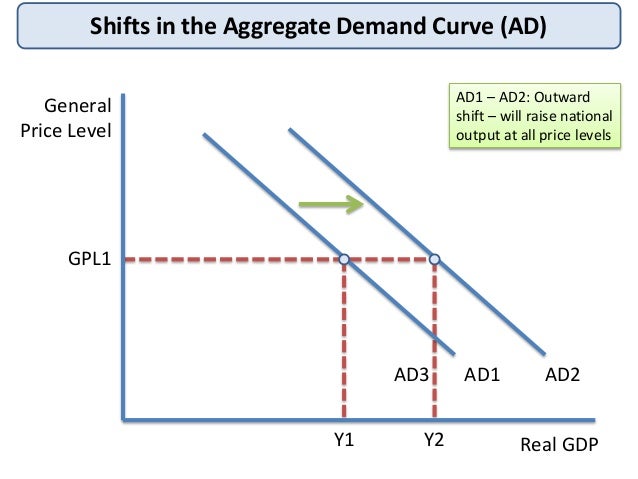 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
If the stock of physical capital is high the aggregate demand curve will. Unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as aggregate demand shifts the economy along the short-run aggregate supply curve. D the economy is in short-run macroeconomic equilibrium. In this example the multiplier is 2. An increase in money supply causes a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
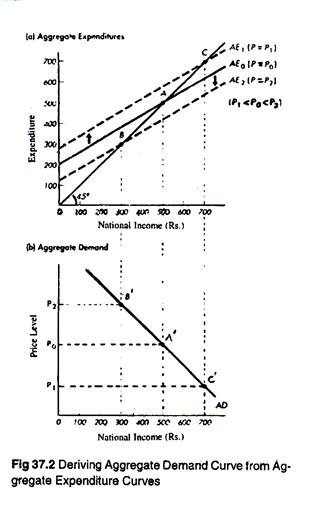 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Consumption would decrease and aggregate demand would shift. Conversely a shift of aggregate demand to the left leads to a lower real GDP and a lower price level. Unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as aggregate demand shifts the economy along the short-run aggregate supply curve. A shift to the left of the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 3 indicates that the quantity demanded of real GDP has decreased at the same price levels. The aggregate demand curve would shift to the left for all the following reasons EXCEPT.
 Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Right if taxes increased. Consumers might spend less because the cost of living is rising or because government taxes have. Decreases so aggregate demand shifts left. When the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left the total quantity of goods and services demanded at any given price level falls. For incorrect answers click the option twice to empty the box.
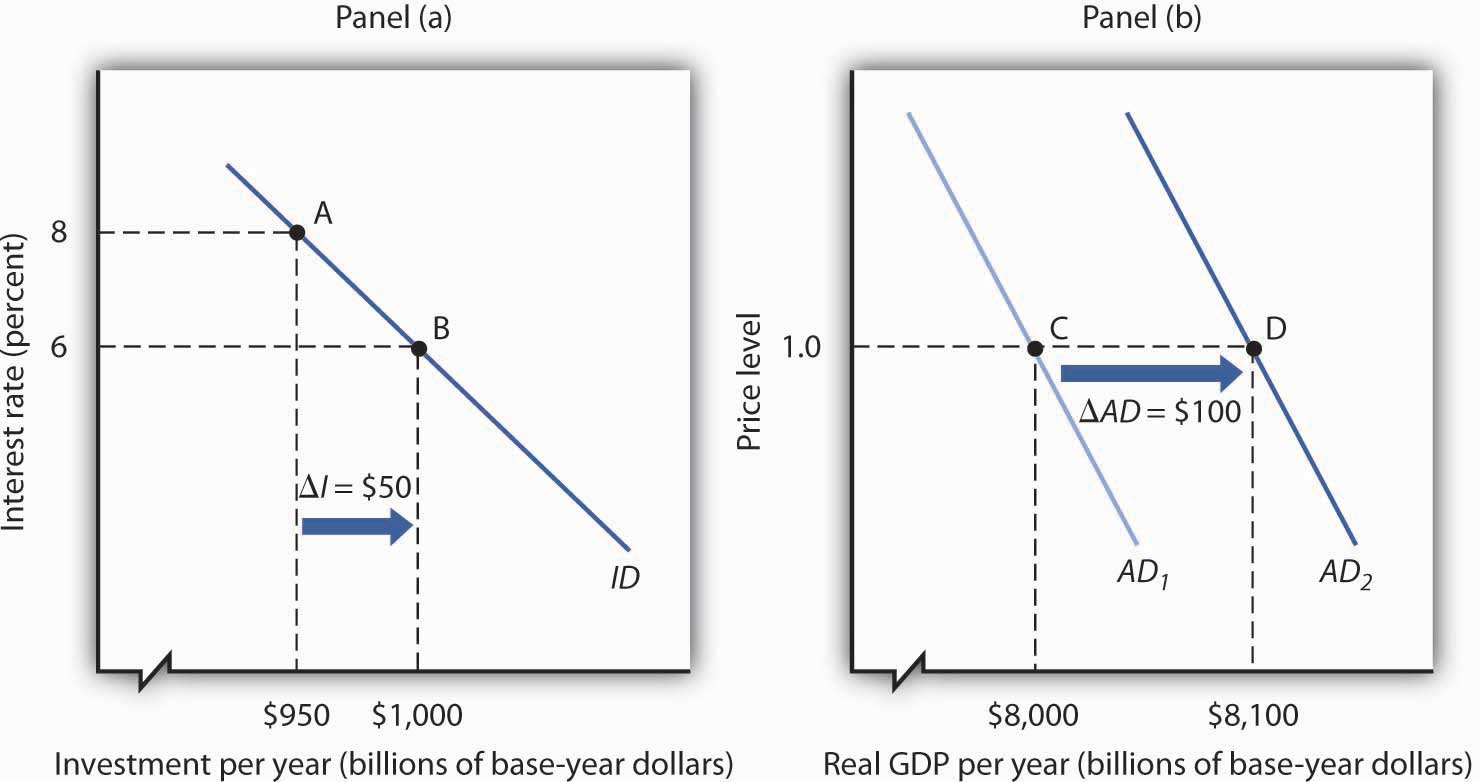 Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
The Keynesian Perspective will discuss the components of aggregate demand and the factors that affect them. Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left. Changes in aggregate demand are not caused by changes in the price level. Changes in the price level. Increases in taxes will decrease consumption and shift the AD curve to the left while decreases in taxes will increase consumption and shift the AD curve to the right.
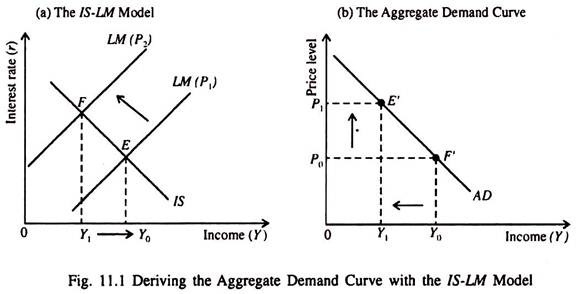 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Here the discussion will sketch two broad categories that could cause AD curves. A shift to the left of the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 3 indicates that the quantity demanded of real GDP has decreased at the same price levels. A decrease in consumer business confidence because of a terrorist attack B. C The aggregate supply curve would shift to the left. Decreases so aggregate demand shifts left.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
The aggregate-supply curve might shift to the left because of a decline in the economys capital stock labor supply or productivity or an increase in the natural rate of unemployment all of which shift both the long-run and short-run aggregate-supply curves to the left. A shift to the left of the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 3 indicates that the quantity demanded of real GDP has decreased at the same price levels. Conversely a shift of aggregate demand to the left leads to a lower real GDP and a lower price level. In order to receive full credit you must make a selection for each option. The Keynesian Perspective will discuss the components of aggregate demand and the factors that affect them.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Right if taxes increased. B the SRAS curve shifts more to the right than the AD curve. In this example the multiplier is 2. When the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left the total quantity of goods and services demanded at any given price level falls. Whether these changes in output and price level are relatively large or relatively small and how the change in equilibrium relates to potential GDP depends on whether the shift in the AD curve is happening in the relatively flat or.
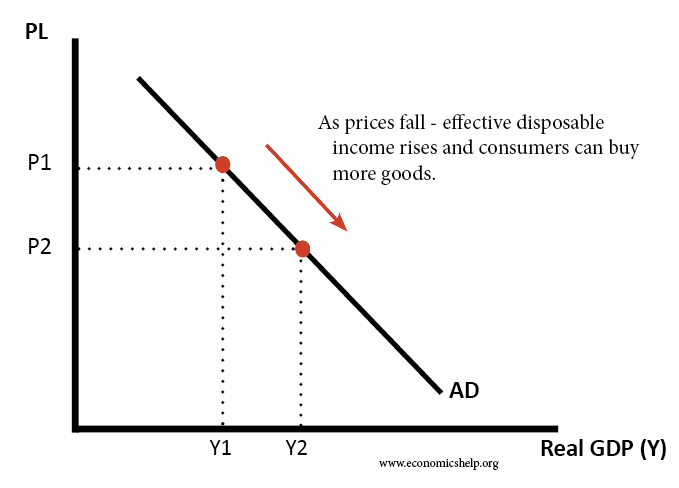 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
In Panel a an initial increase of 100 billion of net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by 200 billion at each price level. Decreases so aggregate supply shifts left. D The aggregate supply curve would shift to the right 2 Suppose that initially equilibrium real GDP is 13 trillion. Unemployment and inflation that arise in the short run as aggregate demand shifts the economy along the short-run aggregate supply curve. A decrease in the interest rate C.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title aggregate demand curve must shift to the left by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.