Your Aggregate demand and supply curve explained images are ready. Aggregate demand and supply curve explained are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Aggregate demand and supply curve explained files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for aggregate demand and supply curve explained pictures information linked to the aggregate demand and supply curve explained topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Aggregate Demand And Supply Curve Explained. The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods and services demanded by the economy at different price levels. Instead of quantity on the X-axis we have Real GDP a. If aggregate demand increases to AD 2 long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of 12000 billion per year but at. This downward slope indicates that increases in the price level of outputs lead to a lower quantity of total spending.
 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Curves Article Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Curves Article Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Explain the factors of shifting AS curve. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. Downward sloping demand curve becomes aggregate demand curve. Explain the factors of shifting AD curve. The intersection of the economys aggregate demand curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve determines its equilibrium real GDP and price level in the long run. Find the equation of the LM curve.
Find the equation of the LM curve.
Movements along these curves are caused by price level variations while shifts of these curves happen when another variable other than the price level affects the. Use the ASAD model to describe the consequences of changes in fiscal policy monetary policy supply shocks and investor and consumer confidence depending on whether. Explain the factors of shifting AD curve. Real GDP and inflation. This problem has been solved. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Curves It is noted that when we consider demand and supply in a specific market the behaviour of buyers and sellers depends on the ability of resources to move from one market to another.

The aggregate demand curve. Like the demand and supply for individual goods and services the aggregate demand and aggregate supply for an economy can be represented by a schedule a curve or by an algebraic equation The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods and services demanded by the economy at different price levels. In economics the law of supply and demand is a common term and one of the fundamentals of economic theory. This downward slope indicates that increases in the price level of outputs lead to a lower quantity of total spending. Differentiate between the change and shift in AD and AS.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
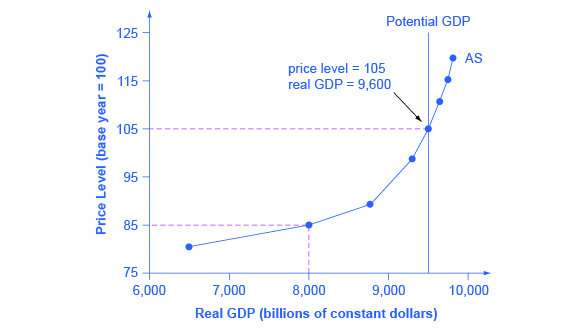
To correctly understand the aggregate supply curve time is an essential factor. 2 P a g e Figure 31. To understand the ASAD model we need to explain both aggregate demand and aggregate supply and then the determination of prices and output. Differentiate between the change and shift in AD and AS. Explain the factors of shifting AS curve.

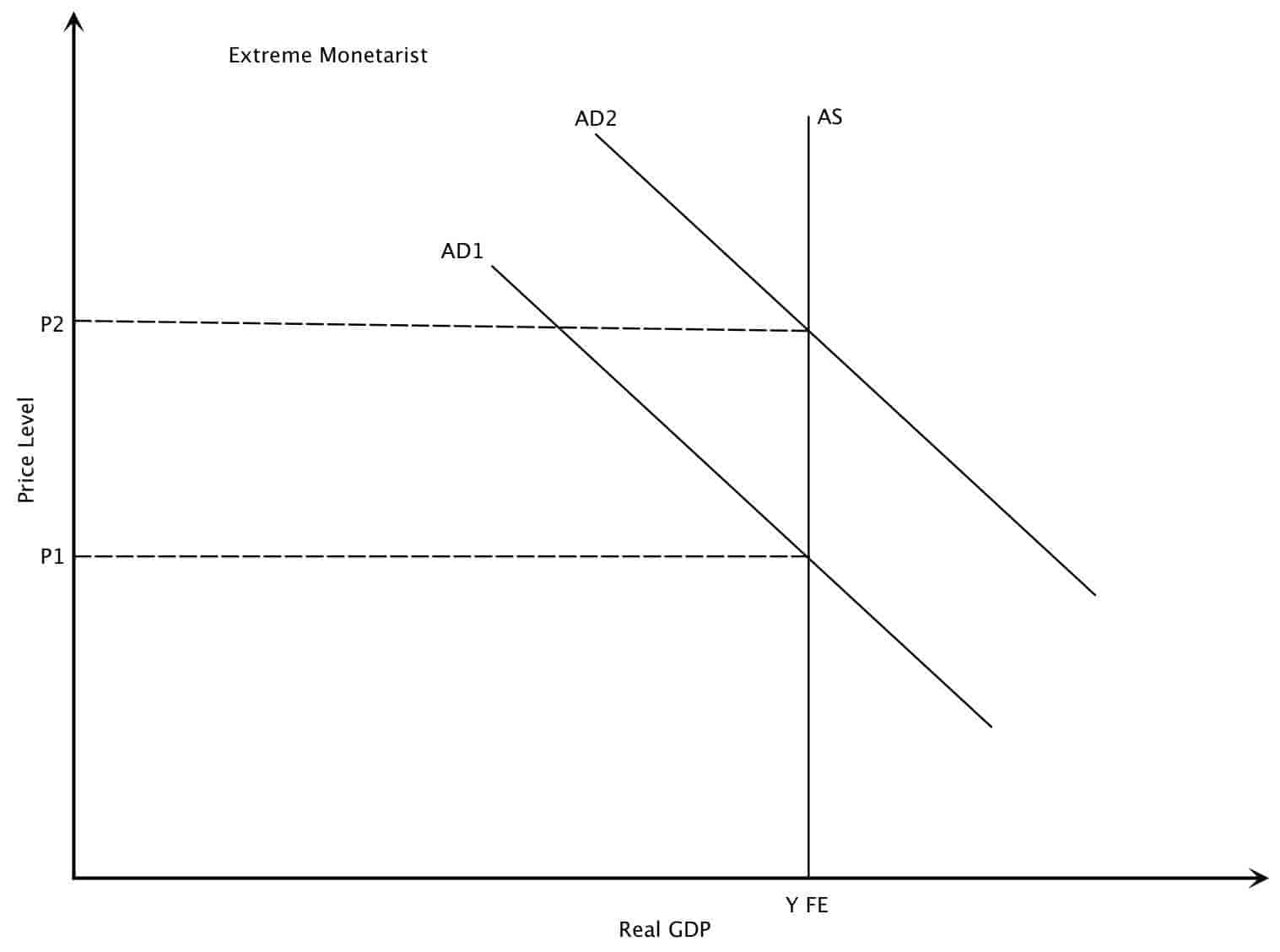
In the long-run the aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand curve are only affected by capital labor and technology. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. If aggregate demand increases to AD 2 long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of 12000 billion per year but at. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators. What are aggregate demand AD and aggregate supply AS curves.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
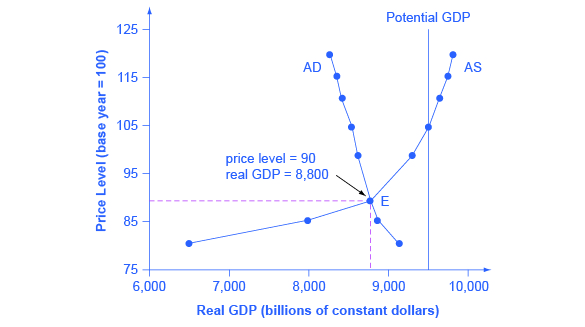
Furthermore how is aggregate demand and supply different than regular demand and supply. A curve that shows the relationship in. The graph shows a downward sloping aggregate demand curve showing that as the price level rises the amount of total spending on domestic goods and services declines. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. If aggregate demand increases to AD 2 long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of 12000 billion per year but at.
 Source: rhayden.us
Source: rhayden.us
Furthermore how is aggregate demand and supply different than regular demand and supply. Different factors explain the upward slope of the AS curve. A curve that shows the relationship in. This downward slope indicates that increases in the price level of outputs lead to a lower quantity of total spending. The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods and services demanded by the economy at different price levels.
 Source: rhayden.us
Source: rhayden.us
See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Explain the derivation of the Aggregate Demand curve relating inflation and output levels and how it shifts. Heres how to calculate it. In the long-run the aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand curve are only affected by capital labor and technology. In the aggregate demandaggregate supply model presented in this chapter it is the number by which we multiply an initial change in aggregate demand to obtain the amount by which the aggregate demand curve shifts as a result of the initial change.
 Source: bohatala.com
Source: bohatala.com
Everything in the economy is assumed to be optimal. Use the ASAD model to describe the consequences of changes in fiscal policy monetary policy supply shocks and investor and consumer confidence depending on whether. Explain the derivation of the Aggregate Demand curve relating inflation and output levels and how it shifts. 2 P a g e Figure 31. The AD-AS aggregate demand-aggregate supply model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level.
 Source: ctaar.rutgers.edu
Source: ctaar.rutgers.edu
Explain the factors of shifting AD curve. What are aggregate demand AD and aggregate supply AS curves. In economics the law of supply and demand is a common term and one of the fundamentals of economic theory. In the long-run the aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand curve are only affected by capital labor and technology. The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods and services demanded by the economy at different price levels.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Different factors explain the upward slope of the AS curve. Instead of quantity on the X-axis we have Real GDP a. Explain the derivation of the Aggregate Demand curve relating inflation and output levels and how it shifts. The aggregate supply curve shows the amount of goods that can be produced at different price levels. In economics the law of supply and demand is a common term and one of the fundamentals of economic theory.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
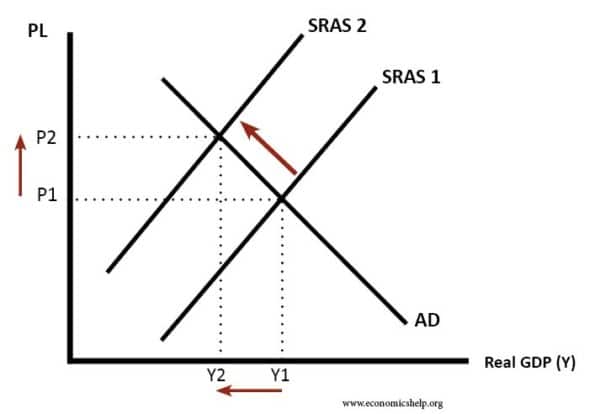
What are aggregate demand AD and aggregate supply AS curves. The aggregate supply curve is vertical which reflects economists belief that changes in aggregate demand only temporarily change the economys total output. Explain the factors of shifting AD curve. In the short run rising prices ceteris paribus or higher demand causes an increase in aggregate supply. Instead of quantity on the X-axis we have Real GDP a.

To understand the ASAD model we need to explain both aggregate demand and aggregate supply and then the determination of prices and output. Movements along these curves are caused by price level variations while shifts of these curves happen when another variable other than the price level affects the. Aggregate supply is the total value of goods and services produced in an economy. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply. The AD-AS aggregate demand-aggregate supply model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level.
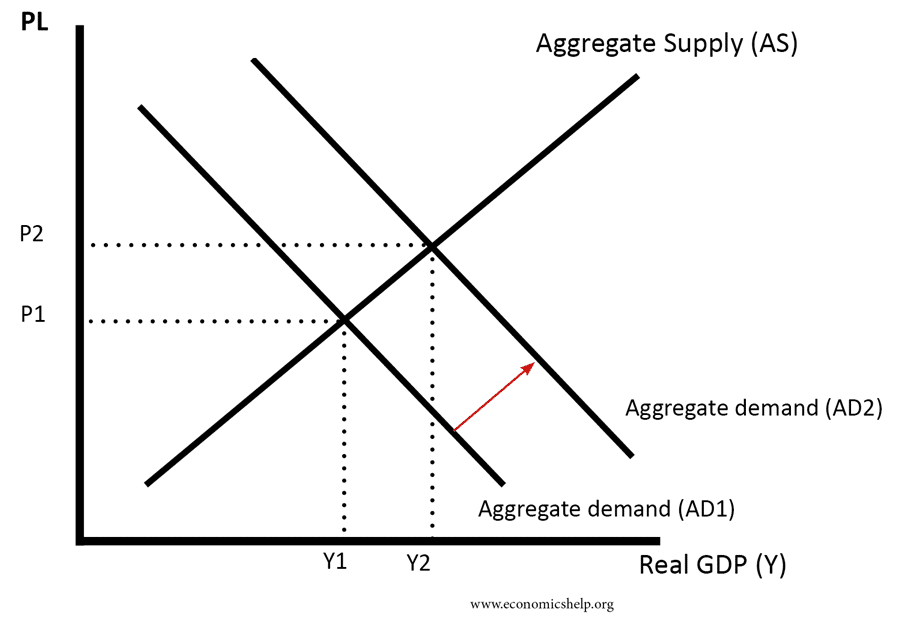 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The aggregate demand curve tells us the level of expenditure in an economy for a given price level. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Curves It is noted that when we consider demand and supply in a specific market the behaviour of buyers and sellers depends on the ability of resources to move from one market to another. Explain the derivation of the Aggregate Demand curve relating inflation and output levels and how it shifts. In the long-run the aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand curve are only affected by capital labor and technology.
 Source: web.mnstate.edu
Source: web.mnstate.edu
Different factors explain the upward slope of the AS curve. Movements along these curves are caused by price level variations while shifts of these curves happen when another variable other than the price level affects the. Use the ASAD model to describe the consequences of changes in fiscal policy monetary policy supply shocks and investor and consumer confidence depending on whether. Everything in the economy is assumed to be optimal. To correctly understand the aggregate supply curve time is an essential factor.

Use the ASAD model to describe the consequences of changes in fiscal policy monetary policy supply shocks and investor and consumer confidence depending on whether. Example of LM Curve. Explain the derivation of the Aggregate Supply curve relating inflation and output levels and how it shifts. When the economy reaches its level of full capacity full employment when the economy is on the production possibility frontier the aggregate supply curve. Different factors explain the upward slope of the AS curve.
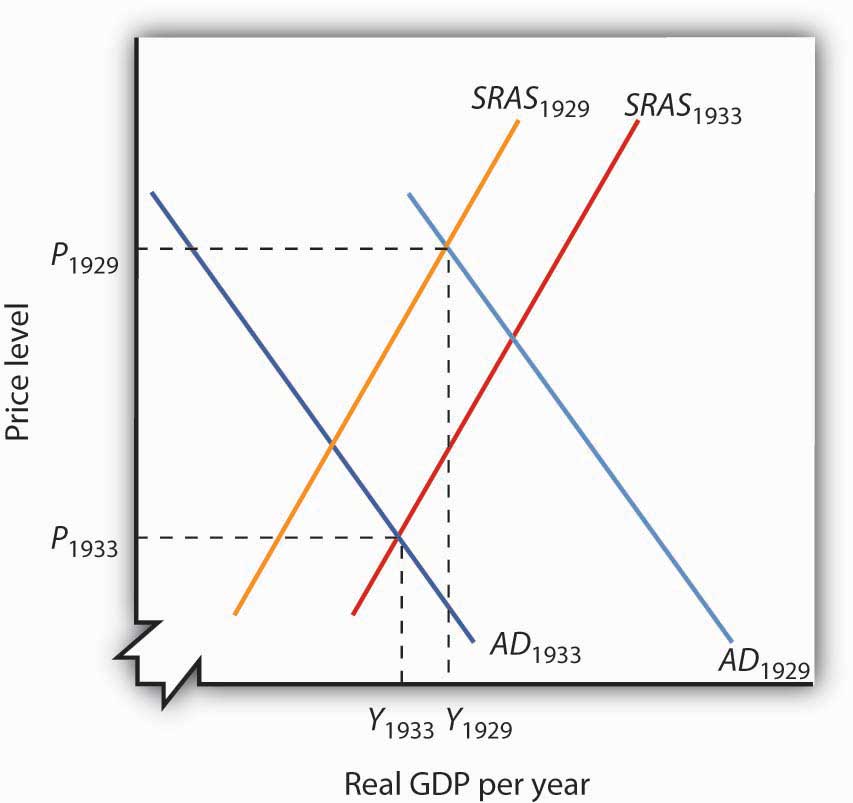 Source: socialsci.libretexts.org
Source: socialsci.libretexts.org
Like the ordinary supply curve for an individual commodity the aggregate supply curve also slopes upward from left to right. This problem has been solved. The aggregate demand curve tells us the level of expenditure in an economy for a given price level. Explain the derivation of the Aggregate Supply curve relating inflation and output levels and how it shifts. When the economy reaches its level of full capacity full employment when the economy is on the production possibility frontier the aggregate supply curve.
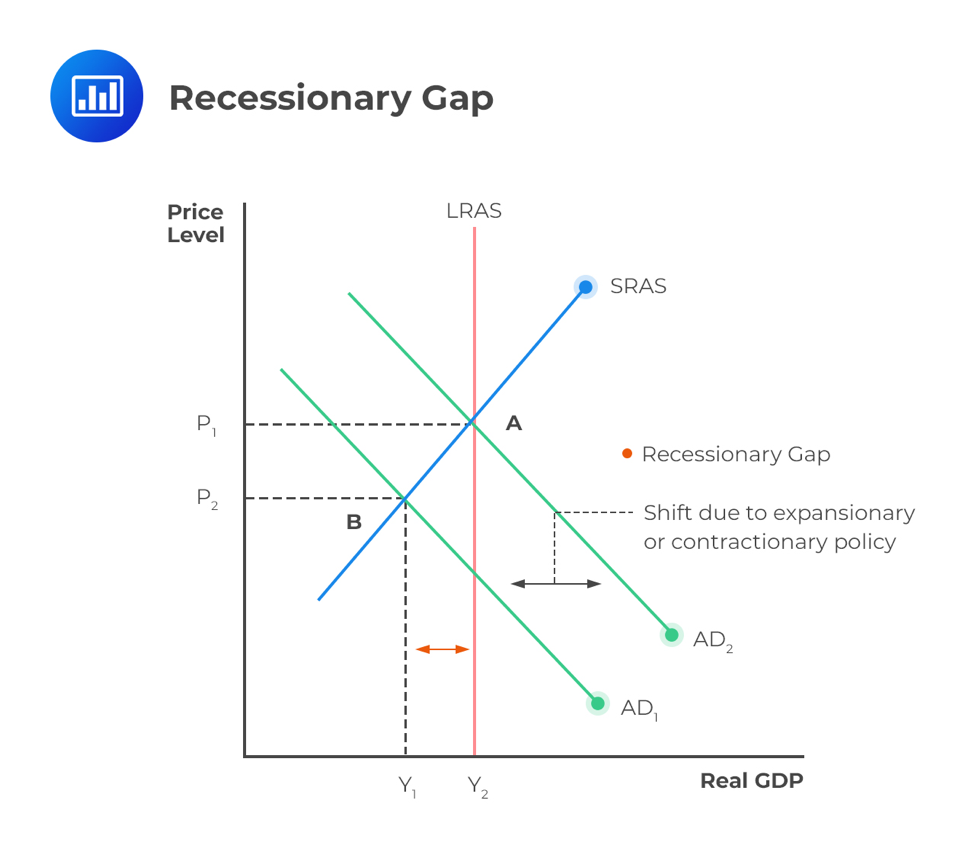 Source: analystprep.com
Source: analystprep.com
2 P a g e Figure 31. Downward sloping demand curve becomes aggregate demand curve. 2 P a g e Figure 31. The intersection of the economys aggregate demand curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve determines its equilibrium real GDP and price level in the long run. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Producers do this by increasing the utilization of existing resources to meet a higher level of aggregate demand. However this microeconomic substitution from one market to another is impossible for the economy as a whole. The AD-AS aggregate demand-aggregate supply model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level. Long-run aggregate supply curve. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Heres how to calculate it. Like the demand and supply for individual goods and services the aggregate demand and aggregate supply for an economy can be represented by a schedule a curve or by an algebraic equation The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods and services demanded by the economy at different price levels. Different factors explain the upward slope of the AS curve. Furthermore how is aggregate demand and supply different than regular demand and supply. Equilibrium Levels of Price and Output in the Long Run.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title aggregate demand and supply curve explained by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






