Your Aggregate demand and supply curves intersect images are available. Aggregate demand and supply curves intersect are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Aggregate demand and supply curves intersect files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for aggregate demand and supply curves intersect pictures information related to the aggregate demand and supply curves intersect interest, you have come to the right blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Aggregate Demand And Supply Curves Intersect. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied. In short-run macroeconomic equilibrium the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves often intersect at a point off the long-run aggregate supply curve. Anything that changes the quantity supplied at a given price level can shift an aggregate supply curve. Shape of the aggregate demand curve.
 Aggregate Demand Curve And Aggregate Supply From economicsdiscussion.net
Aggregate Demand Curve And Aggregate Supply From economicsdiscussion.net
Anything that changes the quantity supplied at a given price level can shift an aggregate supply curve. Aggregate demand and short run aggregate supply curves. The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines an economys equilibrium price level and real GDP. The equilibrium price level and equilibrium level of real GDP occur at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied. Therefore the point of intersection between aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve is called effective demand as at this point all the output produced in the economy is used by the consumers of the economy owing to full employment.
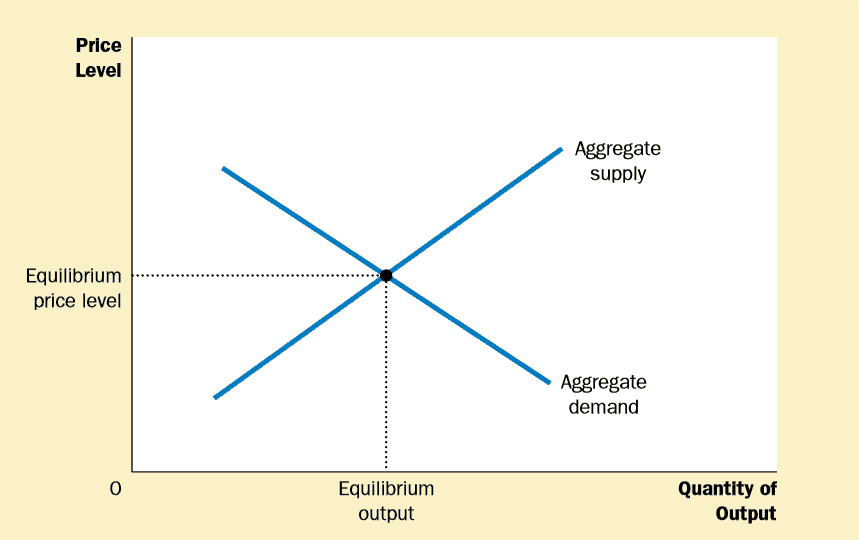
Its where the aggregate supply AS and aggregate demand AD curves intersect showing the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy.
At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied. The equilibrium price level and real gdp are determined by the intersection of the. Per-unit cost of production in the economy. It is the higher interest rate that causes aggregate output to fall. The intersection of the short-run aggregate supply curve the long-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve gives the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of output. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied.

Then for each situation determine whether Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply and Long-run Aggregate supply shift in the short run and in what direction. Lets begin by looking at the point where aggregate supply equals aggregate demandthe equilibrium. Anything that changes the quantity supplied at a given price level can shift an aggregate supply curve. The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the economys equilibrium price level and real GDP. We can find this point on the diagram below.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
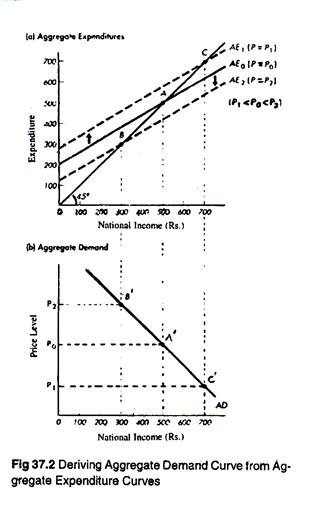
Aggregate Demand Curve Aggregate demand falls when the price level increases because the higher price level causes the demand for money to rise which causes the interest rate to rise. Demand and short-run aggregate supply curves intersect at a point on the long-run aggregate supply curve. Changing one of the determinants of aggregate supply will cause the aggregate supply curve to. This is the starting point for all problems dealing with the AS- AD model. After studying the AD and AS curves separately we may now put both the curves in the same diagram to determine the equilibrium level of price and national income.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
For each of the following assume Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply and Long-run Aggregate supply curves are in their long-run equilibrium all three intersect. In short-run macroeconomic equilibrium the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves often intersect at a point off the long-run aggregate supply curve. Its where the aggregate supply AS and aggregate demand AD curves intersect showing the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. Long-run aggregate supply curve. When the aggregate demand and SAS short-run aggregate supply curves are combined as in Figure the intersection of the two curves determines both the equilibrium price level denoted by P and the equilibrium level of real GDP denoted by Y.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Demand and short-run aggregate supply curves intersect at a point on the long-run aggregate supply curve. 379 shows such an equilibrium. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied. At all points along the AD curve both the goods market and the money market are in equilibrium. Equilibrium occurs at point a where AD 1 intersects both AS LR and AS 1 and the economy achieves its full-employment or.

At a relatively low price level for output firms have little incentive to produce although consumers would be willing to purchase a. Its where the aggregate supply AS and aggregate demand AD curves intersect showing the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. A curve that shows the relationship in. Anything that changes the quantity supplied at a given price level can shift an aggregate supply curve. View the full answer.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
379 shows such an equilibrium. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. Therefore the point of intersection between aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve is called effective demand as at this point all the output produced in the economy is used by the consumers of the economy owing to full employment. The aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves intersect at a point on the long-run aggregate supply curve. After studying the AD and AS curves separately we may now put both the curves in the same diagram to determine the equilibrium level of price and national income.

Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. Captures the effect of the price level on output and is derived from the equilibrium conditions in the goods and financial markets. The intersection of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves shows the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. Anything that changes the quantity supplied at a given price level can shift an aggregate supply curve. After those adjustments long-run equilibrium occurs where the aggregate demand curve vertical long-run aggregate supply curve and short-run aggregate supply curve all intersect.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The intersection of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves shows the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. Equilibrium occurs at point a where AD 1 intersects both AS LR and AS 1 and the economy achieves its full-employment or. Anything that changes the quantity supplied at a given price level can shift an aggregate supply curve. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied. 10 7 Where the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve intersect A the long-run aggregate supply curve must also intersect at the same point.
 Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
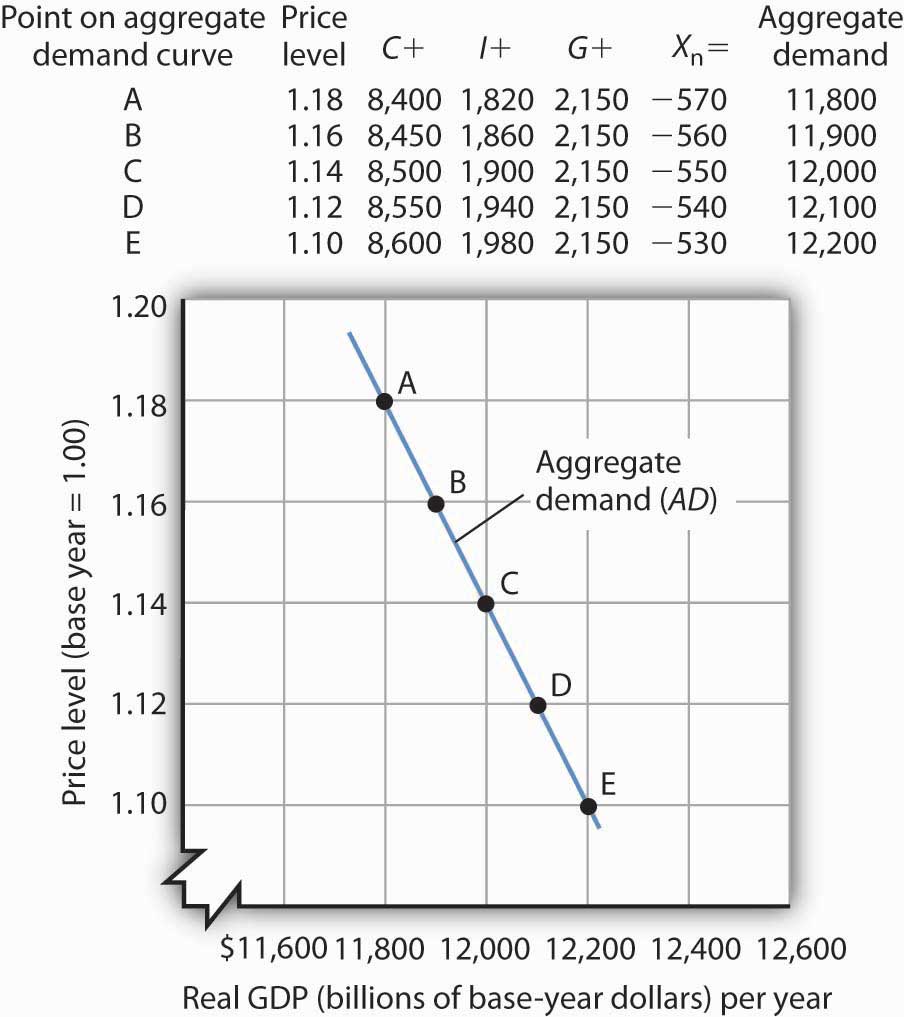
Aggregate Demand Curve Aggregate demand falls when the price level increases because the higher price level causes the demand for money to rise which causes the interest rate to rise. Aggregate Demand and Supply Equilibrium. At all points along the AD curve both the goods market and the money market are in equilibrium. Economics questions and answers. If it is further assumed that the economy is fully employing all of its resources the equilibrium level of real GDP Y will.
 Source: financetrain.com
Source: financetrain.com
P Pe 3. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. Per-unit cost of production in the economy. Aggregate Demand and Supply Equilibrium.
 Source: ilearnthis.com
Source: ilearnthis.com
If it is further assumed that the economy is fully employing all of its resources the equilibrium level of real GDP Y will. The intersection of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves shows the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. This is the starting point for all problems dealing with the AS- AD model. The equilibrium price level and equilibrium level of real GDP occur at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve. Economics questions and answers.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
An automatic mechanism drives the economy to long-run equilibrium. Economics questions and answers. Lets begin by looking at the point where aggregate supply equals aggregate demandthe equilibrium. The intersection of the short-run aggregate supply curve the long-run aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve gives the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of output. Demand and short-run aggregate supply curves intersect at a point on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Changing one of the determinants of aggregate supply will cause the aggregate supply curve to. Increase in the expected price level Pe shifts the AS curve up vice versa 82 Aggregate Demand AD Aggregate Demand Relation. Then for each situation determine whether Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply and Long-run Aggregate supply shift in the short run and in what direction. After those adjustments long-run equilibrium occurs where the aggregate demand curve vertical long-run aggregate supply curve and short-run aggregate supply curve all intersect. AS curve goes through point A where Y YN.
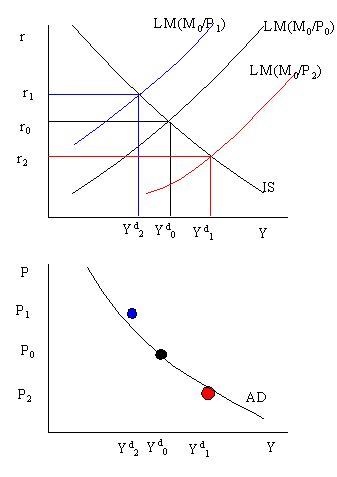 Source: faculty.washington.edu
Source: faculty.washington.edu
Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. When the aggregate demand and SAS short-run aggregate supply curves are combined as in Figure the intersection of the two curves determines both the equilibrium price level denoted by P and the equilibrium level of real GDP denoted by Y. Long-run aggregate supply curve. After those adjustments long-run equilibrium occurs where the aggregate demand curve vertical long-run aggregate supply curve and short-run aggregate supply curve all intersect. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
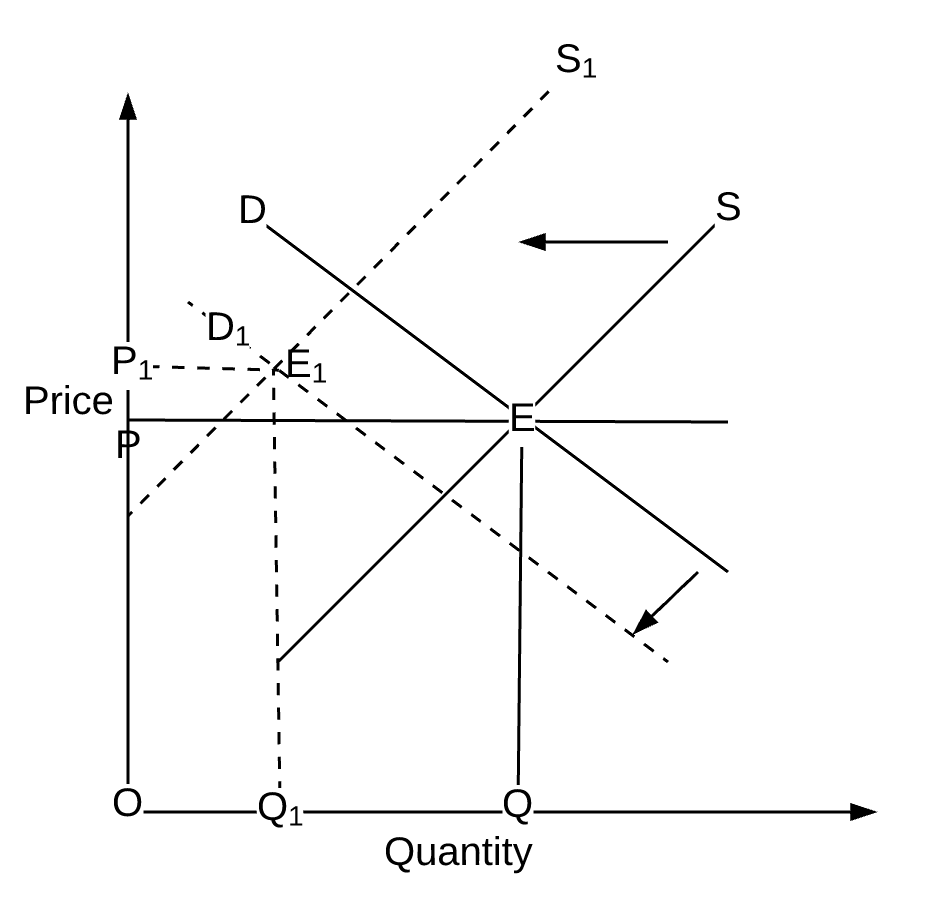
Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Therefore the point of intersection between aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve is called effective demand as at this point all the output produced in the economy is used by the consumers of the economy owing to full employment. Shape of the aggregate demand curve. Initially equilibrium occur at point 1 at which the AD 1 and AS 1 curves intersect. At the intersection the quantity of real GDP demanded equals the quantity of real GDP supplied.
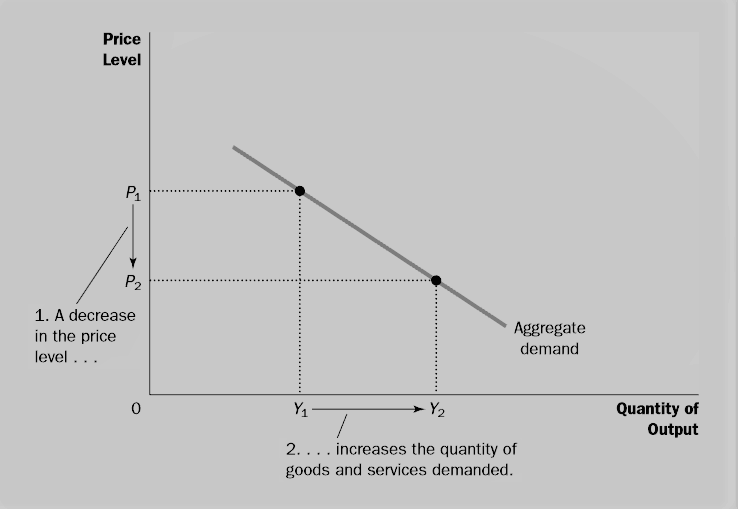 Source: ilearnthis.com
Source: ilearnthis.com
When the aggregate demand and SAS short-run aggregate supply curves are combined as in Figure the intersection of the two curves determines both the equilibrium price level denoted by P and the equilibrium level of real GDP denoted by Y. Figure 15-2 shows the long-run outcome. At a relatively low price level for output firms have little incentive to produce although consumers would be willing to purchase a. B inflation must be increasing. The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the.
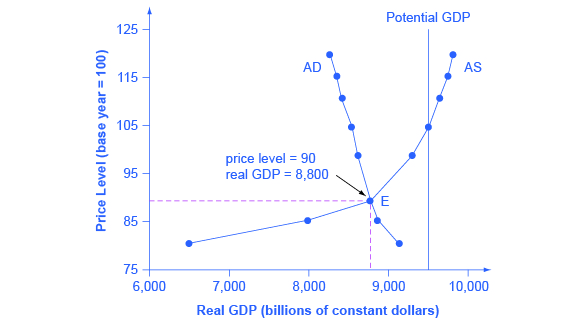 Source: pl.khanacademy.org
Source: pl.khanacademy.org
After studying the AD and AS curves separately we may now put both the curves in the same diagram to determine the equilibrium level of price and national income. An automatic mechanism drives the economy to long-run equilibrium. The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines the economys equilibrium price level and real GDP. 10 7 Where the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve intersect A the long-run aggregate supply curve must also intersect at the same point. The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves determines an economys equilibrium price level and real GDP.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
The equilibrium price level and equilibrium level of real GDP occur at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve. Then for each situation determine whether Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply and Long-run Aggregate supply shift in the short run and in what direction. The equilibrium price level and real gdp are determined by the intersection of the. In short-run macroeconomic equilibrium the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves often intersect at a point off the long-run aggregate supply curve. Per-unit cost of production in the economy.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title aggregate demand and supply curves intersect by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






